| We have looked at installing and configuring the Windows Server 2003 WINS Server service. Next, we need to look at managing and monitoring the server now that it is running. If your job is typical of most, you will spend a great deal more time managing WINS servers than installing them. Although the WINS server includes limited monitoring capabilities, you do have access to the WINS statistics referenced in the "Troubleshooting" section of the chapter. To get the server statistics, just open WINS Manager and right-click the server in question. From the context menu, select Display Server Statistics, and a snapshot of the server statistics is displayed, as seen previously in Figure 4.18. The WINS statistics display should be a starting point for you when you are unsure of what the problem might be or just want to get a quick snapshot of what is going on with your WINS server. The WINS manager application has additional capabilities. From the open WINS manager application, you can select the WINS server and then use the Action menu to access these actions: Display Server Statistics This option displays statistics discussed in a previous section of this chapter. Scavenge Database This option enables you to manually clean unused entries from the WINS database. Verify Database Consistency This option causes the server to go out to the network hosts and verify the entries in the WINS database. This process can be very processor and network intensive, so be sure to run it after hours. Verify Version ID Consistency This option forces the WINS server to go to all the other WINS servers on the network and then check the database version numbers to ensure that they are consistent. This is potentially another long operation, so it should be run after hoursor at least not when everyone in the office is trying to read email. Start Push Replication This option manually performs a push replication. Start Pull Replication This option manually performs a pull replication. Back Up Database This option enables you to make a backup copy of the WINS database. Always be sure you have a copy of this database, just in case. If you specify the backup directory, the server will automatically back up the database every 24 hours. Restore the Database This option enables you to restore a backup copy of the database. Tasks This option leads to a menu consisting of the following commands: Start Starts the WINS Server service. This option is available only if the service is stopped or paused. Stop Stops the WINS Server service. Available when the service is running or paused. This option causes the server statistics to be reset. Pause Pauses the WINS Server service. This option does not reset the statistics. Resume Resumes the WINS Server service when paused. This option is available only when the service is paused. Restart Restarts the WINS Server service. This option is available unless the server is stopped.
Delete This option deletes a WINS server from the WINS manager. Refresh This option causes all the displayed information to be refreshed with a current status. Export List This option enables you to export the information from the WINS server to a tab- or comma-delimited text or Unicode text file. Properties This option opens the server properties, as discussed in a previous section of this chapter.
The Windows Server 2003 WINS service also includes some new functionality for managing the WINS database. If you open the WINS manager and click Active Registrations, you will see a list of all the dynamically added entries in the WINS database. Although this is useful, it would be nice to be able to search for a specific entry, or even to filter on specific record types. The good news is that you can. If you right-click the Active Registration folder and select Find by Name or Find by Owner, you can search the WINS database for specific entries. Under Find by Owner, you can even filter which WINS record types should be shown. If you are working in a large environment (500 computers or more), you will find these capabilities invaluable because computers can often enter 10-12 entries each into the WINS database. You probably won't relish reading through 5,000-6,000 WINS records looking for a specific machine. The Windows Server 2003 WINS service enables you to delete not only static records, but also dynamic records. This is a major improvement over previous versions of WINS, in which you couldn't delete dynamic entries. Now that we have examined the options for managing the WINS server, let's take a look at some of the ways to monitor the service. Before you do Step by Step 4.5, you should look at which counters you can use to monitor WINS. The WINS object has the following counters associated with it: Failed Queries/Sec Gives you the number of failed WINS queries per second. If this number is very high or suddenly spikes, you might have an issue with WINS resolution. Failed Releases/Sec Gives you the number of failed WINS released per second. If this number is very high or suddenly spikes, you might have an issue with WINS resolution. Group Conflicts/Sec The rate at which group registrations by the WINS server resulted in conflicts with the database. Group Registrations/Sec The rate at which group registrations are being received. Group Renewals/Sec The rate at which group registrations are being renewed. Queries/Sec The rate at which queries are being received. Releases/Sec The rate at which releases are being received. Successful Queries/Sec The number of successful queries per second. This is useful if you are trending your WINS usage. Successful Releases/Sec The number of successful releases per second. This is useful if you are trending your WINS usage. Total Number of Conflicts/Sec This is the sum of the unique and group conflicts per second. Total Number of Registrations/Sec This is the sum of the unique and group registrations per second. Total Number of Renewals/Sec This is the sum of the unique and group renewals per second. Unique Conflicts/Sec The rate at which unique registrations and renewals causes conflicts with the database. Unique Registrations/Sec The rate at which unique registrations are received by the server. Unique Renewals/Sec The rate at which unique renewals are received by the server.
To configure WINS performance monitoring, follow Step by Step 4.5. Step By Step 4.5. Monitoring WINS Performance 1. | Open the Performance application by selecting Start, Programs, Administrative Tools, Performance.
| 2. | In the Performance console, select System Monitor node, as seen in Figure 4.19.
| 3. | To create an entry in System Monitor, click the Add (+) icon. The Add Counters windows opens. By default, it opens to the Processor performance object.
| | | 4. | Select the WINS Server performance object. You will see the list of counters that are available for the WINS service, as seen in Figure 4.20.
Figure 4.19. The System Monitor enables you to monitor the performance of your server's statistics in real-time. 
Figure 4.20. The counters associated with WINS enable you to comprehensively examine the WINS server's activities. 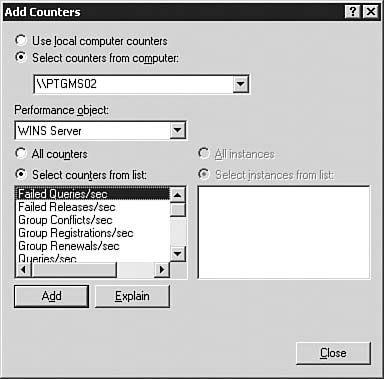
| 5. | After you have decided which counter you want to monitor, click Add. You can add multiple counters either by selecting each counter and clicking Add or by holding down the Ctrl key while you select all the counters you want to monitor and clicking Add. Click Close when you are done. You will see your counters being graphed in a manner similar to those shown in Figure 4.21.
|
Figure 4.21. Once you've added counters, you can view the performance of the server. 
We've looked at the management options available in the WINS manager application, and we've discussed how to monitor the performance of the various WINS counters using the Performance console. At this point, you should have a good understanding of the Windows Server 2003 WINS Server service and WINS in general. |


