Configuration Issues
| Many potential issues can arise from improper configuration of your Internet devices or TA. Most of these improper settings result in outright failure, but some may be more subtle. Most of the subtle items, such as QoS and PPPoE Keep Alive, were discussed in the previous section. Let's take a look now at the show-stoppers. Tip If you need to know more about home networking than I cover here, Peachpit Press offers books that cover this topic in much more detail. Gateway configurationPerhaps you bought an Internet gateway at the same time you purchased your VoIP kit. Maybe your gateway was included in the VoIP kit (TA/gateway combo). Either way, you should be aware of several settings that might make your gateway installation more challenging. Your Internet access provider can assist you if you have any questions about the actual values to use for certain settings. Internet Address ConfigurationMost Internet access providers automatically assign the Internet (or external) address for your gateway. If this is not the case, and you must set an address manually, you will be given a configuration guide that specifies the address to use for the gateway. Internal addresses those addresses assigned to devices inside the gateway are left to your discretion. Most gateways use a feature called Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to assign IP addresses automatically to computers and devices such as TAs on your internal network (Figure 6.5). All you have to do is ensure that each device is set to accept these addresses. Consult the user manual for your TA to determine its default setting and for directions on changing the setting if necessary. Figure 6.5. Configuring a Linksys gateway to provide IP addresses to network devices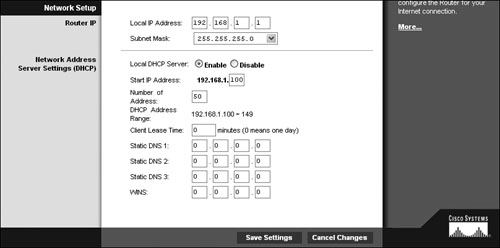 Likewise, your PC usually obtains its own address automatically from DHCP, but use your system's help screens for assistance on setting the address manually, if desired. PPPOE SettingsIn addition to Keep Alive settings, discussed in "PPPoE issues" earlier in this chapter, PPPoE requires you to provide a user name and password before communications can be established (Figure 6.6). Enter the user name and password specified by your Internet provider in this configuration screen. After saving your settings, wait a few minutes before testing your connection, as it may take some time for your gateway to locate and connect with the appropriate systems. Figure 6.6. Setting the PPPoE user name and password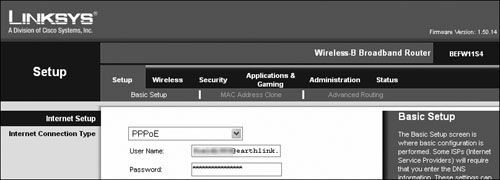 MAC SpoofingSome Internet access providers register the media access control (MAC) ID of your computer when you subscribe to their services. If your access provider is expecting the registered MAC and does not see it, you will not be able to connect. Gateway vendors have cleverly bypassed this issue by designing their products to pretend that they are your PC (Figure 6.7). This process, called MAC cloning or MAC spoofing, uses the computer's registered MAC ID that you configure into the gateway when communicating with the Internet provider's systems. By using your PCs MAC ID, the gateway effectively fools the provider's network into thinking that your computer is making the connection. The reality is, you now have an entire network sharing the same address! Figure 6.7. Configuring MAC spoofing on a Linksys gateway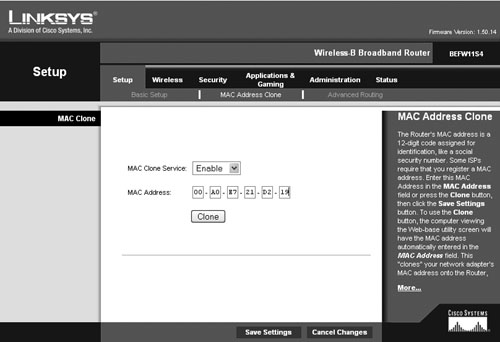
Port-Range ForwardingWhen you place your TA behind a gateway, sometimes the firewall functionality of the gateway restricts your ability to connect to your VoIP provider. This is relatively rare, as most gateways are configured to allow all outbound communications, and your TA will communicate outbound first to initiate the connection with your VoIP provider. If you do need to open your gateway to the TA, you will need to know which Internet ports are required for your service. Most services use certain well-known port numbers for their communications. Those for your VoIP systems can be obtained from your VoIP provider's Web site or support staff. You probably will find port listings in the user guide for your TA as well. Table 6.1 lists an example of ports used by a Linksys TA.
TA configurationThe TA provided by your VoIP provider or included in your VoIP kit usually works right out of the box with no modification. Some exceptions are when your home network uses static (not dynamically assigned) IP addresses or more than one gateway device (not likely). TAs usually have two methods of configuration: They can be configured via a Web browser by accessing a small Web server built into the device, or they can be programmed over your touchtone phone. Often, your VoIP provider will lock out the Web interface to be able to support your TA remotely from its central support department. If this is the case, you will be restricted to using the voice-response menu. Using the Voice-Response MenuWhen you use your TA's voice-response menu, follow the instructions carefully; they should be included in the user guide that comes with the device. You usually enter a code such as **** to access the voice-response menu. Then you use your keypad to access and change different settings. Note Due to the nature of gateways, you will always have access to the networking portions of your gateway setup. Voice portions will be locked by your VoIP provider. Setting IP Address and Gateway Settings ManuallyUsing the voice-response menu, you can configure your TA to use a fixed IP address and fixed gateway address. Check the instructions that came with your TA for exact details on how to do this. Use an IP address that will be valid for your network and your gateway's address for the gateway address on your TA. |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 94