IS-IS Metric Extensions
Two newly proposed LSP TLVs specify wider fields for the default metric, allowing larger interface metric values than the previous 63 maximum. This enhancement can be leveraged for basic IP routing, as well as MPLS-based traffic engineering applications. These new TLVs are as follows :
-
Extended Intermediate System Reachability TLV (Type 22)
-
Extended IP Reachability TLV (Type 135)
The Extended IS Reachability TLV is an extension of the Intermediate System Neighbors TLV (Type 2), and the Extended IP Reachability TLV extends the IP Internal Reachability TLV (Type 128). These TLVs take advantage of the fact that current and most widely deployed implementations of the IS-IS protocol do not support the QoS metric types, namely delay, expense, and error metrics. The fields reserved for these metrics are, therefore, wasted . These TLVs are designed to reassign the QoS metric fields to the default metric. TLV Type 22 dedicates 24 bits for metric, and TLV Type 135 dedicates 32 bits compared to the 6 bits originally specified.
Another new TLV is the Traffic Engineering Router ID TLV (Type 134), which is used to designate the address on a stable interface, such as a loopback interface, for configuring various capabilities of the router. The Router ID TLV contains the 4-octet Router ID of the router originating the LSP, and it is essentially relevant only for MPLS traffic engineering. This TLV is not discussed further because MPLS is beyond the scope of this book.
Extended IS Reachability TLV (Type 22)
The Extended IS Reachability TLV is intended to replace the IS Neighbors TLV (Type 2) with a primary objective to provide support for larger metric values, in general, and also to support IS-IS-dependent MPLS traffic engineering. The proposed format for this TLV is as follows:
-
Type (1 byte) ” 22
-
Length (1 byte) ” Total length of the Value field
-
Value ” 3 bytes of default metric
-
- 1 byte of length of sub-TLVs
-
- 6 bytes of system ID + 1-byte pseudonode number
-
- 0 “244 bytes of sub-TLVs
-
The 3 bytes of the metric field are used to encode the metric as a 24-bit unsigned integer. For practical purposes, a maximum path value (0xFE000000) is specified to prevent computation overflows by existing implementations of the SPF algorithm. Also links with the maximum possible metric of 2^24 “ 1 are to be ignored in path calculations.
Sub-TLVs are used for MPLS traffic engineering purposes.
Extended IP Reachability TLV (Type 135)
The Extended IP Reachability TLV embodies the same ideas behind the Extended IS Reachability TLV and is designed to replace TLV 128. Its primary goal is to utilize theQoS metric fields to support large metric values for IP prefixes while using sub-TLVs for distributing MPLS traffic engineering resource information. The format of this TLV is as follows:
-
Type (1 byte) ” 135
-
Length (1 byte) ” Total length of the Value field
-
Value ” 4 bytes of metric information
-
- 1 byte of control information, composed of the following:
1 bit of up/down status
1 bit of sub-TLV presence bit
6 bits of prefix length
-
- 0 “4 bytes of IPv4 prefix
-
- 0 “249 bytes of optional sub-TLVs made up of:
1 byte of length of sub-TLVs
0 “250 bytes of sub-TLVs
-
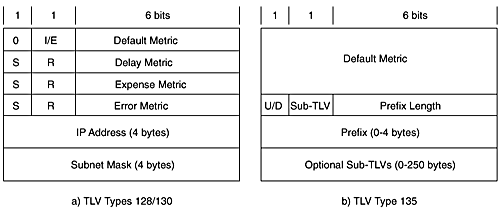
The up/down status bit is intended to prevent routing loops , and it is set when a route is advertised from Level 2 into Level 1. This prevents such routes from being re-advertised back into Level 2. Sub-TLVs specify MPLS traffic engineering attributes. The 4-byte (32-bit) metric field permits large metric values limited to a maximum of MAX_PATH_METRIC (0xFE000000). Prefixes with metrics larger than MAX_PATH_METRIC are ignored in SPF computations . Figure 5-10 shows a side-by-side comparison of graphical representations of TLV Types 128/130 and TLV Type 135.
Figure 5-10. Comparison of TLV 128/130 and TLV 135.
Example 5-6 shows an LSP with entries for TLV 22 and TLV 135 in italics captured on a Cisco router with the show isis database detail command.
Example 5-6 LSP with Extended TLVs
RTX# show isis database RTB.00-00 level-1 detail IS-IS Level-1 LSP RTB.00-00 LSPID LSP Seq Num LSP Checksum LSP Holdtime ATT/P/OL RTB.00-00 0x000000FE 0x59C3 1185 1/0/0 Area Address: 49.0001 NLPID: 0xCC Hostname: RTB IP Address: 11.1.1.2 Metric: 10 IP 10.1.1.0/24 Metric: 10 IP 192.168.2.0/30 Metric: 100 IP 11.1.1.2/32 Metric: 100 IS-Extended RTB.02 Metric: 10 IS-Extended RTA.01 Metric: 0 ES RTB Support for TLV Types 22 and 135 (IS-IS wide metrics) is available in recent Cisco IOS releases of the 12.0S and 12.0T trains. The router-level command metric-style wide enables a Cisco router running the appropriate IOS release to send LSPs with wide metrics and to receive and correctly interpret LSPs with TLV Types 22 and 135. The command metric-style transition allows smooth migration from old narrow metrics to the new wider metrics. This option works by allowing a router to send and receive both narrow and wide metrics. In particular, MPLS traffic engineering configuration requires use of the new wide metric option. The command metric-style narrow reinstates original and default behavior. Metric configuration and use of the metric-style command are discussed in more detail in Chapter 8, "Network Design Scenarios" and Chapter 9, "Configuring IS-IS for IP Routing on Cisco Routers."
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 144