Certification Objective 4.03: Discussing the Features of Independent Management Architecture
|
| < Free Open Study > |
|
The Independent Management Architecture is an advanced server-to-server communications protocol as well as a management design that is the foundation of Citrix's ability to scale MetaFrame XP beyond previous versions and enhance its management capabilities. IMA provides a single integrated platform to manage, maintain, and support your entire company's installation and security efforts on all your application servers. IMA also allows administrators to group servers into farms logically, rather than geographically, to provide the best in performance, fault tolerance, and manageability.
| Exam Watch | All IMA traffic is on TCP port 2512 and can be changed if necessary. |
IMA and MetaFrame XP provide a lot of new features and capabilities. Some of the benefits of IMA are listed in the following.
-
Administrative actions are now auditable.
-
Session shadowing can now be logged and audited.
-
MetaFrame XP now supports SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) to provide alerts and administrative action.
-
All Citrix configuration information is now stored in a central location.
-
The CMC provides a centralized management tool to administer Citrix servers and license data.
-
ICA clients no longer need UDP broadcasts to locate servers and published applications.
While IMA and CMC have replaced the older architecture that Citrix was built on, it is still fully backwards-compatible with all previous ICA client software. Citrix has also provided all the older management utilities to assist in making your transition as smooth as possible. This design extends Citrix's Digital Independence slogan to include the ability to manage from anywhere, anytime as well.
Zones
Zones are a new concept with MetaFrame XP. They can be used to group MetaFrame servers together in logical collections. By using zones, server farms can span multiple geographic locations. Each zone has its own data collector, which acts much like a master browser in MetaFrame 1.8. By default, a zone consists of all the XP servers on a single subnet. You can create and configure additional zones from the Zones tab on the Farm Properties dialog box. See Figure 4-8 for an illustration of the zone properties page.
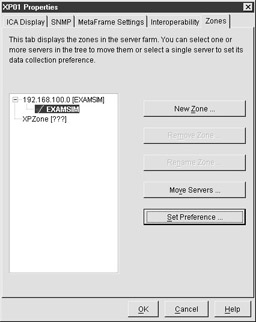
Figure 4-8: Zones configuration page
| Exam Watch | There is only one data collector per zone and no backups. All MetaFrame servers contain the information necessary to become the data collector. |
Single farms with member servers in different geographic locations benefit from using multiple zones to localize the data collection services and reduce WAN traffic. Making servers members of different zones is very easy. Simply select the server from the list of zones in the Zones tab and move it to another zone.
| On The Job | There is a preset limit of 256 open connections to the data collector. Refer to the documentation to increase this number if you have more than 256 servers in a zone. |
Data Store
MetaFrame XP introduces a new method of storing server configuration data, as well as licensing data and farm administrators. The data store is created when you install the first MetaFrame XP server, and can use Microsoft Access, Microsoft SQL Server, or Oracle as the database engine. Microsoft Access is suitable for farms of up to 50 servers, while SQL Server and Oracle are suitable for farms of any size. See Table 4-2 for the supported versions of each product. This centralized database of information is the core to XP's scalability and stability.
| Database | Supported Versions |
|---|---|
| Microsoft Access | Terminal Server and Windows 2000 include compatible drivers |
| Microsoft SQL | Microsoft SQL Server 7 Service Pack 2 and SQL 2000 Version 3.70.08.20 SQL ODBC driver 2000 includes this driver, Terminal Server requires MDAC 2.6 |
| Oracle | Oracle8i, Version 8.1.6 Oracle 7, Version 7.3.4 Oracle 8, Version 8.0.6 |
Connections to the data store can be of two types: direct and indirect. Direct connections require that the XP server have the correct ODBC driver installed and configured so the server can communicate directly with the database server. Indirect connections use a central XP server to connect via direct mode to the database server, while other XP servers connect indirectly through that server. Indirect connections eliminate the need to install ODBC (Open Database Connectivity) drivers on every server, but the intermediary server becomes a single point of failure.
| Exam Watch | Be sure to know the databases that the data store supports. |
Data Collectors
Data collectors in MetaFrame XP are analogous to an ICA master browser. Each zone contains one MetaFrame XP server that is configured as the data collector. The data collector receives information from each of the other XP servers in the zone. Like the master browser in previous versions, the data collector maintains a list of all servers and the applications they serve, along with the TCP/IP addresses of each server. XP servers use TCP connections for server-to-server communications unlike previous versions that used UDP.
Data collectors are chosen via elections much like NT domain controllers and MetaFrame 1.x ICA master browsers. If a new server joins the farm or the data collector becomes unavailable, the farm holds an election for a new data collector. There are four levels of preference in selecting a new data collector. The levels are shown in Figure 4-9.
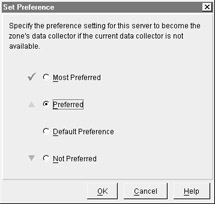
Figure 4-9: Data collector preference levels
By default, all servers are set to the default preference except for the first server in the farm, which is set to most preferred and is the farm's first data collector. You can change these levels via the Zones tab on the farm properties page in the CMC. When an election occurs, the farm attempts to select a server from the highest preference level: most preferred. If no servers from the level are available, it continues down the list until, as a last resort, it attempts to select one from the not preferred list.
Exercise 4-3: Setting the Data Collector Preference Level
In this exercise, we will set the preference level to lowest on a server that is to be used for data collection only as a last resort.
-
Open the CMC and log in to your farm.
-
Select the farm name in the left pane and choose Properties from the Actions menu.
-
Choose the Zone tab from the properties page, as shown in Figure 4-8.
-
Expand the zone by clicking the plus sign (+) next to the zone name.
-
Select the server to change, then click the Set Preference button.
-
Set the preference to Not Preferred in the dialog box shown in Figure 4-9.
-
Click OK and then OK again to close out the dialog boxes.
Data collectors also act as communication gateways between the zones of a farm. All servers in a zone send their unique information only to the local data collector, thus only data collectors send data across WAN links to other data collectors. Figure 4-10 depicts an example of how zones are used in conjunction with data collectors to minimize the amount of data sent across the WAN.
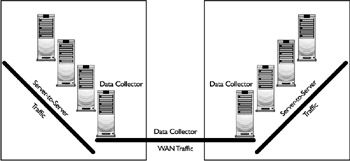
Figure 4-10: Data collector and zone architecture
The Local Host Cache
The local host cache is an Access database that is stored locally on each server in the farm to cache farm information. This database increases performance because it is not necessary to contact the data store every time a client queries the server. The database contains the following types of information:
-
Basic information on all servers in the farm
-
All Windows domain trust relationships in the farm
-
Names and properties of all applications published within the farm
-
Information specific to itself
The local host cache also maintains enough information to allow the server to operate for up to 48 hours in the absence of the data store. During this period, the server will continue to attempt to contact the data store on a regular basis. If the data store is not contacted within 48 hours, the server will invalidate its licensing information and discontinue taking new connections.
If the local host cache gets out of sync with the data store, it can manually be refreshed by issuing the command: dsmaint refreshlhc. The cache will only get out of sync if the IMA service (which is responsible for maintaining the cache) misses a sync or change event. If the cache database becomes corrupt, it can be re-created from the ODBC object in the Control Panel. Refer to your documentation for the specific procedure.
Now that you have a better idea of IMA, here are some possible scenario questions and their answers:
| What port does IMA use for communication? | TCP 2512 |
| What enhancements does IMA bring to shadowing? | Logging / auditing |
| How many farms can be in one zone? | No farm can be in a zone. Zones are a part of farms. |
Bandwidth Requirements for a Server Farm
MetaFrame XP uses a central data store and data collectors to manage all the configuration and event data for a farm. This task generates network traffic each time a farm event occurs. Bandwidth considerations must be made when designing a server farm to control the amount of bandwidth used for IMA traffic. A single server retrieves approximately 275KB of data from the data store each time it starts up. In larger farms, the data read is a function of the amount of servers in the farm, the number of published applications, and the number of printers in the farm. The total data read can be estimated by using the formula 275 + (0.5 × #Applications) + (5 × #Servers in Farm) + (92 × #Print Drivers in the Farm) = Total KB read. This is an approximate formula from a test lab, so your mileage may vary.
In a farm with multiple sites, it is recommended that the data store be replicated to reduce the amount of WAN traffic. If a replicated data store is not an option, the use of third-party bandwidth management devices may help control IMA traffic across the WAN. As the farm grows and the amount of data to transmit increases, the data the server tries to read may take longer to transfer across the connection than the service normally allows. In some cases, the servers may display error messages indicating the IMA service did not start. This error is normal and can be disregarded, as the service will start normally after all data is received.
Data Collector Traffic
Each zone will contain one data collector to maintain farm information for that zone. Each data collector updates all other data collectors each time an event occurs in its zone. These events cause WAN traffic and must be taken into consideration when calculating WAN usage. Table 4-3 lists some of the events and the associated WAN traffic.
| Event | Approximate Data Transmitted |
|---|---|
| Session connection established | 3KB |
| Session disconnect | 2.3KB |
| Session reconnect | 3KB |
| User logoff | 1.5KB |
| CMC server inquiry | 2.2KB |
| Publishing a new application | 9.0KB + 1KB × #Servers in Farm |
| Starting a new data collector | 20KB |
If not properly designed and managed, data collector traffic can consume a large amount of bandwidth very quickly. Consider all the options when designing your zone and farm strategy. A zone is typically only one subnet, but that is not a limitation. A zone can span multiple subnets and even sites. If you have a farm that spans four sites, you could configure it as one zone. A central data collector would reside at the main location and all data would be sent to it. As each event occurs, the data only traverses the WAN one time from the client to the central data collector. Otherwise, the data would travel over the WAN three times, once from the data collector for the zone to each of the data collectors for the other zones.
-Travis Guinn, MCSE, CCA, A+, CCSE, MCP+I
The use of zones must be carefully considered when designing farms. For each zone, there is one data collector. Each time an event occurs in one zone, the data collector must update every other data collector. For a farm with six zones, the event data must be transmitted from the originating zone five times to be replicated to the other zones.
|
| < Free Open Study > |
|
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 169