Section 17.1. Template Basics
Templates let you build pages that share a similar structure and graphic identity, quickly and without having to worry about accidentally deleting or changing elements. Templates come in very handy when you're designing a site for which other, less Dreamweaver-savvy individuals are responsible for adding new pages. If you use a template, these underlings can modify only the areas of a page that you, the godlike Dreamweaver guru, define.
Tip: Tip: Macromedia Contribute, a simple, word processorlike program for updating Web sites, works very well with sites built using Dreamweaver templates. If you build sites that are updated by people who don't know the first thing about Dreamweaver or building Web pages, Contribute can help. You can find more information about this program at Macromedia's Web site: www.macromedia.com/contribute/.
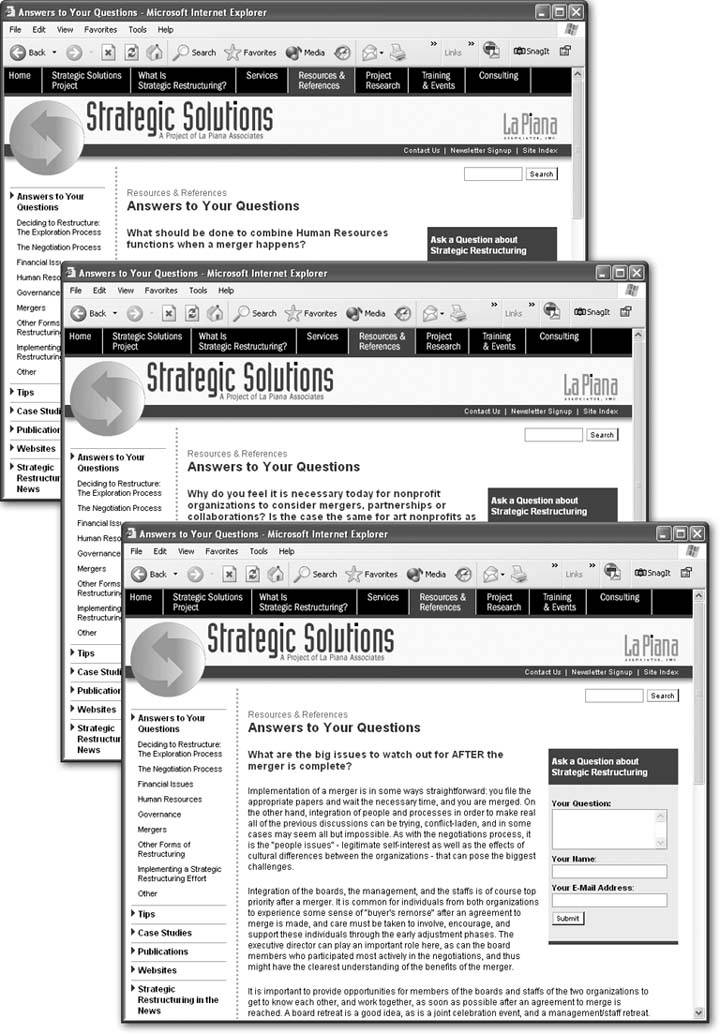
A new page based on a templatealso called a template instance , or child page looks just like the template, except that you can edit only certain areas of the page, called, logically enough, editable regions . In the example shown in Figure 17-1, one editable region includes the question-and-answer text area; the rest of the page remains untouched and is, in fact, locked.
Figure 17-1. These three Web pages are part of a section of a Web site dedicated to answering frequently asked questions. The pages each provide the answer to a different question, but are otherwise identical, sharing the same banner, navigation buttons , sidebar, and footer. This is a common scenario for Web sites that include news stories, employee profiles, product pages, or press releases. In fact, it's so common that Dreamweaver has a special featureTemplatesto help you build such pages.
A Dreamweaver template can be very basic: one or more areas of a page (the editable regions) can be changed, others can't ( locked regions ). But Dreamweaver also includes many subtle ways for controlling template instances. Here's an overview of the features you'll encounter when creating and using templates:
-
Editable regions . These are the basic building blocks of a template. An editable region is a part of a pagea paragraph, table cell , or headline, for examplethat people can change on each template instance. A template page can have multiple editable regionsfor example, one in a sidebar area and another in the main content section of a page.
-
Editable tag attributes . There may be times when you want to make a particular tag property editable. For instance, if you want to specify a different background color for each page, you'll want to permit changes to the <body> tag's Bgcolor property, or let people set the tag's class property to a particular CSS class style.
Or perhaps you've built a template that includes a photo with some complex formatting (left-aligned by a Cascading Style Sheet, perhaps). Turning the entire image into an editable region could pose problems: When someone creates a new page from the template and then inserts a new photo, all of the formatting information can get lost. Instead, you could make just the image's Src property editable. People would then be able to insert new images for each page without inadvertently ruining the photo's formatting. (If the Width and Height properties vary from image to image, you could also make those attributes editable.)
-
Repeating regions and repeating tables . Some Web pages include lists of items: catalogs of products, lists of news articles, albums of photos, and so on. Dreamweaver lets you define repeatable regions for pages like this.
For example, a page of product listings can include a picture, name , and price for each product in a catalog, organized using a table with multiple rows (Chapter 7).
As template builder, you may not know in advance how many products the page will eventually list, so you can't fully design the page. However, you can use Dreamweaver to define a rowor any selection of HTMLas a repeating region, so that page authors can add new rows of product information when needed.
-
Optional regions and editable optional regions . Optional regions make templates even more flexible. They let you show or hide content on a page-by-page basis.
Suppose you create a template for your company's products. When some products go on sale (but others remain full price), you could add an optional region on the template that displays a big "On Sale!" logo. When you create a new product page, you could show the optional region for products that are on sale and keep it hidden for the others.
Editable optional regions are similar, but they have the added benefit of being editable. Maybe you're creating a template for an employee directory, giving each employee a separate Web page with contact information. Some employees also want their picture displayed on the page, while others don't (you know the type). Solution: Add an editable optional region that would let you show the space for a photo and add a different photo for each page. For the shyer types, you would simply hide the photo area entirely.
Furthermore, Dreamweaver can create nested templates, which inherit design elements from a master template. In this way, you can create a general unified design that's shared by other templates; this feature is described on Section 17.5.
But facilitating page creation is only one of the benefits of templates. You'll also find that templates can greatly simplify the process of updating a Web site's design. Like Library items, pages based on templates retain a reference to the original template file. Any changes made to the template pass on to all pages created from it, which can save you hours of time and trouble when it comes time to update the look or structure of your site. Imagine how much time you'll save when your boss asks you to add "just one more" button to the site's navigation bar. Instead of updating thousands of pages by hand, you need to update only a few template files.