Hack 89 NoCatAuth Captive Portal
|
Provide cryptographically sound access control using only a web browser. NoCatAuth is an open source implementation of a captive portal. The idea behind a captive portal is fairly straightforward. When a user behind a captive portal attempts to browse to any web page, they are redirected to a page with a login prompt as well as information about the wireless network they are connected to. If the gateway consults with a central authority to determine the identity of the connected wireless user, once satisfied, it then relaxes its firewall rules accordingly. Until the user logs in, no other network traffic is permitted to pass through the gateway. Rather than rely on the built-in security features of 802.11b, the network is configured with no WEP and as an open network. The AP is also in bridged mode and connected via a crossover cable to an Ethernet card on a Linux router. It is then up to the router to issue DHCP leases, throttle bandwidth, and permit access to other networks. Written in Perl and C, NoCatAuth takes care of the dirty work of implementing the portal itself. It presents the user with a login prompt, consults a MySQL database (or other authentication source) to look up user credentials, and securely notifies the wireless gateway of the user's status. On the gateway side, the software manages local connections, sets bandwidth throttling and firewall rules, and times out old logins after a user-specified time limit. The software is freely available and released under the GPL. We are designing the system so that trust is ultimately preserved: the gateways and end users need trust only the Auth system, which is secured with a registered SSL certificate. Passwords are never given to the wireless gateway (thus protecting the users from "bad guy" node owners), and gateway rules are only modified by a cryptographically signed message from the Auth system (protecting the gateway from users or upstream sites trying to spoof the Auth system). We provide for three possible classes of wireless user: Public Class, Co-op Class, and Owner Class:
The typical connection process is shown in Figure 7-3. Figure 7-3. The user's web traffic is "captured" by the gateway.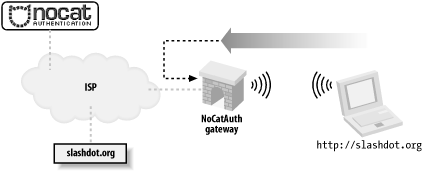 A roaming user associates with the AP and is immediately issued a DHCP lease. All access beyond contacting the Authentication Service is denied by default. When the user tries to browse the Web, she is immediately redirected to the gateway service, which then redirects her to the Auth system's SSL login page (after appending a random token and some other information to the URL line). This process is completely transparent to the user, as shown in Figure 7-4. Figure 7-4. The user is redirected to an SSL-encrypted page on the Authentication Server.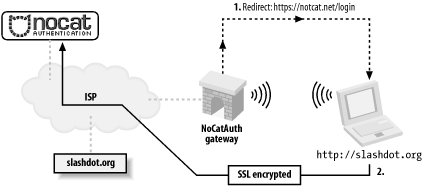 The user is then presented with three choices: log in with their pre-arranged login information, click on a link to find out more about membership, or click the Skip Login button. Once the user has either logged in correctly or skipped the process, the Auth system then creates an outcome message, signs it with PGP, and sends it back to the wireless gateway, as shown in Figure 7-5. The gateway has a copy of the Authentication Service's public PGP key, and can verify the authenticity of the message. Since part of the data included in the response is the random token that the gateway originally issued to the client, it makes it very difficult to fake out the gateway with a "replay attack." The digital signature prevents the possibility of other machines posing as the Authentication Service and sending bogus messages to the wireless gateway. Figure 7-5. The user presents their credentials to the Authentication Service, which then notifies the gateway.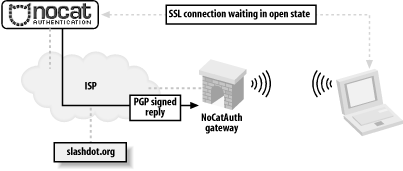 Now, if all has gone well for the user, the wireless gateway modifies its firewall rules to grant further access, and redirects the user back to the site to which they were originally trying to browse see Figure 7-6. Figure 7-6. The user is redirected to their original site, and goes about their merry way.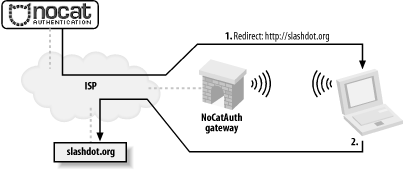 In order to keep the connection open, a small window is opened on the client side (via JavaScript) that refreshes the login page every few minutes. Once the user moves out of range or quits his browser, the connection is reset and requires another manual login. The requirements on the gateway side are minimal (the system was designed to run under Linux 2.4, on a 486 with 16 Mb RAM). The Authentication Service is designed to be administered by a group that maintains its user database in whatever way they see fit. It can easily be configured to provide "Members Only" access, so rather than use a graded, class-based mechanism, users are either granted full access or none at all. The NoCatAuth system is under active development and has a variety of new features. "Passive" mode now allows operation without the connect-back phase (to allow installation behind a NAT firewall). There are also many additional backend authentication methods, including PAM, RADIUS, TACACS+, and even IMAP. The gateways can be configured to throttle inbound and outbound traffic to a specified rate, as well as filter ports, protocols, services, and anything else that iptables can track. If you use the Pebble distribution [Hack #53], it comes with the NoCat gateway preconfigured. You can always get the latest version of NoCatAuth from http://nocat.net/. |
EAN: N/A
Pages: 158
- The Effects of an Enterprise Resource Planning System (ERP) Implementation on Job Characteristics – A Study using the Hackman and Oldham Job Characteristics Model
- Context Management of ERP Processes in Virtual Communities
- Distributed Data Warehouse for Geo-spatial Services
- Healthcare Information: From Administrative to Practice Databases
- A Hybrid Clustering Technique to Improve Patient Data Quality