Directives
System.IO.Path
In the past, manipulating paths (such as removing a file name) required writing your own string manipulation routines. Table 12-4 lists the most commonly used members of the Path class. The beauty of the Path class is its ability to perform its duties quickly and easily; calling a single method is much easier than writing code to process a string. In addition, its parsing methods, such as GetExtension, take into consideration the platform-specific separator character so that you don't have to worry about such details.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| DirectorySeparatorChar | Provides a platform-specific character used to separate directory levels in a path string that reflects a hierarchical file system organization |
| PathSeparator | A platform-specific separator character used to separate path strings in environment variables |
| ChangeExtension | Changes the extension of a path string |
| GetDirectoryName | Returns the directory information for the specified path string |
| GetExtension | Returns the extension of the specified path string |
| GetFileName | Returns the file name and extension of the specified path string |
| GetFileNameWithoutExtension | Returns the file name of the specified path string without the extension |
| GetFullPath | Returns the absolute path for the specified path string |
| GetPathRoot | Gets the root directory information of the specified path |
| GetTempFileName | Returns a unique temporary file name and creates a zero-byte file by that name on the disk |
| HasExtension | Determines whether a path includes a file name extension |
| IsPathRooted | Gets a value indicating whether the specified path string contains absolute or relative path information |
Using System.IO.Path is simple. For example, to display the extension of a filename, you could use a statement such as this:
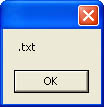
MessageBox.Show(System.IO.Path.GetExtension("C:\temp\test.txt")) This statement displays the message box shown in Figure 12-2. Note that the period is returned with the extension you need to take this into consideration when writing your code.
Figure 12-2. The string returned by System.IO.Path.GetExtension includes the period.
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 84