Chapter 12. Virtual LAN (VLAN) Introduction
This chapter covers the following topics:
VLAN Memberships
VLAN/WAN Integration
VLANs create logically separate LANs on the same physical switch. VLANs also can be used to group physically separate LANs so they behave as though they are on the same physical network segment (wire). Each switch port switch is assigned to a VLAN and in the case of the Cisco Catalyst, VLAN operation is performed at Layer-2 (OSI Model Data-Link Layer), requiring a Layer-3 (Network) device (such as a router, to move traffic between VLANs). You configure VLANs through software rather than hardware, which make VLANs flexible in their implementation. The biggest advantage of a VLAN is that when you move a workstation to another location, it can stay on the same VLAN without any hardware reconfiguration. VLANs are used in both EtherNet and Token Ring LAN configurations.
NOTEVLANs support Ethernet, Token Ring, and FDDI LAN implementations. |
Figure 12-1 illustrates a VLAN implementation, with two VLANS: VLAN 100 and VLAN 200.
Figure 12-1. VLAN Implementation with Two VLANS (100 and 200)
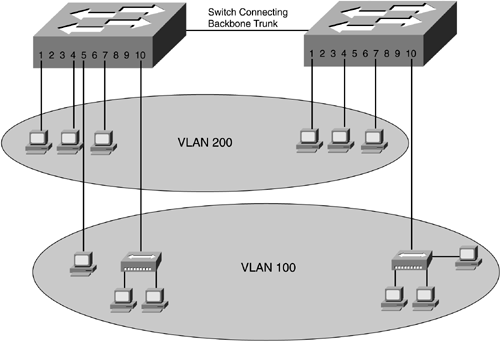
The LAN switch is the core component of the VLAN for example, Cisco Catalyst 2900/3500/6500 Series switches. The following list details the significant benefits of using VLANs over traditional LAN implementations (for example, shared media):
Reduction in the cost of handling user moves and changes Any node can be moved or added quickly and conveniently from the network management console rather than the wiring closet. VLANs provide a flexible, easy, and less costly way to modify logical groups in changing environments.
Forming "virtual workgroups" VLANs provide independence from the physical network topology by enabling physically diverse workgroups to be connected logically within a single broadcast domain. If an organization expands or relocates, it is more efficient to add ports in new locations to existing VLANs.
VLANs can increase network performance By reducing the number of collision (Ethernet) domains, VLANs increase performance. Forming logical networks improves network performance by limiting broadcast traffic to users within defined workgroups.
VLANs can enhance network security In a switched network, frames are delivered only to the intended recipients and broadcast frames only to other members of the VLAN. This containment enables network managers to segment users who require access to sensitive information into VLANs separate from the general user community.
Another VLAN application is web-hosting centers. Hosting center customers sometimes prefer to avoid accessing their servers in these hosting centers across the public Internet because of security concerns. VPNs give you one way to address these concerns, and VLANs provide another, depending upon the customer's bandwidth requirements for file transfer in and out of the data center. A WAN component is required in the VLAN method, such as Frame Relay or ATM. Frame Relay is discussed in more detail in Chapter 10, "Frame Relay Introduction," and ATM is discussed in more detail in Chapter 9, "Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) Introduction."
Data centers can reduce their investments by using VLANs to create a separate dedicated LAN to each customer's server with the same physical LAN infrastructure. Because each VLAN uses its own IP subnet, the customer's private address spaces also can be preserved.
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 269