CCNA-Practice Test 9
Directions: For each of the following questions, select the choice that best answers the question or completes the statement.
| 1. | Which of the following will allow "Unauthorized access prohibited!" to be displayed before the login prompt when someone tries to initiate a Telnet session to a router?
| |
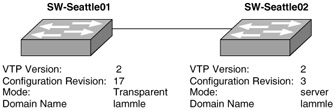
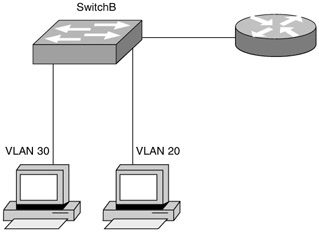
| 2. | Look at the following diagram. Switch SW-Seattle01 has recently been added to the network but has yet to get appropriate VLAN information from the VTP domain. What is causing this problem? (Choose two.)
| |
| 3. | Which of the following information will you not find in a routing table?
| |
| 4. | Which of the following is a correct subinterface used in Frame Relay networks?
| |
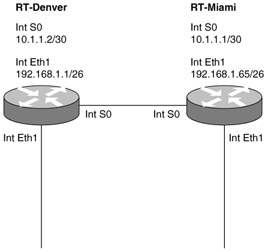
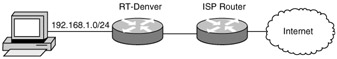
| 5. | Look at the following diagram. The following line appears in the routing table of the RT-Denver router:
?? 192.168.1.0/26 is directly connected, Ethernet 0 What would you expect the first character to be?
| |
| 6. | What are the valid hosts for the subnet on which 192.168.10.40 255.255.255.224 resides?
| |
| 7. | Which of the following are benefits of segmenting your network with routers? (Choose three.)
| |
| 8. | What is the purpose of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)?
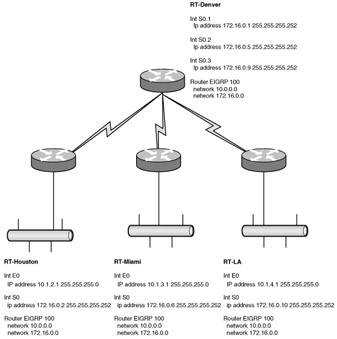
| |
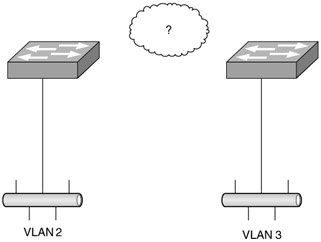
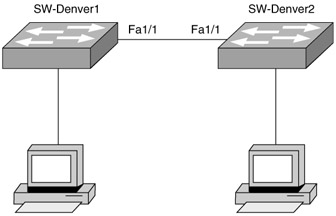
| 9. | Look at the following diagram. You have been asked to connect these two switches. What type of device do you need to install to provide full communication?
| |
| 10. | Which of the following messages displays the code image running in router memory?
| |
| 11. | Which of the following cables do you use to connect a switchport on a switch to a router's Ethernet interface?
| |
| 12. | You have a Class C network address and need eight subnets using the 255.255.255.224 mask. What command must be in effect to allow the use of eight subnets with this mask?
| |
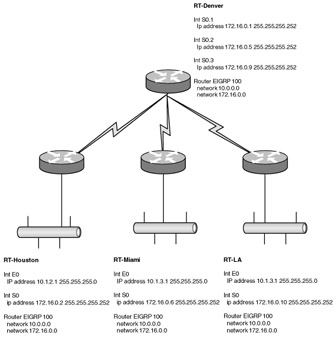
| 13. | Look at the following diagram. You have been asked to troubleshoot a problem. Users in LA and Miami are having issues sharing files with each other. What is the likely cause of the problem?
| |
| 14. | What are the valid hosts for the subnet on which 192.168.10.5 255.255.255.252 resides?
| |
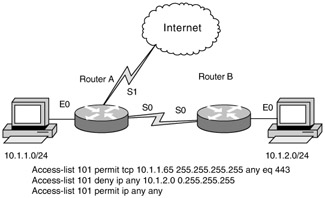
| 15. | Look at the following diagram. You have an administrator at 10.1.1.65 who manages several servers on the 10.1.2.0/24 subnet using SSL. No other users should be accessing that subnet. You have created the access list shown. Which interface and direction should you apply it on to achieve the desired result?
| |
| 16. | Which of the following series of commands restricts Telnet access to the router?
| |
| 17. | If you want to deny ping traffic entering your network, which protocol should you filter?
| |
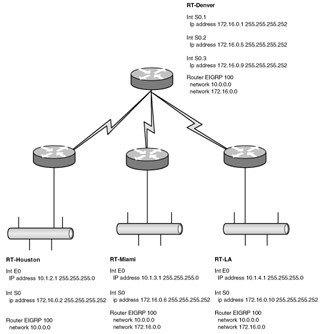
| 18. | Look at the following diagram. You have been asked to troubleshoot a problem. This network has failed to converge. What is the likely cause of the problem?
| |
| 19. | What does a router do with a received packet that is destined for an unknown network?
| |
| 20. | You have the following routing table. Which of the following networks will not be placed in the neighbor's routing table?
R 192.168.30.0/24 [120/15] via 192.168.40.1, 00:00:12, Serial0 C 192.168.40.0/24 is directly connected, Serial0 172.16.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets C 172.16.30.0 is directly connected, Loopback0 R 192.168.20.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.40.1, 00:00:12, Serial0 R 10.0.0.0/8 [120/5] via 192.168.40.1, 00:00:07, Serial0 C 192.168.50.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0
| |
| 21. | Look at the following diagram. You have been asked to install the router shown in the diagram. What kind of cable and connection do you need to configure between the router and the switch?
| |
| 22. | What happens if you do not set the VTY password?
| |
| 23. | What does the following command mean?
access-list 110 permit ip any 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255
| |
| 24. | What is the default encapsulation used on Cisco serial links?
| |
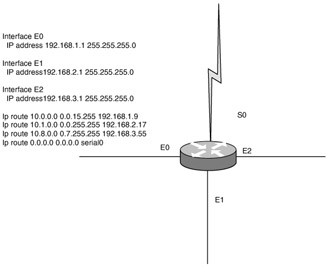
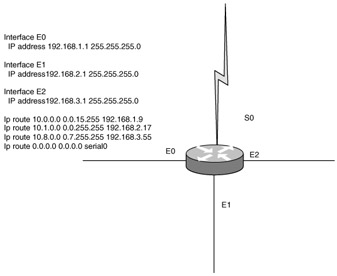
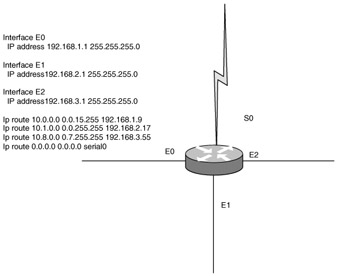
| 25. | Look at the following diagram. You have a router with routing configured as illustrated. Suppose that a packet destined for 10.1.174.254 enters the router. Which interface will the router send it out?
| |
| 26. | A port in the STP ___________________ state populates the MAC address table but doesn't forward data frames.
| |
| 27. | What configuration commands configure a router for fallback? (Choose three.)
| |
| 28. | The command copy tftp flash initiates what event?
| |
| 29. | A route is being advertised by both RIP and EIGRP. Why is only the EIGRP-learned route injected into the routing table?
| |
| 30. | Which configuration task must you complete if a remote Frame Relay router does not support Inverse ARP?
| |
| 31. | Look at the following diagram. You have been asked to troubleshoot a problem. This network has failed to converge. What is the likely cause of the problem?
| |
| 32. | You're given the following criterion when connecting access from a remote site to your LAN: "Restrict access on interface e0 for Telnet and FTP." Which of the following lines should come last when you configure your access list?
| |
| 33. | Which of the following are true regarding Frame Relay? (Choose two.)
| |
| 34. | What is the suggested mask used with VLSM that provides the most efficient use of addressing on a point-to-point serial link?
| |
| 35. | Which of the following is a valid IP extended access list?
| |
| 36. | What does a bridge use to filter traffic on a network?
| |
| 37. | You have a Frame Relay network. What type of encapsulation is necessary if the routers are from different vendors?
| |
| 38. | Look at the following diagram. In the network pictured, how many host addresses will be in the MAC forwarding table on each switch? Assume that the network and hosts have been running for some time.
| |
| 39. | Which of the following describes a full-duplex transmission?
| |
| 40. | Which of the following describes the steps of data encapsulation?
| |
| 41. | Look at the following diagram. You have a router with routing configured as illustrated. Suppose that a packet destined for 10.11.128.255 enters the router. Which interface will the router send it out?
| |
| 42. | What is the IEEE version of spanning tree?
| |
| 43. | You want to back up the IOS on your router to a network server. Which three things should be done prior to performing this task?
| |
| 44. | You connect a new host into the Sales VLAN; however, this new host cannot see the Sales server. What could be the problem?
| |
| 45. | Which statements are true regarding classless routing protocols? (Choose two.)
| |
| 46. | What command do you type at a CLI prompt to see the configuration register setting?
| |
| 47. | What command shows the Frame Relay protocol statistics?
| |
| 48. | Which of the following use ICMP to test IP connectivity? (Choose two.)
| |
| 49. | What is the default encapsulation for Cisco routers running Frame Relay?
| |
| 50. | You type show interface serial 0 and see this:
Serial 0 is up, line protocol is down In which layer of the OSI could the problem be?
| |
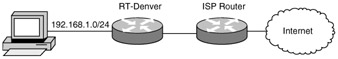
| 51. | Look at the following diagram. You have been asked to create an access list that will allow access to a web server at the 192.168.1.27 subnet but will not allow any other communication with the Internet. Which of the following should you choose?
| |
| 52. | What does a switch do with a multicast frame received on an interface?
| |
| 53. | Look at the following diagram. You have been asked to create an access list on the RT-Denver router that will block telnet access from the Internet to a server at 192.168.1.198 and allow any other communications with the Internet.
access-list 101 deny tcp any host 192.168.1.198 eq telnet access-list 101 permit ip any any Which interface, and in which direction, should you apply this access list?
| |
| 54. | You need a routing protocol that supports both discontiguous networks and VLSM. It must also provide the lowest impact on router CPU and WAN utilization. Which of the following will provide this?
| |
| 55. | Look at the following diagram. You have a router with routing configured as illustrated. Suppose that a packet destined for 10.16.112.17 enters the router. Which interface will the router send it out?
| |
Answers
| 1. | C Explanation: C. The "Message Of The Day" (motd) is an old Unix command that allows you to display a message when anyone connects to a router or switch device. |
| 2. | B, C Explanation: B, C. VTP is not updating because the switch is in transparent mode, not server or client mode. If the switch is placed in an incorrect mode, the wrong mode will prevent it from receiving updates. |
| 3. | C Explanation: C. The purpose of a default gateway is to provide an access point that is external to the Cisco router and capable of routing packets destined for remote networks. The command ip default-gateway is used when the router is not routing IP; the default gateway does not appear in the routing table. |
| 4. | B Explanation: B. Frame Relay runs on serial interfaces and creates a subinterface using the interface type number.subinterface command. |
| 5. | D Explanation: D. The identifier for directly connected routes in a routing table is C. |
| 6. | C Explanation: C. The 224 mask is 3 bits for subnets and 5 bits for host addressing. That means you have 8 subnets, each with 30 hosts. The valid subnets increment by 256 - 224 32: 0, 32, 64, 96, 128, 160, 192, 224. The valid hosts are the numbers between the subnets, except for the all-zeros and all-ones hosts. The valid hosts in the 32 subnet are 33 through 62, and 63 is the broadcast address. |
| 7. | B, C, D Explanation: B, C, D. Routers filter by logical address, create internetworks, and stop broadcast storms. |
| 8. | B Explanation: B. Bridges use the spanning-tree algorithm, enabling a learning bridge to dynamically work around loops in a network topology by creating a spanning tree. |
| 9. | B Explanation: B. Only a router can route between separate VLANs. Although switches can carry multiple VLANs, they cannot route between them. |
| 10. | C Explanation: C. Although a lot of information is displayed during startup, only option C has the code image name. |
| 11. | A Explanation: A. A standard Ethernet cable is all you need to connect a router to a switch. If you had two switchports, you would need a crossover cable. |
| 12. | B Explanation: B. To allow the use of eight subnets with a /27 Class C mask, you must have implemented the ip subnet-zero command, which is on by default on all Cisco routers using the 12.x IOS. |
| 13. | C Explanation: C. The LA and Miami LANs have the same address assigned. |
| 14. | B Explanation: B. A 252 mask gives you 6 bits for subnets and 2 bits for hosts. This gives you 64 subnets, each with 2 hosts. The host specified in the question is in the second subnet, 0 being the first (the increment is 256 - 252 = 4). The valid hosts are 5 and 6. 7 is the broadcast for the 4 subnet. |
| 15. | A Explanation: A. This ACL can only be placed on RouterA, E0, in to achieve only the desired result. Placing the ACL on any other interface would either do nothing or impact more than is stated in the policy. |
| 16. | C Explanation: C. Telnet access to the router is restricted by using either a standard or extended IP access list on the VTY lines on the router. The command access-class is used to apply the access list to the VTY lines. |
| 17. | A Explanation: A. The ping (Packet Internet Groper) utility uses Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) echo messages to test network connectivity. |
| 18. | D Explanation: D. The Houston router is missing the 172.16.0.0 network statement. Without this, it will not enable EIGRP on the serial interface and thus will not form a neighbor relationship with Denver. |
| 19. | B Explanation: B. If a router receives a packet that is looking for a destination network that is not in the routing table, the router drops the packet. |
| 20. | B Explanation: B. The network 192.168.30.0 cannot be placed in the next router's routing table because it is already at 15 hops. One more hop will make the route 16 hops, and that is not valid. |
| 21. | C Explanation: C. You need a straight-through cable between the router and switch. Because there are multiple VLANs, you must have a trunk link (802.1q) configured. |
| 22. | C Explanation: C. If you do not set the VTY password, you will be denied access when trying to telnet into the router, due to the default presence of the login command and its requirement that a password be set. You can set the password during setup or at any time after you finish the initial configuration of your router. |
| 23. | C Explanation: C. The command access-list 110 permit ip any any (0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 is the same as the any command) is a wildcard allowing any host or network access to any other host or network. |
| 24. | C Explanation: C. Cisco's default encapsulation for serial links is High-Level Data Link Control (HDLC). To use a different encapsulation, you use the encapsulation command in interface configuration mode. |
| 25. | B Explanation: B. This IP address falls into the range 10.1.0.0 0.0.255.255 and thus will be routed out interface E1. |
| 26. | C Explanation: C. A switch port in STP learning state listens to BPDUs and learns all the paths in the switched network. |
| 27. | B, C, D Explanation: B, C, D. If you configure your router using the commands boot system flash, boot system tftp, and boot system rom, in that order, the router first tries to boot from flash. If that is unsuccessful, it tries to boot from a TFTP host; if that is unsuccessful, it boots into ROM mode. |
| 28. | B Explanation: B. By typing copy tftp flash, you tell the router to go to a TFTP host and download the IOS software to the router's flash memory. |
| 29. | B Explanation: B. Routers always look at the administrative distance of a route before using metrics. EIGRP has an administrative distance of 90, and RIP has an administrative distance of 120. |
| 30. | A Explanation: A. Frame Relay can send an Inverse ARP packet to the device on the other side of the virtual circuit. If the other side does not support Inverse ARP, you must configure a static map. |
| 31. | A Explanation: A. The 10.0.0.0 network is discontiguous across the Ethernet interfaces of the branch routers. In this case, EIGRP auto-summarization must be disabled. |
| 32. | D Explanation: D. At the end of all access lists is an implicit deny all statement. Therefore, you must include a permit any any to allow traffic that does not meet your restrictions to continue. Also remember that 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 is the same parameter as any. |
| 33. | A, D Explanation: A, D. Frame Relay subinterface configuration is provided by either point-to-point or multipoint subinterfaces. Even though Frame Relay can use an SVC, it is not widely supported or implemented and so is not the best answer to this question. Also, point-to-point interfaces have their own subnet addresses. |
| 34. | F Explanation: F. A /30 provides two hosts, which is the most efficient for point-to-point links. |
| 35. | D Explanation: D. Extended IP access lists use access list numbers 100–199 or 2000–2699 and can filter on the protocol field in the Network layer header as well as on port numbers in the Transport layer header. Of course, source and destination IP addresses can be used as well. To filter on an upper-layer protocol, such as WWW, SMTP, or FTP, you cannot use IP in the protocol field; instead, you must use either UDP or TCP, depending on the Application layer protocol. |
| 36. | D Explanation: D. Bridges can read frames and filter only by MAC (hardware) address. |
| 37. | A Explanation: A. The default Frame Relay encapsulation is Cisco's proprietary encapsulation, and that can be used only if you have Cisco routers on both sides of the Frame Relay link. If you have multiple vendors, you need to use Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) encapsulation. |
| 38. | B Explanation: B. Each switch should learn the MAC address of the hosts on the network. Because this diagram shows only two hosts, the correct answer is B. |
| 39. | B Explanation: B. Full-duplex transmission uses a point-to-point connection from the transmitter of the transmitting station to the receiver of the receiving station. Host-to-host means dedicated transmission to the receiving pair as well as dedicated receiving from the transmitting pair. |
| 40. | A Explanation: A. Encapsulation describes the conversion of data for use at each layer. The order of conversion is as follows: user information is converted to data, data to segments, segments to packets or datagrams, packets to frames, and frames to bits. |
| 41. | C Explanation: C. This IP address falls into the range 10.8.0.0 0.7.255.255 and thus will be routed out interface E2. |
| 42. | D Explanation: D. IEEE 802.1D is the Spanning Tree Protocol specification. |
| 43. | A, C, D Explanation: A, C, D. Before you try to back up the IOS on your router to a network server, ping the server from the router to make sure you have connectivity. Also, verify that you have the Trivial FTP (TFTP) server software running, that the default path is set, and that the host running the TFTP software is in the same subnet as the router's LAN connection to the TFTP host. |
| 44. | C Explanation: C. There could be many answers for this problem, but the best answer is that the port has not been assigned to the correct VLAN. |
| 45. | B, D Explanation: B, D. Classless routing protocols send subnet mask information with each route update. This means they support VLSM, CIDR, and discontiguous networking. EIGRP, OSPF, and RIPv2 are considered classless routing protocols. |
| 46. | D Explanation: D. You can see the current setting of the configuration register by using the show version command. |
| 47. | B Explanation: B. The show frame-relay traffic command shows the Frame Relay protocol statistics. |
| 48. | A, C Explanation: A, C. Both ping and traceroute use ICMP to test IP connectivity in an internetwork. Ping uses ICMP echo requests and responses, and traceroute uses destination-unreachable and IP TTL time-exceeded messages. |
| 49. | B Explanation: B. Cisco routers run High-Level Data Link Control (HDLC) over serial interfaces by default; however, if you are running Frame Relay, they will run the Cisco Frame Relay encapsulation by default. |
| 50. | B Explanation: B. The first up in the line is the Physical layer, and the second up is the Data Link layer. |
| 51. | B Explanation: B. The correct range for an extended access list is 100–199, the correct protocol and port is TCP 80, and the source address is any, but the destination is host 192.168.1.27. |
| 52. | C Explanation: C. If a switch receives a broadcast or multicast frame on a switchport, it is flooded out all ports except for the port it was received on. |
| 53. | A Explanation: A. This ACL will work on either A or D; however, A is a better choice. |
| 54. | C Explanation: C. B, D, and E all meet the minimum requirements of supporting VLSM and discontiguous subnets. However, only static routing minimizes router CPU and WAN utilization. |
| 55. | D Explanation: D. This IP address does not fall into any of the specified ranges and thus will follow the default route out interface serial 0. |