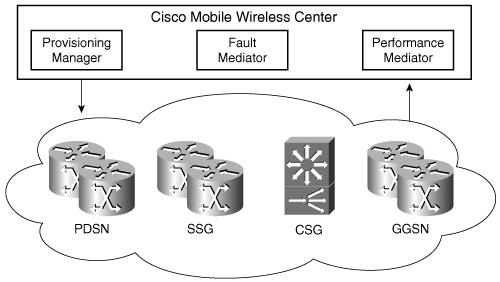
Cisco Mobile Wireless Center
| The Cisco MWC is an automated operational support system (OSS) for mobile wireless domain management, and it is targeted at mobile operators and service providers. Specifically, MWC provides management capabilities to Cisco Mobile Exchange, a framework that links radio access networks (RAN) to IP networks. The Mobile Exchange framework can be managed as if it were a single device, saving time and money when deploying new services, by reducing errors, and when implementing user training. MWC performs device configuration, provisioning, fault mediation, and performance mediation for the following services:
There are three components at work in an MWC:
Figure 3-3 shows how these components fit into the larger MWC picture. Figure 3-3. Provisioning Manager, Fault Mediator, and Performance Mediator Are at the Heart of the Cisco Mobile Wireless Center The sections that follow cover the three MWC components in greater detail. Provisioning ManagerThe Provisioning Manager performs all network configurations and user-level security. This is the component that configures devices on an exchange network. The Provisioning Manager keeps a list of configured devices and provides a simplified way to update configuration information to those devices. Devices are managed via a web-based user interface, which allows the user to manage devices through the Internet. Troubleshooting is aided by an activity log, which tracks all user activity. In addition, the Provisioning Manager uses a template-based tool to make setup and provisioning simple. For example, this template-based tool might be used by a wireless service provider that needs to perform load balancing with its servers or configure its servers based on their geographic locations. Fault MediatorThe Cisco MWC Fault Mediator keeps an eye on the network, and it looks for changes. This is the component used to alert you when network behavior deviates from specified metrics. If a fault is detected, it can be forwarded to management applications, such as Cisco Information Center. Fault Mediator provides broad thresholding capabilities in addition to those that Cisco IOS Software provide. Part of the Fault Mediator is a discovery engine that locates all Cisco Mobile Exchange nodes, Catalyst switches, and service components attached to the IP network. This discovery engine monitors the presence of these devices and the connectivity among them. This information is useful when new devices are added or the network topology changes. Performance MediatorPerformance Mediator supplies performance management functionality that is used to compile information about a network's performance. Performance Mediator provides a single AP to the managed devices for performance data. The use of a centralized approach eliminates the need for additional types of data retrieval. As Performance Mediator collects network performance and usage data, it combines and forwards this information to the network management applications. The data collection mechanisms are dynamic and can be modified as the network administrator sees fit. Configuration is accomplished via either a web browser interface or through a data bus. Data can be delivered via File Transfer Protocol (FTP). Using the Cisco CNS Integration Bus, performance data can be converted into extensible markup language (XML) files for easy integration with the service provider OSSs and other third-party applications. |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 126