8.5 Recipient Update Services
|
| < Day Day Up > |
|
Defining an Address List does not create a one-time, static list. Instead, defining an Address List creates a set of filter rules that are periodically applied to the Active Directory to refresh the items in the list. If new users that meet the Address List selection criteria are added to the Active Directory, those users will be automatically added to the Address List the next time the list is updated. These automatic updates keep you from having to manually update and synchronize the individual Address Lists.
The RUS is responsible for periodically reapplying the filter rules to the Active Directory to produce updated default and custom Address Lists that contain any user changes you may have made. The RUS searches the Active Directory for objects that match the selection criteria. When a matching object is found, the RUS updates the following attributes for the Active Directory object:
-
mail. This contains the recipient's Plain Text primary SMTP address.
-
proxyAddresses. This contains all the proxy addresses available for an object, including the X.400 address, primary SMTP address, and any proxy SMTP or foreign addresses.
-
textEncodedORAddress. This is the X.400 OR address.
-
showInAddressBook. This controls the address books in which the recipient appears.
-
msExchHomeServerName. This is the complete distinguished name of the recipient's mailbox server.
-
homeMTA. This is the complete distinguished name for the Message Transfer Agent on the recipient's mailbox server.
-
homeMDB. This is the complete distinguished name for the recipient's mailbox.
These periodic updates ensure that users always have access to current and accurate Address Lists.
The RUS is run as part of the Exchange System Attendant and must be created and managed by an administrator. You must have a RUS for every domain that has e-mail users. You must identify an Exchange server for each of these domains that will be responsible for generating and updating the Address Lists for the domain.
To create and manage RUSs, you must be an Exchange Full Administratorat the Organization level. When you create a RUS, you identify the domain that is being updated, the Exchange server where the RUS will be run, and the Windows domain controller that the Exchange server will connect to generate and update the Address Lists. If you have an Exchange server that is also a domain controller, you can reduce the network traffic by running the RUS on this server. After you have created a RUS, you can configure how often the RUS updates the Address Lists. This is known as the update interval. By controlling the servers and schedule involved in the update process, you can control how and how often your Address Lists are updated.
8.5.1 Creating a Recipient Update Service
You must have a RUS for each domain in your organization in which you will have mail-enabled or mailbox-enabled users, groups, or contacts.
When you install an Exchange server in a domain, the setup procedure automatically creates RUSs that update the configuration context and Active Directory objects for the domain. When additional Exchange servers are later installed in the domain, the setup procedure detects the presence of the existing RUS and does not create an additional service for the domain. You can use the procedure outlined in Section 8.5.2 to change the Exchange server responsible for running the RUS for the domain.
Domains containing an Exchange server automatically have a RUS. However, what do you do for domains that contain e-mail users but do not contain an Exchange server? An Exchange server that is a member of a different domain must be used to update the Address Lists for these domains (i.e., you run the RUSs on an Exchange server in a different domain). In the domain containing the e-mail users, you must run the Exchange DomainPrep procedure. This will not install Exchange on the server, but it will identify the Address List server and will set permissions within the domain.
You can use the following procedure to create a RUS.
-
If you are creating the RUS for a Windows domain that has e-mail users but does not contain an Exchange server, you must first run the Domain-Prep procedure. You should perform the following steps on a domain controller in the domain that does not contain Exchange:
-
Insert the Exchange 2003 CD-ROM into your CD-ROM drive.
-
Select Run from the Windows Start menu. As the command to run, enter x: \setup \i386 \setup.exe/DomainPrep, where x is your CD-ROM drive. Select OK to start the setup program.
-
-
Start ESM from the Windows Start menu by selecting All Programs →Microsoft Exchange →System Manager.
-
Expand the Recipients section.
-
Right-click on RUSs and select New →Recipient Update Service.
-
You must have a RUS for every domain that has e-mail users. Use the Browse button to select the domain that will be updated by the RUS you are creating (Figure 8.38).
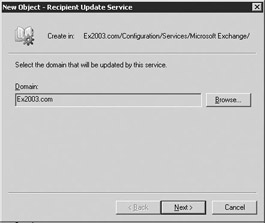
Figure 8.38: New Recipient Update Service dialog box -
Select Next.
-
Use the Browse button to select the Exchange server responsible for generating and updating Address Lists for this domain (Figure 8.39). In the Select Exchange Server dialog box, select the appropriate Exchange server and then select OK to return to the New Object - Recipient Update Service dialog box. This Exchange server is responsible for periodically reapplying the filter rules to the Active Directory to produce updated default and custom Address Lists. The Exchange server you select will automatically be granted rights to modify Exchange attributes for users in this domain. Communication between the Exchange server and the Windows domain controller can place a load on the network. If you have an Exchange server that is also a domain controller, you can reduce the network traffic by running the RUS on this server.
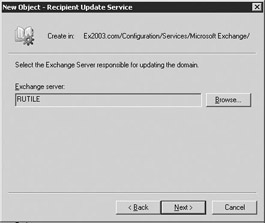
Figure 8.39: New Recipient Update Service - Exchange Server dialog box -
Select Next.
-
Review the RUS to ensure that it is correct, then select Finish to create the RUS for this domain (Figure 8.40). The Windows domain controller is the one that the Exchange server will connect to generate and update the Address Lists.
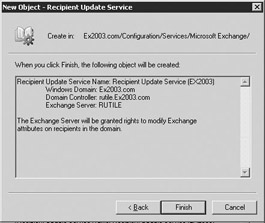
Figure 8.40: New Recipient Update Service - Summary dialog box
By default, the RUS is created with an update interval set to Always run. You can use the procedure outlined in Section 8.5.2 to create a different update interval.
8.5.2 Modifying a Recipient Update Service
You can use the following procedure to modify the Exchange server, to modify the Windows domain controller, or to update intervals associated with a RUS.
-
Start ESM from the Windows Start menu by selecting All Programs →Microsoft Exchange →System Manager.
-
Expand the Recipients and the RUS sections.
-
In the details pane, right-click on the RUS you want to modify, and select Properties (Figure 8.41).
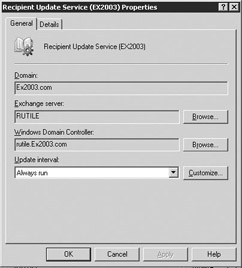
Figure 8.41: Recipient Update Service Properties - General tab -
To change the Exchange server responsible for generating and updating Address Lists for this domain, select the Browse button next to the Exchange Server field. In the Select Exchange Server dialog box, select the appropriate Exchange server and then select OK to return to the RUS Properties dialog box.
-
To change the domain controller that is to be used for updating recipients, select the Browse button next to the Windows Domain Controller field. In the Select Domain Controller dialog box, select the appropriate domain controller, then select OK to return to the RUS Properties dialog box.
-
By default, the RUS is created with an update interval set to Always run. Use the Update interval drop-down list to select how often the RUS will reapply the filter rules to the Active Directory to create updated Address Lists for this domain. You can accept one of the intervals on the dropdown list or select Customize to display the Schedule dialog box where you can specify the desired update interval. The predefined choices in the drop-down list are Always run, Run every hour, Run every 2 hours, Run every 4 hours, and Never run. If you select Never run, the Address Lists will not be updated. Never run is seldom used, but it can be useful for temporarily disabling Address List updates when you are transferring the RUS to a different Exchange server.
If new users that meet the Address List selection criteria are added to the Active Directory, these users will be automatically added to the list the next time that the RUS is run. Similarly, if you create a new Address List, it will not be populated until the next time the RUS is run.
-
Select Apply and then select OK to update the RUS.
8.5.3 Updating Address Lists immediately
The RUS is automatically run according to the schedule you select (see Section 8.5.2). However, there may be circumstances, such as after you have created a new Address List or added many new users to the system, when you do not want to wait until the next scheduled update. You can use the following procedure to manually update Address Lists:
-
Start ESM from the Windows Start menu by selecting All Programs →Microsoft Exchange →System Manager.
-
Expand the Recipients and the RUSs sections.
-
In the details pane, right-click on the RUS for the domain you want to update and select Update Now. This will update all default and custom Address Lists for the domain.
|
| < Day Day Up > |
|
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 128