Virtual Server Administration
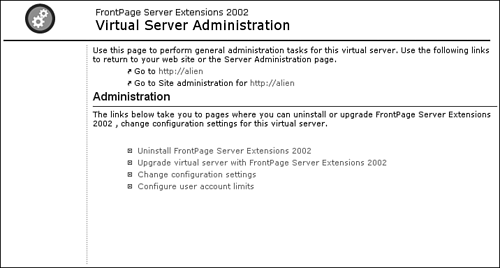
| Virtual server administration is for configuration of all of the Web sites running on a virtual server. A virtual server is a collection of Web sites on a Web server all sharing a common root Web site. On Windows 2000 and XP Professional, only one virtual server is allowed, and it is called the Default Web Site. On Windows 2000 Server and Windows Server 2003, you can create many virtual servers, each with its own configuration settings. At the virtual server level, Server Extensions can be installed and configured, and many of the same settings configurable at the site administration level are available as well. The Virtual Server Administration page (shown in Figure 17.22) is where you configure settings that apply to all Web sites on the virtual server. Figure 17.22. The Virtual Server Administration page is where you configure Server Extensions settings for the virtual server.
The first link on the Virtual Server Administration is Uninstall FrontPage Server Extensions 2002. Clicking this link will take you to the page shown in Figure 17.23. You are given the option to conduct a full uninstall. If you perform a full uninstall, all metadata for the virtual server will be removed as well. Metadata refers to the _vti folders that contain configuration information for the FrontPage Web sites on the server. If these are removed, any FrontPage components in the Web site might not function if the Server Extensions are reinstalled at a later time. Figure 17.23. The Uninstall FrontPage Server Extensions 2002 page allows you to uninstall the Server Extensions from the virtual server.
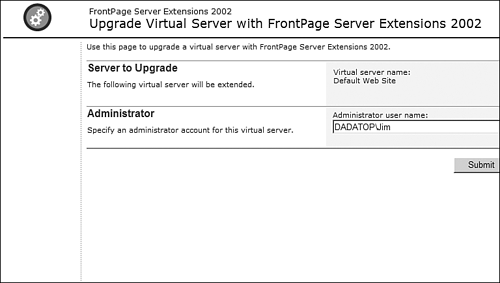
The next link is Upgrade Virtual Server with FrontPage Server Extensions 2002 (see Figure 17.24). Clicking this link will allow you to upgrade the virtual server to the FrontPage 2002 Server Extensions in situations where an earlier version of the Server Extensions is currently installed. Enter a local user who will serve as the Administrator of the virtual server and click Submit to upgrade the virtual server. Figure 17.24. Upgrade a virtual server to FrontPage Server Extensions 2002.
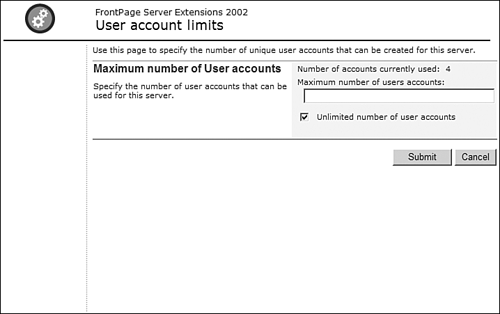
I'll discuss the Change Configuration Settings link in the next section. Let's move on to the Configure User Account Limits link. This link takes you to the User Account Limits page (see Figure 17.25) and simply allows you to restrict the number of user accounts that can be used on a virtual server. By default, the number of user accounts that are allowed is unlimited. By entering a numeric value in the text box and clicking Submit, you can restrict the number of accounts that are allowed. Figure 17.25. The User Account Limits page is where you can restrict the maximum number of user accounts for a virtual server.
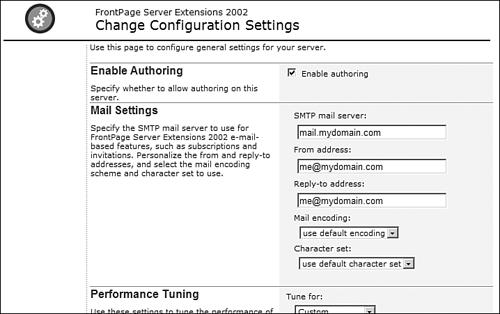
TIP Why would you want to limit the number of user accounts for a virtual server? If there are many virtual servers configured on a Web server, the server might suffer performance problems if too many users are accessing the server. By limiting the number of users that can be created, a server administrator can more carefully control access to the server and maintain proper performance. Configuration SettingsThe Change Configuration Settings link provides an interface for configuring all the general settings for the virtual server via the Configuration Settings page shown in Figure 17.26. The Configuration Settings page is divided into several sections. Figure 17.26. The Configuration Settings page is the place to configure virtual server settings.
Controlling AuthoringThe Enable Authoring section allows you to disable or enable FrontPage authoring. Clear the Enable Authoring check box to turn off authoring for the server. When authoring is disabled, FrontPage users will receive an error message if they attempt to open a Web site on the server, informing them that authoring has been disabled. There is no way to disable authoring for specific Web sites on the server. If authoring is disabled, all Web sites will be inaccessible for authoring from FrontPage. Mail SettingsSeveral features of the Server Extensions allow you to send mail. The FrontPage Save Results component sends email from a Web page. The Server Extensions can also send email to people you have invited to visit your Web site, as you saw previously in this chapter. In order for email to be sent, you must configure the Mail Settings options so that the Server Extensions will have the information necessary to send mail. The SMTP Mail Server box configures the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol mail server that is used to send email. This is very often mail.domain.com, where domain is your hosting domain. The Server Extensions will use the SMTP mail server to relay your email. Therefore, SMTP relay must be enabled. The From Address setting specifies the email address that appears in the From line on emails sent by the Server Extensions. Only one email address can be entered here. You cannot enter multiple addresses. The Reply-to Address specifies the email address that an email will be addressed to if a recipient clicks the Reply button after receiving an email sent by the Server Extensions. The Mail Encoding dropdown allows you to configure the mail encoding of the emails sent by the Server Extensions. Unless you are certain that the encoding needs to be changed, this setting should not be changed. The Character Set dropdown configures the character set that is used to send email. As with the mail encoding settings, this setting should not be changed unless you are certain that it should be changed and are well versed in the ramifications of any change. If you are unsure about changing this setting, check with your server administrator. Performance TuningThe Performance Tuning section allows you to configure a Web server for maximum performance. There are preset values for a Web server hosting fewer than 100 pages, one hosting between 100 and 1000 pages, and one hosting 1000 pages. There is also a custom setting to allow you to configure your own performance settings. These settings are configurable at the Web site level, but only through the command line. When using the browser interface, you can only configure the settings for the entire virtual server. NOTE For more information on command-line administration of the Server Extensions, see the SharePoint Team Services Administrator's Guide available at http://fpserk.frontpagelink.com. Document CachingThe In-memory Document Cache setting configures the number of documents that the Server Extensions hold in cache. When the Server Extensions are being used for authoring and when they are writing files for browse-time components, they are able to store metadata for your files in the Web server's memory in order to improve performance. By default, the Server Extensions will hold metadata for up to 4,096 files in memory. When document number 4,097 is accessed, the Server Extensions completely clear and the process starts over with one file. The Include File Cache setting specifies the maximum number of include files (those that are included using the FrontPage Include File component) that are cached on the Web server while pages are being saved and while the Web site is being recalculated using the Recalculate Hyperlinks command. For maximum efficiency, if you have more than 16 files included with the Include File Component, you will want to change this value. It should be changed to the total number of included pages that you have in your Web site. The Image File Cache setting specifies the number of cached images. The Server Extensions do not cache image files themselves. Instead, they cache the height and width attributes for images in your Web site when pages are saved and links are recalculated. This setting should only be changed from the default value of 16 if pages on your Web site frequently contain more than 16 images. Configuring Full-text SearchThe Full-text Search Index Size setting specifies the number of megabytes the Server Extensions use for the FrontPage Wide Area Information Service (FreeWAIS) search engine. The FreeWAIS search engine is commonly used by server administrators who do not enable the Microsoft Index Services option for Server Extensions.
The Max Cached Document Size setting allows you to configure the maximum size of documents that the Server Extensions will cache in memory. The default size is 256KB, and considering that anything over that would be extremely large for a Web document, that should suffice for most users. Configuring Scripting LanguagesOne of the features of FrontPage forms is that they allow you to configure the form-field validation that runs on the client (the Web browser) to enforce restrictions on the data that can be entered in a form field. The Server Extensions generate client-side VBScript or JavaScript (based on certain settings) when the page is saved. There are a couple of places where you can set the scripting language that the Server Extensions use. One is in the FrontPage client by selecting Tools, Site Settings and clicking the Advanced tab. The other is here on the General Settings page using the Scripting Language dropdown. The setting on the General Settings page will override whatever is set in the FrontPage client. Therefore, if you set the Script Language dropdown to No Scripting, client-side scripting will not be generated by FrontPage even if the Web developer chooses a scripting language in the FrontPage client.
Configuring Security SettingsThe Security Settings section allows for configuration of three security settings for the Server Extensions.
All three of these settings are discussed in detail in the "Setting Installation Defaults" section of this chapter. |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 443

 For more information on the FrontPage FreeWAIS search engine,
For more information on the FrontPage FreeWAIS search engine,