| After you configure your update options, you will be presented with the screen shown in Figure 1.8. The Manage Your Server screen is a front end to the Configure Your Server Wizard. This wizard is an automated way to tune your server by letting you select a role from a list and then guiding you in the configuration of this role by prompting you for the desired configuration settings. The wizard can assist you in either adding or removing a role from your server. It will appear at every logon until you select the Don't Display This Page at Logon check box in the lower-left corner of the page. The Manage Your Server page can be opened at any time by clicking Start, All Programs, Administrative Tools, Manage Your Server. Figure 1.8. The Manage Your Server page enables you to start the Configure Your Server Wizard, which is used to configure your server for various roles. 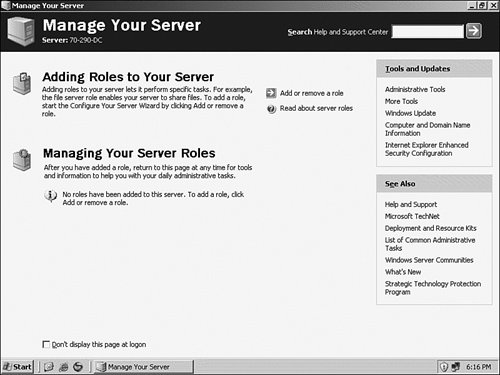
Note: Run Separately After you become more familiar with the different options provided by Manage Your Server and the Configure Your Server Wizard, you can bypass the Manage Your Server page and directly select the Configure Your Server Wizard in the Administrative Tools folder.
Servers can host a variety of roles. If the server is large enough, it can support several roles. A server can supply the storage for those important files you need for your presentation; it can host a database of all the left-handed people in Bangladesh, or it can supply something as simple as email. The following roles are available via the wizard: File server A file server is used to provide centralized storage of files. This allows users to access them when needed and share them with other users, without having to pass them around on diskettes or CDs. A file server also allows files to be secured so that only certain users will have access to them. Domain Controller Domain controllers are used to provide centralized storage and management of user accounts, process logons to the network, and authenticate user access to network resources. DNS server A DNS server is used to register and resolve DNS domain names and provide name-to-IP address mapping for TCP/IP. WINS server A Windows Internet Service (WINS) server is used to register and resolve NetBIOS names and provide name-to-IP address mapping. Print server A print server is used as a centralized location where users can print to various printers. Printing will be covered at length in Chapter 6, "Implementing Printing." Application server This is a new name for Internet Information Services (IIS) and refers to web servers, File Transfer Protocol servers (FTP), and their various components. IIS is covered in Chapter 5, "Administering Windows Server 2003." Mail server This role provides a limited version of POP3 and SMTP functionality. Remote Access/VPN server This role provides access to remote users, either via dial-up or via VPN over the Internet. Streaming Media server This role is used to efficiently stream audio and video content over your local network or the Internet. Terminal server Terminal Services provides an environment where users can run applications that are not installed on their PCs. Terminal Services will be covered in Chapter 11, "Managing and Maintaining Terminal Services."
It should be pointed out that these roles can be configured manually by an experienced network administrator who has done it many times before. For the novice, there are checklists generated either by your company or downloaded from Microsoft or third-party companies. However, to ensure consistency and avoid human error, the Configure Your Server Wizard offers a guided approach to ensure that you don't leave out any important steps. Another descriptive term that we need to cover is the type of server. There are three types: Standalone A standalone server is a server that is not a member of a domain. It can be the only machine used, or it can be part of a workgroup to provide distributed storage of files and printers. Although users can share resources in a workgroup, they might have to keep track of different passwords for each resource because there is no common source of security in a workgroup. Domain Controller A domain controller is used to provide centralized storage of user accounts and provide authentication for users who need to access resources in the domain. A domain is a group of user accounts and network resources that share a common security database and common security policies. The domain controller is used to control access to these resources. We will cover domains and domain controllers in Chapter 2. Member server A member server is any server that is a member of a domain that is not a domain controller. It can serve one or more of the roles that we discussed earlier.
|
