155.
| [Cover] [Contents] [Index] |
Page 237
then the following terms can be deleted from both the numerator and denominator of Equation (6.8):
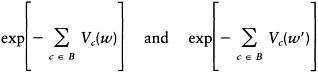 |
|
Hence, this probability depends only on the potential functions Vc of the pixels containing r, which gives the relationship:
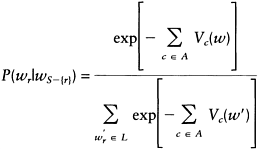 |
(6.9) |
That is, the conditional probability P(w|wS−{r})=P(w|wNr) depends on the neighbours of site r. This proves that Gibbs random field is a Markov random field as far as the cliques are concerned.
The proof of MRF-GRF equivalence provides a simple way for dealing with MRF-based context. It also reduces the complexity of the MRF model, as we can specify the MRF model in terms of GRF model formation. That is, the joint probability P(w) is specified through the energy function U(w) via the potential Vc(w), as shown in Equation (6.4).
6.1.4 Simplified form of MRF
The choice of the form and the parameters of the function shown in Equation (6.4) for the energy function U(w) is a major topic in MRF modelling. When all the parameters and the form of the energy are defined, the model is completely specified. The results of image segmentation are thus dependent both on the classification algorithm and on how well the form and parameters of the function are defined.
The most general form of energy function U(w) is based on up to pairwise clique potential functions that allow the following expression:
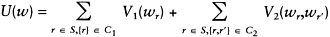 |
(6.10) |
Equation (6.10) is a special case of Equation (6.4). When the label set L
| [Cover] [Contents] [Index] |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 354