Advanced XML Features in Excel
| We will use the mapped spreadsheet we have created to consider some other XML features in Excel. Importing XML and Refresh XML DataTo import XML from an XML file into our mapped spreadsheet, follow these steps:
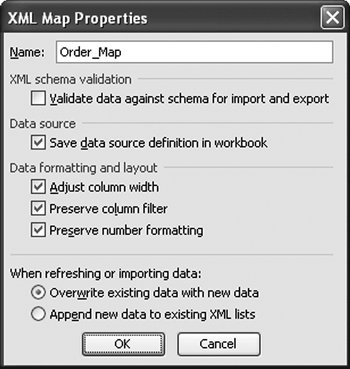
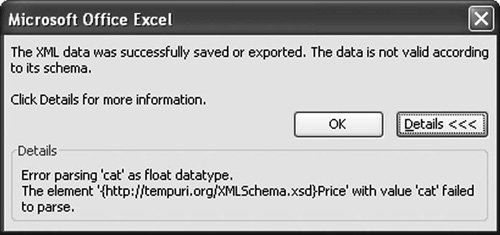
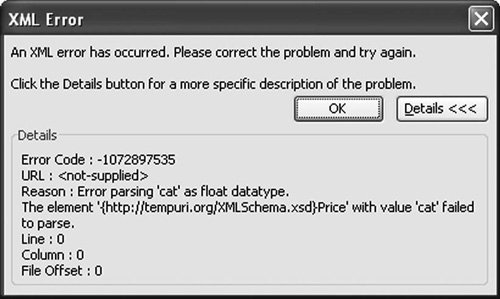
Note that Excel does not remember the XML file you last imported if you uncheck Save Data Source Definition in Workbook in the XML Map Properties dialog box (discussed in the next section). The XML Map Properties Dialog BoxFigure 21.18 shows the XML Map Properties dialog box, which you can display by choosing Data > XML > XML Map Properties. Note that you must select a cell in the worksheet that is mapped to XML for this menu item and some of the other menu items in the XML menu to be available (not grayed out). Figure 21.18. The XML Map Properties dialog box. XML Schema ValidationThe first setting we consider in this dialog box is the XML schema validation setting. With this setting unchecked, set the price of one of the books to a value such as cat. This is clearly not a valid floating-point number. Choose Data > XML > Export, and export the XML to a file. No error will occur. Now check the Validate Data Against Schema for Import and Export check box in the XML Map Properties dialog box. Export the XML again. This time, you will get the error dialog box shown in Figure 21.19 for using the value of cat in a place where a number was expected. Figure 21.19. A schema validation error on export. If you try to import XML that has the value cat for a floating-point number, you also get errors with the Validate Data option checked. Figure 21.20 shows the first error dialog box that appears. Figure 21.20. A schema validation error on import.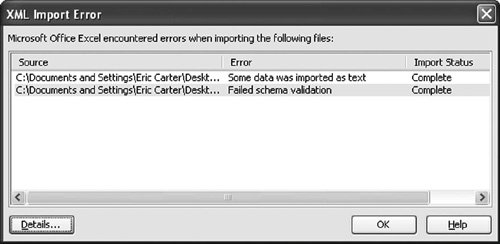 The first line warns that some data was imported as textnamely, the value cat was imported as text rather than as a floating-point number. When you click the second error line and click the Details button, the dialog box shown in Figure 21.21 displays. Figure 21.21. Details of the validation error on import. Data Formatting and LayoutThe XML Map Properties dialog box provides settings for controlling the data formatting and layout of lists that are XML-mapped. The Adjust Column Width check box, when checked, will make it so that an import of XML into a list will automatically adjust the column width to fit the data that is imported. Excel will make a column wider up to two thirds the width of the screen. To prevent automatically adjusting the column width of a list when XML is imported, uncheck this check box. The Preserve Column Filter check box, when checked, will preserve the filtering settings for a list when XML is imported into the list. If you have the list set to show only books whose publisher is Addison-Wesley, for example, importing new XML will preserve that setting. If you uncheck this check box, whenever XML is imported into a list, any existing filters will be cleared. The Preserve Number Formatting check box, when checked, will preserve any number formatting in the list that the XML is imported into. If a column is set to display the book price in red if it is greater than $20, for example, this setting will be preserved when XML data is imported into the list. If this check box is not checked, any number formatting in the list will be cleared when XML data is imported into the list. Appending Data to ListsThe XML Map Properties dialog box provides for two different behaviors when importing XML or refreshing XML and when updating a mapped list. If you choose Overwrite Existing Data with New Data, a mapped list will be cleared of its data before loading data from the XML data file on import or refresh. If you choose Append New Data to Existing XML Lists, the data in the list will be preserved, and the data from the XML data file will be appended on import or refresh. So with the append setting set, importing the XML in Listing 21.5 into a blank list generates three book orders on the first import, and on refresh it appends the three book orders to the list, for a total of six book orders. |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 221