Testing Your Cygwin Installation
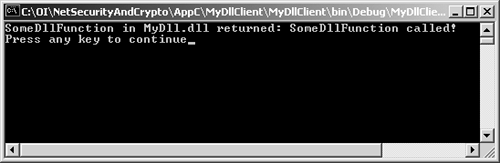
| You can now test your Cygwin installation by compiling a simple DLL with the gcc utility and calling it from a C# .NET program. Here is an example of how to do this. Create the following C source code file named MyDll.c . This will be compiled with the gcc utility to create a Windows DLL. //MyDll.c #include <windows.h> int WINAPI DllMain( HANDLE hInst, ULONG reason, LPVOID lpReserved) { return 1; } __declspec(dllexport) char* SomeDllFunction() { return "SomeDllFunction called!"; } Here is the command line for compiling and generating MyDll.dll . This can be executed at an ordinary Windows command prompt or at the Cygwin Bash Shell prompt. gcc -shared MyDll.c -o MyDll.dll -e DllMain@12 Here is the C# client program that will be used to test MyDll.dll . //MyDllClient.cs using System; using System.Runtime.InteropServices; class MyDllClient { //NOTE: MyDll.dll must be in dll search path [DllImport("MyDll.dll")] public static extern String SomeDllFunction(); static void Main(string[] args) { String str = SomeDllFunction(); Console.WriteLine( "SomeDllFunction in MyDll.dll returned: " + str); } } The result of running this C# client program is shown in Figure C-11. If you achieve this result, then you have set up your Cygwin installation properly. Figure C-11. The result of running the C# client program. If this simple example worked, you should now install and test the GMP library. |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 126