Recipient Administration
In Chapter 10, "Managing Recipients," we will go in to a lot more detail on recipient administration. For now, we want to introduce the Recipient Configuration work center of the Exchange Management Console and the show you many of the recipient management EMS cmdlets. Recipients management is most easily performed using the Recipient Configuration work center of the EMC (see Figure 8.23).
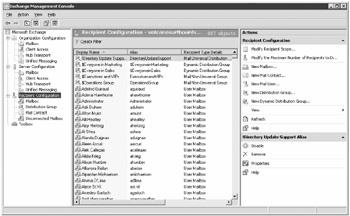
Figure 8.23: Managing Exchange 2007 recipients using the Exchange Management Console
For many medium and large businesses, the EMS will prove most useful for managing mail-enabled recipients. For that reason, we wanted to provide a fairly comprehensive list of the EMS cmdlets available. In the following sections, we will review the management of each type of recipient and provide you with a list of the EMS cmdlets that can be use for each.
Mailbox Management
If you select the Mailboxes subcontainer of the Recipient Configuration work center of the EMC, you can see just the mailbox-enabled users in the organization. This could potentially be a pretty big list, so you can apply filters to narrow the scope of the list to just what you want to see. From here, you can select the properties of a mailbox (such as those shown in Figure 8.24).
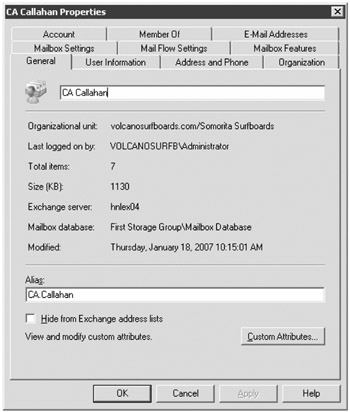
Figure 8.24: Managing a mailbox's properties using the Exchange Management Console
The mailbox properties you see in Figure 8.24 include attributes of the user account that are not really Exchange specific. For example, you can change information such as telephone numbers, department, web page, address, manager, and office location. There are quite a few tasks and actions you can perform against a mailbox and not all of them can be performed via the graphical user interface. The following list includes some of these tasks:
-
Managing user account attributes such as phone, address, and organization properties
-
Moving mailboxes to another mailbox store (or even another Exchange organization)
-
Assigning storage limits, messages size limits, recipient limits, and deleted item retention settings for a mailbox
-
Defining message delivery restrictions and e-mail forwarding options
-
Enabling web service features such as ActiveSync and Outlook Web Access as well as enabling or disabling MAPI connectivity
-
Assigning ActiveSync and messaging records management policies to a mailbox
-
Managing permissions that other users have to a mailbox
-
Managing the ActiveSync devices associated with a mailbox
Let's take a look the cmdlets that are used to manage mailboxes and user accounts:
| Cmdlet | Description |
|---|---|
| Get-User | Retrieves account information about a user in the Active Directory |
| Set-User | Sets the properties of a user account |
| Get-Mailbox | Retrieves mailboxes and properties of mailboxes |
| Get-MailboxStatistics | Retrieves mailbox storage statistics for a mailbox database or a specified mailbox |
| Get-MailboxFolderStatistics | Retrieves mailbox folder statistics for a specified mailbox |
| Get-MailboxCalendarSettings | Retrieves the Calendar Attendant settings for the specified mailbox |
| Get-UMMailbox | Retrieves the Unified Messaging properties for the specified mailbox |
| Get-CASMailbox | Retrieves the Client Access server properties for a specified mailbox |
| Get-MailboxPermissions | Retrieves the permissions that are assigned or inherited for the specified mailbox |
| Get-UMMailboxPIN | Retrieves a Unified Messaging PIN for the specified mailbox |
| Move-Mailbox | Moves a mailbox from one mailbox database to another |
| Connect-Mailbox | Reconnects an existing user account to a mailbox that was previously deleted |
| Enable-UMMailbox | Enables a mailbox to support Unified Messaging |
| Restore-Mailbox | Copies mailbox data from a recovery storage group to the production mailbox location |
| Export-Mailbox | Exports mailbox content to an alternate location |
| Remove-ActiveSyncDevice | Removes an ActiveSync device that is associated with the specified mailbox |
| Clear-ActiveSyncDevice | Performs a remote wipeout of the specified ActiveSync device the next time it connects |
| Get-ActiveSyncDeviceStatistics | Retrieves usages statistics and device information about the specified ActiveSync device |
| New-Mailbox | Creates a new user account and mailbox |
| Enable-Mailbox | Enables an existing user so that it has a mailbox |
| Remove-Mailbox | Deletes the specified user account and mailbox |
| Disable-Mailbox | Removes a mailbox from the specified user but does not delete the use account |
| Set-Mailbox | Sets mailbox properties |
| Set-UMMailbox | Sets Unified Messaging-related properties on a mailbox |
| Set-CASMailbox | Sets Client Access server-related properties on a mailbox |
| Add-MailboxPermission | Adds permissions to a mailbox |
| Remove-MailboxPermission | Removes permissions from a mailbox |
| Set-UMMailboxPIN | Sets the Unified Messaging PIN for a mailbox |
| Disable-UMMailbox | Disable a mailbox's UM features so that it no longer supports Unified Messaging |
| New-MailUser | Creates a new user account and associates an external e-mail address with that user |
| Enable-MailUser | Associates an external e-mail address with an existing user account |
| Remove-MailUser | Removes a mail-enabled user account from the directory |
| Disable-MailUser | Removes an external e-mail address that is associated with a user |
| Get-MailUser | Retrieves a list of mail-enabled users or properties of mail-enabled users |
| Set-MailUser | Sets properties of a mail-enabled user account |
Mail-Enabled Group Management
Mail-enabled groups are managed from the Distribution Group subcontainer of the Recipient Configuration work center. From here you can create new Active Directory groups, mail-enable existing groups, and edit the properties of existing groups. One of the more common tasks an administrator performs on mail-enabled groups is to add or remove members. Figure 8.25 shows the Members property page of a mail-enabled group.
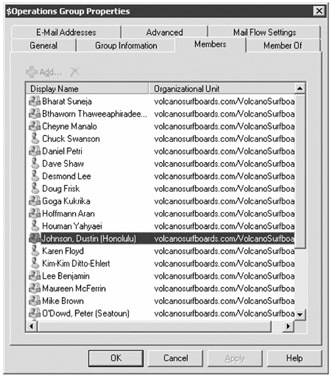
Figure 8.25: Managing the membership of a mail-enabled group
Here is a list of tasks you may need to perform on mail-enabled groups:
-
Managing group membership
-
Configuring messaging restrictions such as maximum message size and who can send mail to a group
-
Specifying if a group can receive anonymous messages
-
Assigning additional SMTP addresses for a group
-
Configuring an expansion server
-
Configuring delivery report behavior
If you want to manage mail-enabled groups from the EMS, here are some of the cmdlets available:
| Cmdlet | Description |
|---|---|
| Set-Group | Manages the properties of a security or distribution group |
| Get-Group | Retrieves a list of security and distribution groups (regardless of mail-enabled status) in the Active Directory |
| Enable-DistributionGroup | Mail-enables an existing group in the Active Directory |
| Disable-DistributionGroup | Disables the mail features of an existing group but does not delete it |
| New-DistributionGroup | Creates a new group in the Active Directory and mail-enables it |
| Remove-DistributionGroup | Deletes a mail-enabled group from the Active Directory |
| Set-DistributionGroup | Sets the properties of a mail-enabled group |
| Get-DistributionGroup | Retrieves a list of mail-enabled groups or the properties of specified mail-enabled groups |
| Add-DistributionGroupMember | Adds a user to a mail-enabled group |
| Get-DistributionGroupMember | Retrieves the membership of a mail-enabled group |
| Remove-DistributionGroupMember | Removes a member from a mail-enabled group |
| New-DynamicDistributionGroup | Creates a new dynamic distribution group |
| Set-DynamicDistributionGroup | Sets the properties of a dynamic distribution group |
| Get-DynamicDistributionGroup | Retrieves a list of dynamic distribution groups or the properties of a specific dynamic distribution group |
| Remove-DynamicDistributionGroup | Deletes a dynamic distribution group |
For more information on mail-enabled group management, see Chapter 10, "Managing Recipients."
Mail-Enabled Contact Management
Mail-enabled contacts appear in the Exchange global address list, but they do not need to be security principals. You can use the EMC to create and manage enabled contacts in the Mail Contacts subcontainer of the Recipient Configuration work center. Figure 8.26 shows the E-Mail Addresses property page of a mail-enabled contact. This page includes the e-mail addresses that will be accepted for this recipient as well as the external e-mail address of the recipient (the address to which the message will be forwarded).
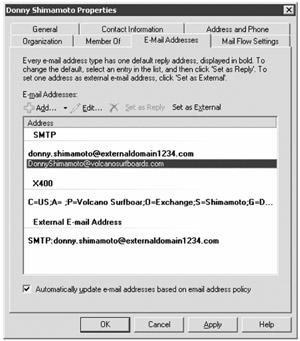
Figure 8.26: Managing a mail-enabled contact's e-mail addresses
Mail-enabled contacts can be managed from the EMS as well as the EMC. Here are the EMS cmdlets you can use for managing mail-enabled contacts:
| Cmdlet | Description |
|---|---|
| Get-Contact | Retrieves the contacts from the Active Directory or retrieves the properties of specified contacts |
| Set-Contact | Sets the properties of a contact in the Active Directory |
| Enable-MailContact | Mail-enables an existing Active Directory contact |
| Disable-MailContact | Disables the mail attributes for an Active Directory contact but does not delete the contact |
| Remove-MailContact | Deletes a mail-enabled contact from the Active Directory |
| Get-MailContact | Retrieves a list of the mail-enabled contacts in the Active Directory or the properties of specified contacts |
| Set-MailContact | Sets the properties of a mail-enabled contact |
You can find more information on creating and managing mail-enabled contacts in Chapter 10, "Managing Recipients."
Public Folder Management
One thing that tends to confuse experienced Exchange 2000/2003 administrators is that there is not an Exchange Server 2007-based graphical user interface for managing public folders. This means that either you have to keep a copy of the Exchange 2003 System Manager program running or you have to manage the public folder properties entirely from the Exchange Management Shell. Here is a list of the EMS cmdlets that can be used to manage public folders:
| Cmdlet | Description |
|---|---|
| Remove- PublicFolderClientPermissions | Removes client permissions from a public folder |
| Add- PublicFolderClientPermissions | Adds client permissions to a public folder |
| Get- PublicFolderClientPermissions | Retrieves a list of client permissions for a public folder |
| Get-PublicFolderAdministrativePermissions | Retrieves the public folder administrative permissions |
| Add-PublicFolderAdministrativePermissions | Adds administrative permissions to a public folder |
| Remove-PublicFolderAdministrativePermissions | Removes administrative permissions from a public folder |
| New-PublicFolder | Creates a new public folder |
| Remove-PublicFolder | Deletes a public folder |
| Get-PublicFolder | Retrieves public folders or the properties of specified public folder properties |
| Set-PublicFolder | Sets public folder properties |
| Enable-MailPublicFolder | Mail-enables a public folder |
| Disable-MailPublicFolder | Disables mail properties of a public folder |
| Get-MailPublicFolder | Retrieves a list of mail-enabled public folders or properties of a mail-enabled public folder |
| Set-MailPublicFolder | Sets mail-enabled public folder properties |
| Update-PublicFolder | Forces an update of public folder content |
| Update-PublicFolderHierarchy | Forces an update of the public folder hierarchy |
| Get-PublicFolderStatistics | Retrieves public folder statistics |
You can find more information about public folder man in Chapter 14, "Public Folder Administration."
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 198