4. Distributed Search
4. Distributed Search
Video — a composition of moving pictures and audio clips — possess many more dimensions of searchable attributes than text or web documents. Consequently, a video-centric P2P system must allow users to search for video based on a large and diverse set of syntactic and semantic attributes. While costly manual annotations may exist in special — but rare — cases, a video-catering peer service must be able to extract information automatically from media content to assist search, browsing, and indexing.
MAPS Distributed Search subsystem therefore provides
-
A toolbox to extract syntactic and semantic attributes automatically from media (including MPEG-7 audio and video descriptors), and
-
A powerful search mechanism beyond hash keys, file names and keywords.
Enhanced search specification: For search, the MAPS Media Search subsystem allows each node to have different search capabilities. Besides standard search methods based on keyword matches, SQL queries are used. If a node does not support SQL queries, it either ignores the request or maps it automatically to a keyword-based search.
Automatic extraction of Meta-descriptions: The MAPS Distributed Search subsystem exploits two sources for acquiring Meta information:
-
Meta information encoded in the media files or the media files accompanying description files,
-
Information derived by automatically analyzing the media content.
The most prominent examples of standardized meta information extracted by MAPS from media files are ID3 tags [11] from audio clips, e.g., describing album, title, and lyric information, Exif (Exchangeable Image File) tags from images captured with digital cameras, e.g., describing camera make and model [8], and general information such as frame size, bitrate, duration, and, if available, the date and time of recording [2]. In the future, MPEG-7 media descriptions will be parsed, too.
Furthermore, by extracting semantic information automatically from media, our MAPS Video Content Analysis module supports search beyond standard Meta information. Currently, the MAPS Video Content Analysis module incorporates several types of automatic information extraction, for example, visible text in images and video (see Figure 38.8) [13], faces and their positions, key frames for efficient video summarization [12][26], and colour signatures for similarity search (Figure 38.9). The list of media content analysis tools is not exhaustive as automatic content analysis algorithms are ongoing research topics [23]. Many of the state-of-the-art tools can be plugged into the MAPS Video Content Analysis module.

Figure 38.8: Example of text extraction in videos.
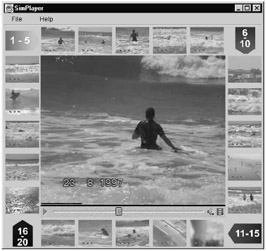
Figure 38.9: Sample results of color-based similarity search. Similar videos are showed in small icons surrounding the displaying video in the center.
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 393
- Key #3: Work Together for Maximum Gain
- Key #4: Base Decisions on Data and Facts
- Making Improvements That Last: An Illustrated Guide to DMAIC and the Lean Six Sigma Toolkit
- The Experience of Making Improvements: What Its Like to Work on Lean Six Sigma Projects
- Six Things Managers Must Do: How to Support Lean Six Sigma