Troubleshooting NAP
Let’s end this chapter with some more meat from the Windows Server 2008 product team. If you plan on deploying NAP soon in your enterprise, the following pages alone might be worth the price of the book. And if you don’t want to keep the whole book, you can always tear these pages out and throw away the rest!
First let’s look at some general tips on how to diagnose various kinds of NAP enforcement issues:
The following is designed to be a support aid to diagnose Network Access Protection issues in various enforcements, including IPSec, 802.1x, and DHCP. It is meant to provide additional information to the administrator to identify the root cause of the problem and refers to Microsoft troubleshooting procedures and related information. These Network Access Protection diagnostics involve the Vista/XP client (we will use the term NAP Client to refer to them), the network access devices (DHCP Server, HRA Server, 802.1x switch), and the Network Policy Server.
The goal is to collect information to help classify the problem. The first step in diagnosing the NAP system is collecting the following information for diagnosis:
-
Client operating system and the corresponding version (example: Is it Windows Vista or Windows XP?)
-
Network connection information (ipconfig /all details)
-
NAP Client configuration
-
Event logs for the NAP and corresponding enforcement components
The key to identifying the problem quickly is getting to know the scope of the issue. “Who is affected by the problem?” If the problem is shared by many users, it is better to start the investigation by verifying the connectivity and the health of NAP servers-for example:
-
Are the servers running as expected?
-
Are there any errors in the server event logs pointing to various issues?
-
Are the clients receiving the configuration from group policy?
In the following section, we will focus on the NAP client-specific problems-that is, NAP Client Diagnostics.
Information Gathering
Open a command prompt with administrator credentials, and issue the following commands:
ipconfig /all netsh nap client show state sc query
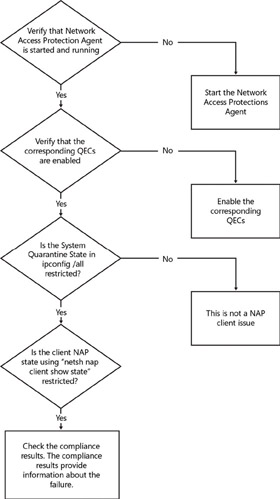
Troubleshooting Flowchart
Detailed Investigation
The following steps help identify failures and misconfigurations in the NAP system. The NAP system can have various points of failure. The following diagram illustrates the failure points and the process for debugging them.
The diagnosis of a NAP client failure starts with the verification of NAP client configuration:
-
-
Is NAP turned on? (Is NAPAgent service running?)
-
Is the corresponding NAP Enforcement client enabled?
-
Are there any NAP client events in the event logs?
There are a number of events on the client that provide information about the failures. The following diagram shows the informational events logged on the client when the NAP transaction crosses the component boundaries.
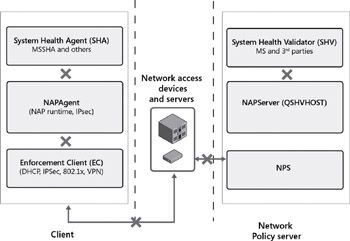
 Open table as spreadsheet
Open table as spreadsheet Event ID
Event Details
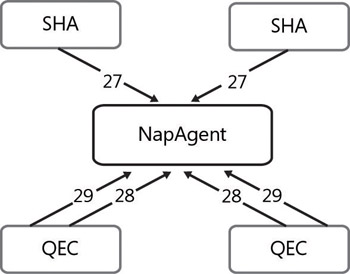
27
Indicates that a Statement of Health (SoH) was received from the System Health Agent (SHA)
28
Indicates that the Statement of Health (SoH) was received by the Quarantine Enforcement client indicated in the event
29
Indicates the Statement of Health Response from the server, and it also contains the client health state
18
Indicates a NAP Health state change
The following is a description of various NAP events that can help the diagnosis:
All the events have a unique correlation ID that identifies a NAP transaction.
–Chandra Nukala
Program Manager, Network Access Protection
–Ram Vadali
Software Design Engineer, Network Access Protection
Next let’s examine how to troubleshoot NAP IPSec enforcement. We’ll start by troubleshooting on the client side because this is generally the best way to begin your troubleshooting when an issue arises.
Here are the client-side troubleshooting steps to identify the root cause of the problem when the client fails to acquire a health certificate in the NAP IPSec environment. These are common to both Windows Vista and Windows XP clients (we will use the term NAP IPSec Client to refer to them and the term NAP Server to refer to the Windows Server 2008 system, with HRA/NPS/IIS).
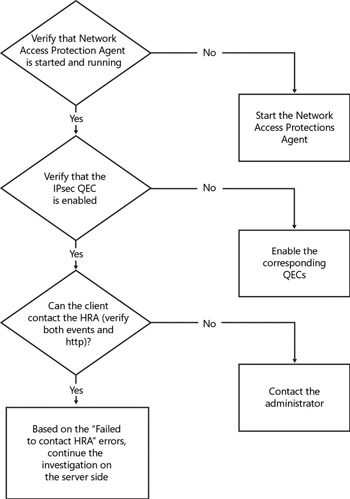
Verify Client Configuration
-
Check for the NAP health certificate in the client’s machine store.
Mmc.exe Certificates Snap-in Computer Account Local Computer Personal Certificates Store
Proceed to the following troubleshooting steps if the health certificate is not found. A client would not have acquired a certificate if any of the following aren’t true.
-
Verify NAP Agent service is running–sc query napagent.
-
Verify Security Center service is running–sc query wscsvc.
-
Confirm the client is in “nonrestricted” state–netsh nap client show state. If the client is restricted, follow the remediation steps to get the client out of restriction state.
-
Validate IPSec Relying Party (QEC) is “Enabled”.
Make sure the client is configured with the correct URL needed to contact HRA Server.
-
If NAP settings are configured locally–netsh nap client show config
-
If NAP settings are configured through Group Policy–netsh nap client show grouppolicy
Verify Client’s Connectivity
-
-
Try to ping HRA. If it fails, there might be a network issue. (Recheck your firewall settings, IPSec Policies, and potential DNS/DHCP issues.)
-
Validate that the client can access the HRA’s URL by typing the address into a browser (IE). Following is a list of HTTP errors and the possible causes of these errors:
 Open table as spreadsheet
Open table as spreadsheet HTTP Errors
Failures Indicated by the Error Codes
401
Access Denied.
403
Forbidden. This error indicates that the client is sending HTTP requests to HTTPS URL or vice-versa.
404
Page not found. This error indicates that this could be a server-side issue, and investigation has to continue on the server. (Is the HRA installed and set up?)
500
Server error. This error indicates that the client request reached the HRA and because this could be a server-side issue, investigation has to continue on the server.
Client-Side Event Errors
Once the administrator verifies that the client is configured accurately, he can use the following steps to help identify failures and misconfigurations in the IPSec scenario. The administrator can start the investigation by looking at the various “Network Access Protection” events, particularly looking for events 21 and/or 22 in the event log. All NAP-related events are logged in the “Event Viewer/Windows Logs/Applications and Services logs\Microsoft\Windows\Network Access Protection” channel. All NAP events use the event source name “Network Access Protection.”
Event 22 indicates that the NAP Agent successfully acquired a health certificate from the HRA Server.
Event 21 indicates that the NAP Agent failed to acquire a certificate from the HRA. The event also provides an error code associated with the failure. The following table shows various error codes and the corresponding failures:
 Open table as spreadsheet
Open table as spreadsheet Error Codes
Failures indicated by the Error codes
2147954407
Indicates a name resolution problem. This could indicate a DNS problem. Use ping <destination name> and nslookup to further investigate the issue.
2147954430
Indicates a connection error.
2147954429
Indicates a connection error.
2147954575
Indicates secure failure. There is a problem setting up an SSL channel with the server. (This could indicate a SSL Certificate configuration problem.)
–Wai-O Hui
Software Development Engineer in Test, Network Access Protection
–Harini Muralidharan
Software Development Engineer in Test, Network Access Protection
Having seen how to perform client-side troubleshooting of NAP IPSec enforcement, now let’s examine how to approach troubleshooting on the server end of things. Event Viewer is going to be especially useful here.
Here are the server-side troubleshooting steps to identify the root cause of the problem when the client fails to acquire a health certificate in the NAP IPSec environment. It is assumed that you have already gone through the client-side troubleshooting steps in the previous sidebar.
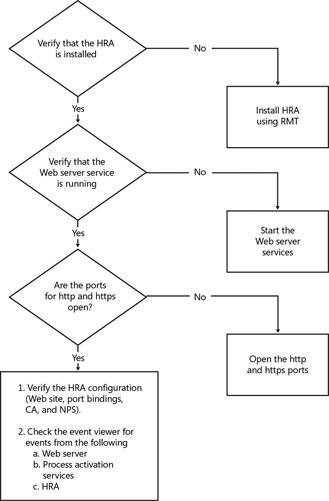
Verify Server Configuration
Use the following steps to verify the server configuration:
-
Verify that HRA and IIS services are installed on the NAP IPSec server.
-
Make sure HRA is configured to point to the correct Certificate Authority.
-
Validate IIS has configured port bindings to support HTTP and HTTPS (SSL) requests.
-
Confirm that the server’s firewall settings have exemption for both HTTP and HTTPS traffic.
-
Make sure that HRA is configured to accept anonymous requests (requests from workgroup clients). This is configured during HRA installation. To verify, in the IIS snap-in check whether a non-domain hra root is configured.
-
When configuring the NAP health certificate validity period, make sure it is greater than 15 minutes or else the client will fail to obtain a certificate.
Verify Certificate Authority Configuration
Use the following steps to verify the Certificate Authority configuration:
-
Confirm that the CA is set to auto-issue certificates. The option is located in CA Properties Policy Module Properties Choose “Follow the settings in cert template, if applicable, otherwise automatically issue the cert”.
-
Verify that the HRA server is configured with permissions to request and delete certificates from the Certification Authority on behalf of the client. Both the Issue And Manage Certificates option and the Manage CA option need to be verified in the security configuration of the CA properties.
-
After making any changes to the Certification Authority, make sure to restart the certificate services to allow the settings to take effect.
Verify Server Connectivity
Make sure that the HRA server could reach the configured CA. If not, there might be a network issue. (Recheck your firewall settings, IPSec Policies, and potential DNS/DHCP issues.)
Server-Side Event Errors
All HRA-related events are logged in the “Event Viewer/Windows Logs/System” channel. All HRA events use the event source name “HRA”.
The following table indicates the HRA error events and the possible failures causing the errors:
 Open table as spreadsheet
Open table as spreadsheet Event Number
Event Type
Event Text
Resolution Steps
7
Error
The Health Registration Authority denied the request with the correlation-id %1 at %2 (principal: %3) because the request could not be authorized (%4) by the provided DNS. Discarding the request.
A client domain configuration problem. Make sure the client is joined to the correct domain.
8
Error
The Health Registration Authority is misconfigured or cannot read its configuration, stopping Health Registration Authority. Verify the Health Registration Authority configuration or contact an administrator for more information.
Certification Authority Configuration error. Verify that Certification Authorities are configured in HRA by doing the following:
In a command window run: netsh nap hra show configuration and verify that the HRA configuration is correct. If no Certification Authorities are configured, set any available Certification Authorities using the MMC Health
Registration Authority snap-in or by using the following netsh command: netsh nap hra set caserver name = “\\server1\CA” processingorder = “1”
9
Error
The Health Registration Authority was unable to acquire a certificate for request with the correlation-id %1 at %2 (principal: %3). Discarding the request. The Certification Authority %4 denied the request with the following error: %5 (%6). Contact the Certification Authority administrator for more information.
Health Registration Authority (HRA) does not have the proper permissions to request a certificate from the Certification Authority (CA). Contact the CA administrator, and configure to grant the HRA permission to request certificates.
10
Error
The Health Registration Authority was unable to acquire a certificate for request with the correlation-id %1 at %2 (principal: %3). The Certification Authority %4 denied the request with the following error: %6 (%7). This failure was possibly due to a network related issue. The request will be discarded if no other Certification Authorities are available. This server will not be tried again for %5 minutes. Contact the Certification Authority administrator for more information.
Unable to connect to a Certification Authority because of a network failure. Perform the following resolution steps:
Verify the server’s network connection.
Verify the CA’s network address, computer name, and connectivity.
Inform the CA administrator of connectivity problems.
11
Error
The Health Registration Authority could not contact NPS: %1
Contact the Network Policy Server (NPS) administrator to verify that the NPS service is running and is not disabled. Ensure that Network Policy Server is installed correctly.
20
Error
The Health Registration Authority failed to validate the certificate request against the HRA configuration. The Health Registration Authority denied the request with the correlation-id %1 at %2 (principal: %3) because it did not satisfy the cryptographic policy (%4). Discarding the request.
A configuration problem between the client and the Health Registration Authority (HRA). Verify the client’s cryptographic policy. If the problem persists or shows up with multiple clients, verify the applied group policy’s cryptographic settings against the
HRA configuration regarding Hash and Asymmetric Key algorithm.
24
Error
The Health Registration Authority was unable to validate the request with the Correlation ID %1 at IP address %2 (Principal: %3). The Network Policy Server had no policy matching the request (%4). Contact the Network Policy Server administrator for more information.
The client did not match any of the policies on the Network Policy Server (NPS). Review the client health state. If the problem appears across multiple clients, consider creating additional NPS policies.
25
Error
The Health Registration Authority was unable to validate the request with the Correlation ID %1 at IP address %2 (Principal: %3). The Network Policy Server denied the request because the request was not authorized (%4). Contact the Network Policy Server administrator for more information.
Network Policy Server (NPS) configuration problem. Verify that the NPS proxy is authorized to forward requests to the correct NPS.
28
Error
The Health Registration Authority was unable to validate the request with the Correlation ID %1 at IP address %2 (Principal: %3). The Network Policy Server (NPS) was unable to contact the Active Directory Global Catalog necessary to validate the request (%4). Contact the Network Policy Server administrator for more information.
NPS cannot connect to the Global Catalog. Verify the Global Catalog status, its network connectivity, and the NPS permissions in the forest.
29
Error
The Health Registration Authority denied the certificate request with the correlation-id %1 at %2 for (principal: %3). Either no Certification Authorities are configured or none are available. Verify the Health Registration Authority configuration or contact its administrator for more information.
Certification Authority Configuration error. Verify that Certification Authorities are configured in HRA by doing the following:
In a command window run netsh nap hra show configuration If Certification Authorities are configured, all of them might be blacked out. Contact the CA administrator, and examine whether the current configuration meets the traffic requirements for the network.
30
Error
The Health Registration Authority was unable to connect to the Certification Authority to remove expired records. The Certification Authority [ca-name] denied the request with the following error: [ca-error-number]. Contact the Certification Authority administrator to check the permissions and for more information.
Health Registration Authority (HRA) does not have the proper permissions to delete expired certificates on the Certification Authority (CA). Contact the CA administrator, and configure to grant the HRA permission to delete expired certificates.
–Wai-O Hui
Software Development Engineer in Test, Network Access Protection
–Harini Muralidharan
Software Development Engineer in Test, Network Access Protection
Now let’s look at troubleshooting NAP 802.1X enforcement. Once again, we’ll begin on the client side, as problems most often begin there-especially if only some clients and not all of them have difficulties.
These instructions are designed to be a support aid to diagnose Network Access Protection issues in 802.1x enforcement. They are meant to provide additional information to the administrator to identify the root cause of the problem and refer to Microsoft troubleshooting procedures and related information. Network Access Protection diagnostics involve the Vista/XP client (we will use the term NAP Client to refer to them), the 802.1x switch, and the Network Policy Server.
Is NAP the Problem?
The goal of this section is to collect the information to help classify the problem. The first step in diagnosing the NAP system is collecting the following information for diagnosis:
-
Client Operating system and the corresponding version (Example: Is it Windows Vista or Windows XP?)
-
Network connection information (ipconfig /all details)
-
NAP Client configuration
-
Event logs for the NAP and corresponding enforcement components
802.1x Enforcement
802.1x provides client authentication to the network devices. When diagnosing 802.1x issues, information can be gathered from the NAP Client, the network device, and the Network Policy Server (NPS).
NAP utilizes the PEAP authentication to pass health data, enabling the use of 802.1x as a NAP enforcement. 802.1x NAP health policy is enforced on the network access device through the use of VLANs, which are assigned through RADIUS attributes from NPS to the switch.
Information Gathering
Use the following steps to gather the necessary information:
-
Open the “services.msc,” and verify that the following services are running (this can also be verified using the command line by using the command 3c – sc query):
-
NAP Agent
-
EAP Host
-
Wired AutoConfig (for wired scenarios)
-
WLAN AutoConfig (for wireless scenarios)
-
-
Open a command prompt with administrator credentials, and issue the following commands:
netsh nap client show config > C:\napconfig.txt netsh nap client show state > C:\state.txt sc.exe query > C:\services.txt
Troubleshooting Flowchart
The following is the troubleshooting flowchart that administrators can use to debug the 802.1x NAP system.
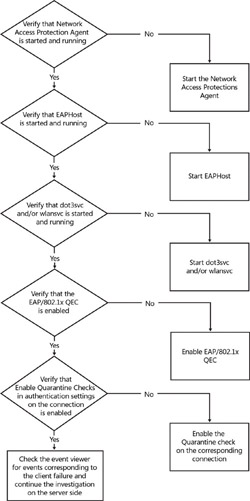
Detailed Investigation
The administrator has to first verify the configuration of the client:
-
The following services are enabled:
-
Network Access Protection Agent (“napagent”)
-
Extensible Authentication Protocol (“eaphost”)
-
Wired AutoConfig (“dot3svc”). This service is used if the administrator is setting up a wired 802.1x environment.
AND/OR
-
WLAN AutoConfig (“wlansvc”). This service is used if the administrator is setting up a wireless 802.1x environment.
-
-
The EAP/802.1x QEC is enabled.
-
The Enable Quarantine Checks option in the Authentication settings for the corresponding connection is configured. ( Enable Quarantine Checks is a setting in the connection profile; this setting is new and enables NAP.)
-
Verify the PEAP configuration on the wired connection profile. (Verify the EAP method configuration, and also verify that the certificate is chained back to the same root for validation of the server certificate.)
Once the administrator verifies that the client is configured accurately, he can use the following steps to help identify failures and misconfigurations in the 802.1x/EAP scenario. The administrator can start the investigation by looking at the various Wired AutoConfig (for wired 802.1x scenarios) and Wireless AutoConfig (for wireless 802.1x scenarios) events, particularly looking for events 15505 and/or 15514 (for wired802.1x scenarios) and events 12013 and/or 12011 (for wireless 802.1x scenarios) in the event log.
Events 15505 and 12011 indicate “Authentication success.”
Events 15514 and 12013 indicate “Authentication failures.” For authentication failures, look for the reason code and reason text to help with further debugging. (The investigation needs to continue on the NPS server.)
–Tom Kelnar
Lead Software Design Engineer, Network Access Protection
–Chris Edson
Software Development Engineer in Test, Network Access Protection
Finally, here’s the server side of NAP 802.1X troubleshooting. Once again, Event Viewer will be of invaluable use in determining the nature of the problem.
Use these instructions if you have already configured 802.1x PEAP-based NAP and have attempted authentication, but you do not see the expected behavior on the client. It is expected that the client-side troubleshooting procedure outlined in the previous sidebar has already been used.
Information Gathering
Use the following steps to gather the necessary information:
-
Dump all NPS events into an Event viewer file for later analysis: wevtutil.exe epl System NPS.evtx /q:"*[System[Provider[@Name='NPS'] and TimeCreated[timediff(@SystemTime) <= 86400000]]]"
Or create a custom (or filtered) view folder in the Event Viewer that displays only the NPS events.
-
Open the Network Policy Server snap-in for examining policy configuration.
Troubleshooting Flowchart
Most 802.1x PEAP-based NAP troubleshooting is done by analyzing the Events posted by NPS into the System event log store. Take a look at the events, and proceed along the flowchart, referring back to the events as needed.
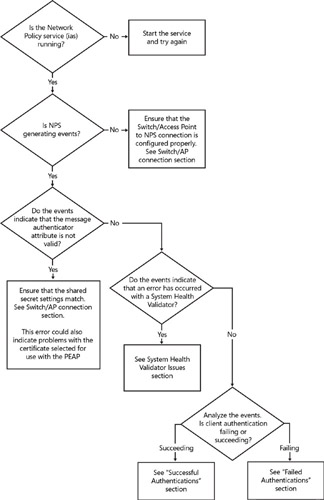
Switch/Access Point Connection
Several issues can prevent the switch or access point from properly communicating with the Network Policy Server:
-
The Network Policy Server machine must have the correct ports open in the firewall to allow the RADIUS requests through to the NPS service:
-
UDP:1812 for authentication
-
UDP:1813 for accounting
-
-
The switch or access point must be configured to forward 802.1x authentication requests to the Network Policy Server; this includes setting the correct IP address for the NPS machine, as well as the proper ports (for some switches).
-
The Network Policy Server must also be configured to recognize the switch or access point; this is done by configuring a RADIUS client table entry within the NPS snap-in, and it requires the IP address of the switch or access point.
-
The Network Policy Server and the switch or access point must both be configured with a common “shared secret.” If the secrets do not match, they will not be able to correctly communicate.
System Health Validator (SHV) Issues
Some common causes and paths of investigation for System Health Validator errors are as follows:
-
Perhaps the most common cause for System Health Validator failures occurs when the versions of Validator (server side) and System Health Agent (client side) do not match. Always ensure that the SHV/SHA pairs in use are matching versions.
-
Another common cause for System Health Validator–related errors is a failure to correctly register with the Network Policy Server. If this occurs, contact the SHV developer.
-
System Health Validator errors can also appear when the Network Policy Server is unable to load the SHV, or when the SHV terminates unexpectedly. If either of these situations occurs, contact the SHV developer.
Failed Authentications
Failed authentications can occur for a number of reasons, many of which are not specifically related to the NAP portion of the transaction.
Reason #1 – No matching policy
Some common causes and solutions for this reason are:
-
A client request arrived that did not exactly match any of the Network Policies configured on the NPS. Always ensure that you have policies in place that will match all possible client requests. Or you might consider making your existing policies slightly less specific by removing nonrequired conditions from the policies.
-
The NPS policy configuration does not include a policy that will match “not NAP capable” clients. When a client machine first boots, the authentication services will start prior to the NAP Agent service, and an authentication will be performed before health information is available. This client will therefore not match any policies with health-based conditions. Whether you grant full access with this policy or not, it still needs to be included in the configuration. Also, know that clients will re-authenticate once the NAP Agent service starts.
Reason #2 – User is denied access
A common cause and solutions for this reason are that, by default, the Network Policy Server will perform an Active Directory account look-up to verify the authenticating user’s dial-in privileges. If the user’s account does not allow dial-in access, the user will be denied access (regardless of the NPS policy settings). If you want to grant the user access, you can do either of the following things:
-
Ensure that the user’s account in the Active Directory is set to allow dial-in access.
-
Select the Ignore User Account Dial-in Properties box for the policy in NPS, which allows NPS to ignore the dial-in access setting and check only whether the user account is active in Active Directory.
Successful Authentications
Because of the possible complexities of 802.1x and the authentications it allows, there are cases in which clients could be successfully authenticating, yet not gaining the expected level of access.
Problem #1 – Client is NAP enabled but matches the “not NAP capable” policy
Two common reasons and solutions for this problem are:
-
Network Policy Server policy evaluation occurs in two stages: Connection Request policies first, and then Network Policies. Because Health is a condition for Network policy evaluation, the health data must be gathered prior to entering the Network Policy stage. Therefore, ensure that the Connection Request Policy being used is configured to Override Authentication and to do PEAP authentication. Also ensure that the PEAP configuration settings include selecting the Perform Quarantine Checks check box. Also ensure that the conditions on the Connection Request Policy are such that only requests from your switches or access points will be matched by that policy.
-
At client boot, the authentication services start prior to the NAP Agent. Thus, for the first authentication, there is no health data for evaluation. Therefore, the client will not match any policies in which health criteria are used as conditions. The client will match only policies with the “not NAP capable” condition. However, once the NAP Agent starts, a second authentication will be initiated, and the client will then be able to match the expected policy.
Problem #2 – Client is placed on the wrong VLAN
The solution to this problem will vary, depending upon the switch or access point hardware and sometimes the firmware that you are using. Consult the documentation or support contacts for your hardware, and determine what RADIUS standard or vendor-specific attributes need to be given to that hardware to achieve the functionality you desire. Once you have determined the values that need to be passed to the hardware, ensure that each policy on the Network Policy Server has these values configured in the Profile Settings section.
–Chandra Nukala
Program Manager, Network Access Protection
–Chris Edson
Software Development Engineer in Test, Network Access Protection
-
Pretty cool stuff, eh? My thanks to the NAP team for contributing these insights. Product teams tend to be especially proud of the features they develop, and NAP is obviously prouder than most because they took the time out of their busy schedule (Ship! Ship!!) to provide this content for my book-thanks, team!
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 138