Recipe 5.9. Recovering a Deleted Mailbox Problem Someone deleted one or more mailboxes and you want them back. Solution Using a graphical user interface For Exchange Server 2003: Open the Exchange System Manager (Exchange System Manager.msc). Expand the Tools node and right-click the Mailbox Recovery Center node. Select the Add Mailbox Store command. The Add Mailbox store(s) dialog box will appear (see Figure 5-2). Enter the name of the mailbox database that formerly contained the mailboxes you want to recover; there's no way to browse them. However, you do not need the name of the server or storage group that hosts the mailbox stores in question. You can use the Check Names button to verify that you've entered a valid database name. Click OK when you're done; ESM will update its right pane and list all deleted mailboxes that are still present in the store. If you don't see the mailbox you want to recover, that means that it's gone past the deleted mailbox retention period specified on the database or that it's actually in a different database. If you do see it, right-click it and select the Find Match command. This starts the Exchange Mailbox Matching Wizard; click Next and the wizard will attempt to match the mailbox to the account formerly associated with it. The completion screen of the wizard will appear; click Finish after verifying that the mailbox was connected to the right mailbox. If it's not, you'll need to right-click the mailbox and choose the Resolve Conflicts command, which shows you a list of potential matches and allows you to pick the correct one. Right-click the mailbox and choose the Reconnect command. This starts the Exchange Mailbox Reconnect Wizard; click Next to skip its welcome screen, and then click Next to indicate that you really do want to reconnect the mailbox to its parent account. Click Finish. Verify the reconnection by having the user log in to the mailbox. (Note that there may be a delay caused by replication; the mailbox may not immediately be available.)
Figure 5-2. You must add each mailbox database before you can recover data from it 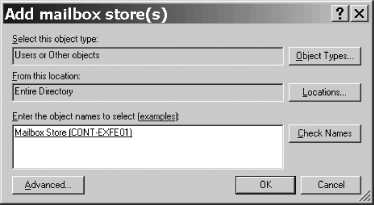
For Exchange 2000: Open the Exchange System Manager (Exchange System Manager.msc). In the left pane, expand the appropriate container beneath Administrative Groups, and then expand the Servers container. Expand the storage group and database that hold the target mailbox. Right-click the database and choose the Run Cleanup Agent command. In the list of mailboxes that appears, right-click the target mailbox and choose the Reconnect command. In the list of Active Directory accounts that appears, select the user account that you want the mailbox connected to, then click OK. Verify the reconnection by having the user log in to the mailbox. (Note that there may be a delay caused by replication; the mailbox may not be immediately available.)
Discussion When you delete a mailbox, sometimes you need to get it back. Strategies for doing this vary according to what version of Exchange you're using: In any version of Exchange, you can use third-party products like Quest's Exchange Recovery Manager or OnTrack's PowerControls to read low-level data from the EDB/STM file and reconstruct the missing data. In Exchange 5.5, you have to restore a backup of the database to a recovery server, then copy the mailbox data to a PST file, then recreate the "real" mailbox and import the PST file's contents. This is a time-consuming (nay, painful) process, because every Exchange 5.5 object has an embedded DN that complicates the recovery process significantly. In Exchange 2000, you can reconnect the mailbox to its own account, or you can restore the database to a recovery server and extract the mail data; it's somewhat easier to do than in Exchange 5.5, but it's still not a lot of fun. In Exchange Server 2003, you can directly restore the deleted mailbox using the Mailbox Recovery Center; you can also use a recovery storage group to mount a backup of the affected database, then move the mailbox data back into the production database.
The Mailbox Recovery Center in Exchange Server 2003 works very much like the deleted item retention behavior for mail items. When you delete an Exchange Server 2003 mailbox, Exchange doesn't actually remove the associated mailbox data from the store immediately. Instead, it replaces the mailbox attribute of the account with a special value known as a tombstone and leaves the mailbox data intact. The tombstone ages over time; when it reaches the end of the retention period (which defaults to 30 days), the store's normal IS maintenance task will remove the associated data. Just as with the deleted item "dumpster," you can recover mailboxes as long as you're within the retention period for the associated store. All the recovery center does is remove the tombstone and reassociate the data in the EDB/STM files with the Active Directory account (to be sure, this is somewhat of an oversimplified explanation). See Also Recipe 5.2 for creating mailboxes, Recipe Recipe 11.10 for using the Mailbox Recovery Center, and Recipe 11.11 for using recovering storage groups |
