21.
| [Cover] [Contents] [Index] |
Page 116
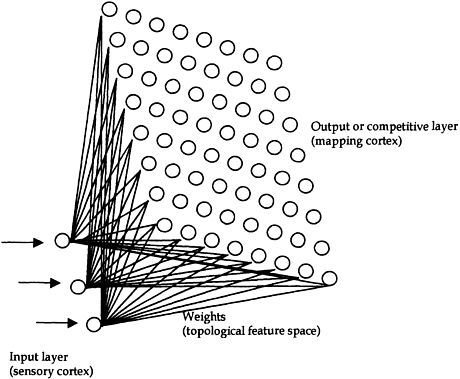
Figure 3.6 Example of the topology of a self-organising map (SOM) with three components: the input layer (sensory cortex) with three neurones, the linking weights (topological feature space), and the output layer (mapping cortex) made up by a grid of 8×8 neurones all equally spaced.
neurone is determined from: min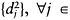 output layer. A competitive Hebbian-type learning law adjusts the synaptic weights of neurone j and its neighbouring neurones:
output layer. A competitive Hebbian-type learning law adjusts the synaptic weights of neurone j and its neighbouring neurones:
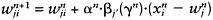 |
(3.12) |
where the learning rate αn is a time-decaying function (i.e. reducing in magnitude as the number of training iterations increases) expressed as:
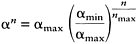 |
(3.13) |
with constraints 1≥α, and αmin, αmax≥0. The neighbourhood function βj(γn) determines a Gaussian neighbourhood range centred on the winning neurone j. βj′ (γn) is calculated by:
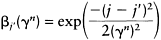 |
(3.14) |
| [Cover] [Contents] [Index] |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 354