Tool 215: What-If Analysis
| AKA | "What-if" Principle |
| Classification | Analyzing/Trending (AT) |
Tool description
The What-if analysis is a very effective idea-generating process that allows a team to question the possible outcomes if a process or procedure is altered. This is also helpful in assessing attempts to do something new or different, or to find a so-far untried solution to a problem.
Typical application
-
To discover and assess alternative ways to use a product or process.
-
To question existing practices and applications and to explore potential changes that might yield product or process improvement or a solution to a problem.
-
To change one's perspective in the idea-generation process.
Problem-solving phase
| → | Select and define problem or opportunity |
| → | Identify and analyze causes or potential change |
| Develop and plan possible solutions or change | |
| → | Implement and evaluate solution or change |
| Measure and report solution or change results | |
| Recognize and reward team efforts |
Typically used by
| Research/statistics | |
| 1 | Creativity/innovation |
| 1 | Engineering |
| Project management | |
| Manufacturing | |
| Marketing/sales | |
| Administration/documentation | |
| Servicing/support | |
| 4 | Customer/quality metrics |
| 2 | Change management |
before
-
SCAMPER
-
Fresh Eye
-
Mental Imaging
-
Problem Analysis
-
Process Analysis
after
-
Creativity Assessment
-
Solution Matrix
-
Opportunity Analysis
-
Activity analysis
-
Process Flowchart
Notes and key points
Option: On a more detailed level for product improvement or development, the What-if analysis could use the SCAMPER technique to generate new ideas: What-if we:
-
S = Substitute?
-
C = Combine?
-
A = Adapt?
-
M = Modify?, Magnify?
-
P = Put to other uses?
-
E = Eliminate?
-
R = Reverse?, Rearrange?
-
the material, part, shape, color, purpose, design, sequennce, components, procedure, etc.
Step-by-step procedure
-
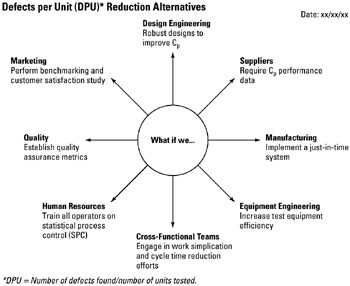
STEP 1 The team identifies the problem or issue to be analyzed. See example Defects per Unit (DPU) Reduction Alternatives.
-
STEP 2 Team participants discuss and explore the "what-ifs" of the different proposed ways of solving the problem or improving the current situation.
-
STEP 3 The facilitator records, on a flip chart, all the finalized alternatives suggested by the team that have merit and need further study.
-
STEP 4 Last, the team prioritizes all potential solutions on the basis of feasibility and resource requirements The flip chart is dated.
Example of tool application
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 326
- ERP Systems Impact on Organizations
- Challenging the Unpredictable: Changeable Order Management Systems
- ERP System Acquisition: A Process Model and Results From an Austrian Survey
- A Hybrid Clustering Technique to Improve Patient Data Quality
- Relevance and Micro-Relevance for the Professional as Determinants of IT-Diffusion and IT-Use in Healthcare