Tool 84: Fresh Eye
| AKA | N/A |
| Classification | Idea Generating (IG) |
Tool description
The fresh eye technique searches for new or unique ideas to a previously analyzed problem. Process owners often have difficulties looking at a problem from an unbiased view. The fresh eye technique allows other, uninvolved people to generate and pass on some innovative ideas on how to solve the problem.
Typical application
-
To stimulate a fresh look at the problem.
-
To search for unique or more promising ideas to solve a problem or improve a process.
-
To involve outside-the-process people in the idea generation.
Problem-solving phase
| → | Select and define problem or opportunity |
| → | Identify and analyze causes or potential change |
| → | Develop and plan possible solutions or change |
| Implement and evaluate solution or change | |
| Measure and report solution or change results | |
| Recognize and reward team efforts |
Typically used by
| Research/statistics | |
| 1 | Creativity/innovation |
| Engineering | |
| Project management | |
| Manufacturing | |
| 2 | Marketing/sales |
| Administration/documentation | |
| 3 | Servicing/support |
| Customer/quality metrics | |
| Change management |
before
-
Reverse brainstorming
-
Double Reversal
-
Pin Cards Technique
-
Activity analysis
-
Brainstorming
after
-
Consensus decision
-
Different point of view
-
Action plan
-
Run-it-by
-
Presentation
Notes and key points
-
There are two variations of the fresh eye technique:
-
Individual or team search for other problem-solving ideas.
-
Asking people outside the team or process to think of problem-solving ideas.
-
Step-by-step procedure
-
STEP 1 The team decides to use the fresh eye technique to improve the chances of discovering additional, unique, or innovative ideas.
-
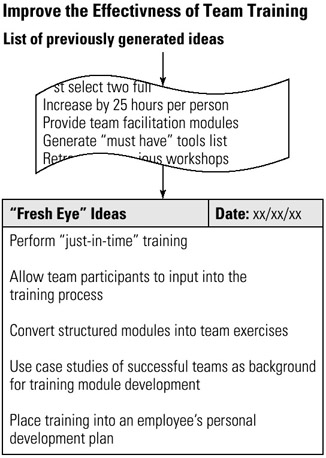
STEP 2 The previously developed problem statement is rechecked for content and clarity. The team may decide to restate the problem in different, yet clear and concise terms. See example Improve the Effectiveness of Team Training.
-
STEP 3 The problem statement is typed and distributed to some people who are interested in assisting but who are outside the problem or have little experience with the undesirable situation.
-
STEP 4 After approximately one week, all ideas from outsiders are collected and their potential evaluated by the team.
-
STEP 5 Finally, the team may find that this process may give them some other fresh ideas or build on their previous list of ideas.
Example of tool application
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 326