2.3 Case study: A simple sales tracking application
|
| < Day Day Up > |
|
2.3 Case study: A simple sales tracking application
The remainder of this book discusses each development option and integration technique in greater detail. To facilitate this discussion, a sample application is used throughout the book to provide examples of how to implement each technique. This sample application is available for download from the IBM Redbooks Web site. For information on how to download this software, see Appendix B, "Additional material" on page 421.
| Note | This application is intended only to provide portlet migration examples. It is not intended for use in a production setting. |
Case study overview
The fictitious company Widget Corp. is using Lotus Domino to support the sales department. Over the years they have built a sales tracking application to help their sales force track interactions with their customers. The databases can be accessed from a Notes client or a Web browser.
There are two main databases in the sales tracking application: the Customers database and the Sales database. Figure 2-1 on page 48 and Figure 2-2 on page 49 illustrate the user interface when accessed from Lotus Notes. A third database, Products, is used for product keywords and is not accessed directly by the sales force.
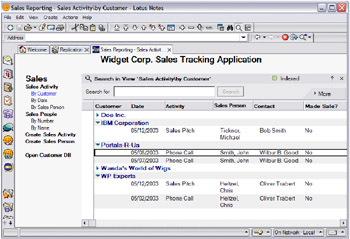
Figure 2-1: The Lotus Notes interface for the Sales Tracking application Sales DB
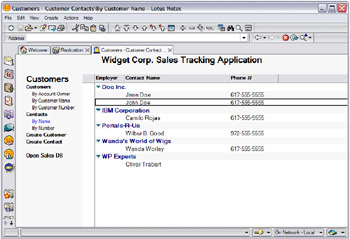
Figure 2-2: The Lotus Notes interface for the Sales Tracking application Customers DB
There are five main types of documents used by this application. They are defined in Table 2-3.
| Document type | Database | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Customer | Customers.nsf | An organization that is a customer or potential customer of Widget Corp. |
| Customer contact | Customers.nsf | An employee of a Widget Corp. customer who is responsible for a purchasing decision. |
| Product | Products.nsf | A product sold by Widget Corp. |
| Sales person | Sales.nsf | A member of Widget Corp.'s sales force. |
| Sales activity | Sales.nsf | A document tracking a specific interaction between a Sales Person and a Customer Contact. |
Case study objective: Sales Workplace
Widget Corp. has decided to build a Sales Force Workplace using WebSphere Portal. On the workplace, they would like to expose the content of the Domino databases that are related to the sales process. They also want to use the portlet's cooperation functionality to create a seamless user experience. Their vision is to present the sales person all the information available on a given customer in context with the products the customer buys and the most recent sales activities with that customer. In addition, they want to use people awareness to allow better communication between the different sales people.
Figure 2-3 shows a prototype of the workplace that they want to build.
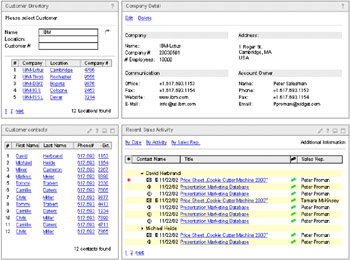
Figure 2-3: Example of a customer information workplace
The Sales Workplace is made up of four portlets:
-
Customer Directory
This portlet allows the sales person to search for a customer by name or customer number. He can also browse through the customers page by page, just as he would through a paper directory.
-
Customer Detail
This portlet displays detailed information from a customer record, like the address or the responsible sales person, in a form-like display.
-
Customer Contacts
The Customer Contacts portlet lists all contacts for a given customer.
-
Recent Sales Activities
The recent sales activities are displayed in this portlet. It allows the user to switch between different views of the date. Supported views are: by date, by activity, and by sales person.
The portlets on this Sales Workplace communicate with each other. Choosing a customer record automatically updates all the other portlets. They immediately display the customer details, all the contacts at this customer, and the most recent sales activities with this customer.
Case study: Application details
The relationships between document types in this application are defined in Table 2-4.
| 1st Document | Relationship | 2nd Document | Key |
|---|---|---|---|
| Customer | 1 to many | Customer Contact | Customer Number |
| Sales Person | 1 to many | Customer | Employee Number |
| Sales Person | 1 to many | Sales Activity | Employee Number |
| Customer Contact | 1 to many | Sales Activity | Contact Name |
| Product | 0-3 to many | Sales Activity | Product Number |
User Roles
The application is designed for two types of users, identified in Table 2-5.
| User type | Access rights | Access method |
|---|---|---|
| Sales person | Author access to all databases. Rights to create Customer, Customer Contact, and Sales Activity documents. No deletion rights. | Notes client or Web browser |
| Application owner | Full rights to create, edit, and delete all record types. | Notes client |
Use Cases
Table 2-6 summarizes the ways in which sales people interact with the system. Many of these use cases are good candidates for use within a portal Environment.
| Activity | Use case |
|---|---|
| Document creation | Create customer document Create customer contact Create sales activity document |
| Document edit | Edit customer document Edit customer contact document Edit sales activity document Edit sales person document |
| View/Lookup/Search documents | Customers by name Customer contacts by Name Customer contacts by customer Sales people by name Sales activities by sales person Sales activities by customer Sales activities by customer contact Sales activities by date |
| Delete documents | None |
Application owners have a superset of the rights given to sales people. Table 2-7 summarizes the additional rights application owners have to the system. While technically feasible, there is a lower business need to provide this functionality in a portal environment.
| Activity | Use case |
|---|---|
| Document creation | Create sales person document Create product document |
| Document edit | Edit product document |
| View/Lookup/Search documents | Products by name Products by number |
| Delete documents | Delete all record types |
Additional application functionality
In order to provide an example as close to the real world as possible, this application uses many development features used by the majority of Notes/Domino applications. These include:
-
Keyword lists based on @DbLookups and other @Functions
-
Input validation and input translation formulas
-
Computed fields, hidden fields, shared fields
-
Hide-when formulas based on keyword changes
-
A page with embedded outline for the sales and customer databases to maintain consistent feel with cross-database navigation
-
Links between related documents from a Web browser. For example, a sales activity record has links to the corresponding customer and sales person records.
-
Use of $$Return field on document save
-
Rich text for additional information
-
Action buttons with hide-when formulas on forms
-
Use of sections
-
Use of subforms
-
Categorized, sorted views
-
Full-text indexed databases
Data dictionary
A complete description of the fields in each document type can be found in Appendix A, "Data dictionary for case study" on page 415.
|
| < Day Day Up > |
|
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 103