| Flash allows you to create and place graphics only on the active layer of a document. But you can copy, cut, or delete elements from any visible, unlocked layer. You can select items on several layers, cut them, and then paste them all into a single layer. Or, cut items individually from one layer, and redistribute them to separate layers. To paste across layers 1. | Create or open a document that contains several layers.
| 2. | Place at least one element on all but one layer.
To make the elements easier to work with, create them as drawing-objects, or group each merge-shape. Leave one layer empty.
| 3. | On the Stage, select a shape.
Flash highlights the layer in the Timeline.
| 5. | Choose Edit > Copy.
| 6. | In the Timeline, select the empty layer.
| 7. | Choose Edit > Paste in Center.
Flash pastes the copy of the shape in the empty layer, in the middle of the window (Figure 6.22). Now you can move the shape to a new position, if you wish.
Figure 6.22. Copying a shape from one layer to another involves selecting the shape (top), copying it, selecting the target layer, and then pasting the copy there. The Paste in Center command (middle) positions the pasted shape in the center of the window (bottom). 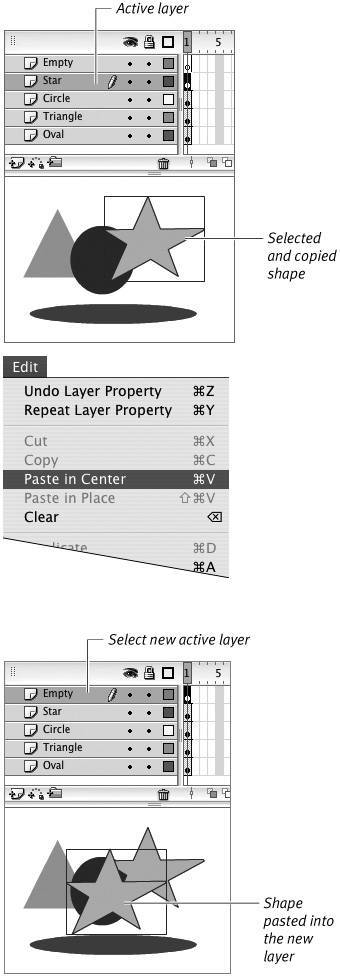
|
To use the Paste in Place command across layers 1. | In a document that has several layers containing shapes and one layer that has no shapes, select one shape.
In the Timeline, the layer containing the selected shape becomes the active layer.
| 2. | Using the techniques you learned in Chapter 4, add other shapes to your selection.
In the Timeline, the layer containing the most recent addition to the selection becomes the active layer.
| 3. | Choose Edit > Cut.
Flash removes the selected shapes (Figure 6.23).
Figure 6.23. The first step in consolidating items from several layers on a single new layer involves selecting all the items and cutting them. Later, you'll paste them into the new active layer. 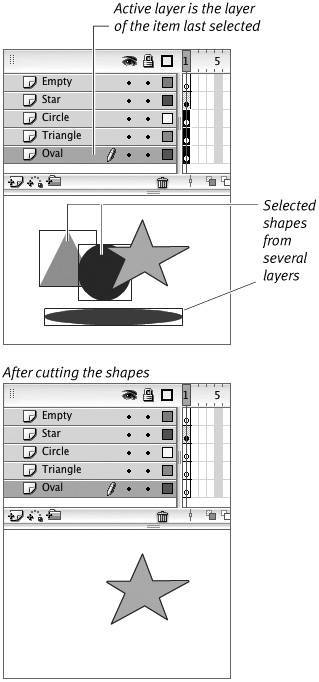
| 4. | In the Timeline, select the empty layer.
Where Do Pasted Graphic Elements Go? A Flash document can have only one layer active at a time. Any new shapes you create wind up on the currently selected, or active, layer. The same is true of placing copies of shapes or instances of symbols; if you copy and paste an element, Flash pastes the copy on the active layer. When you drag a symbol instance from the Library window, it winds up on the active layer. |
| 5. | Choose Edit > Paste in Place (Figure 6.24).
Figure 6.24. Choose Edit > Paste in Place to paste items back into their original positions. 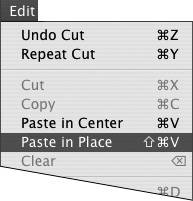
Flash pastes all the shapes back into their original locations on the Stage but on a different layer (Figure 6.25). Try hiding the empty layer temporarily; you should no longer see those shapes.
Figure 6.25. The Paste in Place command positions the pasted items in the new layer. Each shape occupies the same coordinates it had on its former layer, but now all the shapes are together in the new layer. Hide the new layer to make sure you moved the elements from their old layers. 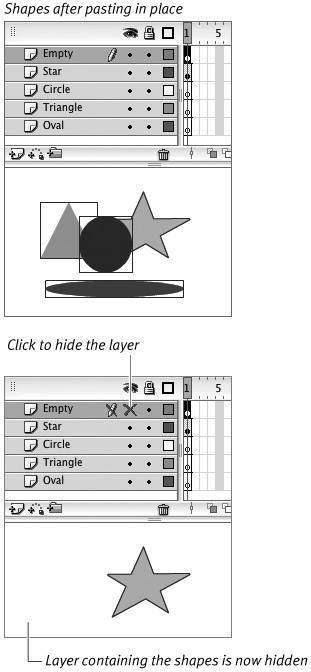
|
 Tips Tips
You've already learned that selecting an element on the Stage causes Flash to select that element's layer in the Timeline. As you move elements between layers, it helps to know that selections work the other way around, too. When you select a layer in the Timeline, Flash selects all the elements for that layer on the Stage. The process of cutting elements and using the Paste in Place command is, obviously, time-consuming, because you have to keep selecting new layers as you place the elements. To automate the process, use the Distribute to Layers command (see "Distributing Graphic Elements to Layers," later in this chapter).
Two Ways to Paste Flash offers two pasting modes: Paste in Center and Paste in Place. Paste in Center puts elements in the center of the open Flash window. (Note that the center of the window may not necessarily be the center of the Stage; if you want to paste to the center of the Stage, you must center the Stage in the open window.) Paste in Place puts an element at the same x- and y-coordinates it had when you cut or copied it. Paste in Place is useful for preserving the precise relationships of all elements in a scene as you move items from one layer to another. |
|




 Tips
Tips