Public Folder Limits
Just as mailbox limits can help you to control growth of mailbox database and prevent abuse, assigning limits to public folders can be equally important in controlling public folder growth. There are a couple of different types of limits you can set with respect to public folders. These include the default limits for the public folder database and individual folder limits.
Defining Limits per Database
Each public folder database has default storage limits that are established and affect all public folders that have a replica on it. The public folder database Limits property page is shown in Figure 9.11. If you are an experienced Exchange 2000/2003 administrator, you may note that there are default limits in Exchange 2007 where none existed previously.
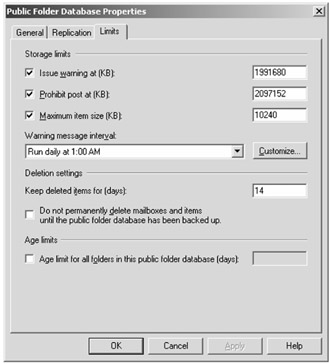
Figure 9.11: Default public folder database limits
The properties that are found on the Limits property page affect all public folder instances on the database. Table 9.2 describes these properties.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Issue Warning At (KB) | Sends a warning message to the folder owner and folder contacts informing them that the folder has reached is storage limit. The default is 1,945MB. |
| Prohibit Post At (KB) | When the folder content exceeds this size, messages can no longer be delivered to this folder (if the folder is mail enabled) and users cannot post to this folder. The default is 2GB. |
| Maximum Item Size (KB) | Specifies the largest message size that can be delivered to this folder (if mail enabled) or the largest item that can be posted to this folder. The default it is 10MB. |
| Keep Deleted Items For (Days) | Specifies the how long deleted folders will be retained before they are permanently purged. During this time, the folder owner can undelete items that were accidentally (or intentionally) deleted. The default interval is 14 days. |
If you are a fond of the EMC, you can also retrieve this information from the PowerShell. In the following example, the public folder database is called Public Folder Database and the server is HNLEX02 and we are piping the output of the Get-PublicFolderDatabase to the Format-List cmdlet:
Get-PublicFolderDatabase "HNLEX02\Public Folder Database" | Format-List Name,MaxItemSize,IssueWarningQuota, ProhibitPostQuota,ItemRetention Name : Public Folder Database MaxItemSize : 10MB IssueWarningQuota : 1945MB ProhibitPostQuota : 2GB ItemRetention : 14.00:00:00
If you want to change one of these limits using the EMS (for example setting the MaxItemSize to 15MB), you would type this command:
Set-PublicFolderDatabase "HNLEX02\Public Folder Database" -MaxItemSize:15MB
Defining Folder-by-Folder Limits
You can also define folder-by-folder limits. These limits override the default limits specified on a public folder database. The Exchange 2007 EMC does not provide an interface for managing individual public folder properties, so you will have to have an Exchange 2003 System Manager console installed somewhere within your organization. Unfortunately, you cannot install the Exchange System Manager from Exchange 2003 on an Exchange 2007 server or any machine with the Exchange Management Console. See Chapter 4, "Installing Exchange Server 2007," for more information on installing and using the Exchange System Manager with Exchange 2007.
To manage individual public folder limits, you need to locate the Folders container in an Exchange administrative group. Once you have found the Folders container, you can browse the public folders, locate the folder you wish to set limits on, and display that folder's properties. Figure 9.12 shows the Limits property page of a folder called Research Documents.
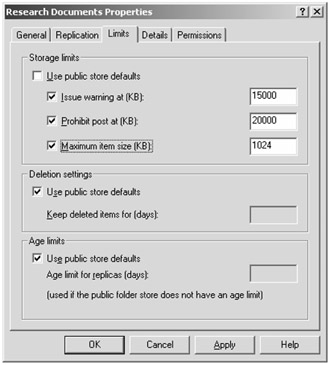
Figure 9.12: Limits property page of the Research Documents folder
Notice in Figure 9.12 that we have cleared the Use Public Store Defaults check box and have provided our own limits (Issue Warning, Prohibit Post, and Maximum Item Size) for this particular public folder.
If you do not have an Exchange System Manager console installed anywhere in your organization, you can still manage individual public folder properties using the Exchange Management Shell. For example, here we retrieve the properties of a public folder called Somorita Surfboards:
C:\>get-publicfolder "\Somorita Surfboards" | FL AgeLimit : 30.00:00:00 EntryId : 000000001A447390AA6611CD9BC800AA002FC45A030037 C54B179C6AC547BE6A36965D18C96700000001C1690000 HasSubFolders : True HiddenFromAddressListsEnabled : True LocalReplicaAgeLimit : MailEnabled : False MaxItemSize : 4MB Name : Somorita Surfboards ParentPath : \ PerUserReadStateEnabled : True PostStorageQuota : 65000KB Replicas : {Public Folders, Public Folder Store (HNLEX01)} ReplicationSchedule : {} RetainDeletedItemsFor : 15.00:00:00 StorageQuota : 50000KB UseDatabaseAgeDefaults : False UseDatabaseQuotaDefaults : False UseDatabaseReplicationSchedule : True UseDatabaseRetentionDefaults : False Identity : \Somorita Surfboards IsValid : True OriginatingServer : hnlex03 To set the prohibit post limit (PostStorageQuota) and the issue warning quota (StorageQuota) using the EMS, here is the command you would type:
Set-PublicFolder "\Somorita Surfboards" -PostStorageQuota:95MB -StorageQuota:80MB
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 198