Tool 166: Responsibility Matrix
| AKA | Accountability Grid |
| Classification | Changing/Implementing (CI) |
Tool description
A responsibility matrix is used to identify decisions to be made, major activities to be completed, and persons or groups involved in a change project. Project management requires constant tracking of activities and schedule; a responsibility matrix provides the assignments and understanding of employees' roles and resources required to complete a project.
Typical application
-
To display decision requirements, activities to be completed, and key personnel involved in a project management setting.
-
To provide a common understanding of a project's people and resource requirements and allocation.
Problem-solving phase
| Select and define problem or opportunity | |
| Identify and analyze causes or potential change | |
| → | Develop and plan possible solutions or change |
| → | Implement and evaluate solution or change |
| Measure and report solution or change results | |
| Recognize and reward team efforts |
Typically used by
| Research/statistics | |
| Creativity/innovation | |
| Engineering | |
| 1 | Project management |
| Manufacturing | |
| Marketing/sales | |
| 3 | Administration/documentation |
| Servicing/support | |
| Customer/quality metrics | |
| 2 | Change management |
before
-
Problem Analysis
-
Checklist
-
Demographic Analysis
-
Circle response
-
Consensus Decision Making
after
-
Resource Histogram
-
Action Plan
-
Basili Data Collection Method
-
Project Planning Log
-
Milestones Chart
Notes and key points
-
No cell may contain more than one role.
-
Avoid splitting primary responsibility (R) for action.
-
Avoid assigning too many approvals (A) to any one item.
-
Coding: Typical codes have been assigned in this example. Additional designations may be needed.
Step-by-step procedure
-
STEP 1 A facilitated planning team or committee identifies major project activities and responsibilities.
-
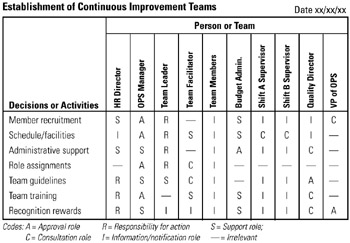
STEP 2 The facilitator creates a responsibility matrix on a whiteboard and requests participants' assistance in completing the matrix. Activities and actors are listed. See example Establishment of Continuous Improvement Teams.
-
STEP 3 Next, participants determine personnel assignments and respective roles in the completion of project activities. A coding scheme is used as shown in this example.
-
STEP 4 Finally, the completed responsibility matrix is checked, revised, and dated.
Example of tool application
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 326