Recipe 14.3. Consuming a Web Service
ProblemYou need to use a web service created by another group in your company to access data your application requires. SolutionAdd a web reference to an existing ASP.NET project using Visual Studio 2005. Create an instance of the web service class in your application and call its methods. To add a web reference to an ASP.NET project in Visual Studio 2005:
Visual Studio 2005 will create all the files needed to consume the web service and will place them in the App_WebReferences folder. The files include a .disco, a .discomap, and a .wsdl file for the web service. After adding the web reference, create an instance of the web service class and call its methods in the code-behind class for the page. Examples 14-8, 14-9 through 14-10 show the .aspx file as well as VB and C# code-behind files for an example we've written to create an instance of the web service class from Recipe 14.1 and call its methods. Figure 14-3. Adding a web reference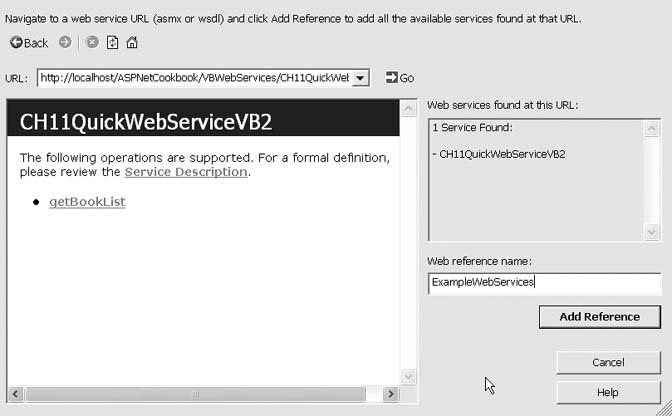 DiscussionVisual Studio 2005 makes consumption of a web service easy by creating all of the plumbing for you. You don't have to worry about creating proxy classes and the SOAP messages; it's all done for you when you add a web reference. In our example that illustrates the solution, the web service created in Recipe 14.1 is used to obtain a list of books and display the list in a DataGrid. We have accomplished this by writing just a few lines of code. The first step in consuming a web service is to add a web reference to your project by selecting the project in the Solution Explorer, right-clicking, and selecting Add Web Reference from the context menu. You need to enter the URL of the web service you want to consume. This is normally the full URL of the .asmx file or the WSDL file of the web service. When the web service resides on your own computer, as is the case with our example for this recipe, a URL such as the following will do:
After entering the URL of the .asmx or WSDL file of the web service, the Add Web Reference dialog box displays the operations provided by the web service in the left pane. The web reference name should be changed to remove the tight coupling to a specific server because the server hosting the web service can change. For our example, we have renamed the web reference to ExampleWebServices, as shown in Figure 14-3. When you click Add Reference, Visual Studio 2005 creates and adds to your project all the files needed to make a web service available to your application, including a disco file, which helps the application locate the service, and a WSDL file, which defines the services available from the web service. Then, it creates a proxy class that you use to access the web service. (The proxy class interfaces with the web service and provides a local representation of the service.) The web reference is given the name provided in the Add Web Reference dialog box.
After you add a web reference to the service you plan to employ, you need to create an instance of the proxy class. For example, here's how we create an instance of the proxy class for the example web service in Recipe 14.1:
In our example, the getBookList method is called to obtain a DataSet containing the book list. Though this method call looks like a standard method call, the proxy class is calling the web service to get the data.
For our example, the DataSet returned by the web service is bound to a DataGrid on the form to display the list of books:
By creating all the plumbing required to access web services, which would be tedious to write and error-prone if you had to do it yourself, Visual Studio 2005 makes using web services in your applications more practical. This is true if the web service provider and consumer are both .NET implementations, because most of the data types provided by the Common Language Runtime (CLR) can be used in the web service interfaces. (See the ".NET Web Service Idiosyncrasies" sidebar in Recipe 14.3 for more on this topic.) Web services provided by other technology platforms, such as Java, can be consumed by .NET applications. Java and other platforms do not have a set of rich data types that match the CLR data types, so the interface must be designed using simple data types. The details of consuming a web service from other technologies are beyond the scope of this book. See AlsoRecipe 14.1; if you need to use web services created with Java, see Java Web Services, by Dave Chappell and Tyler Jewell (O'Reilly). Example 14-8. Consuming a web service (.aspx)
Example 14-9. Consuming a web service code-behind (.vb)
Example 14-10. Consuming a web service code-behind (.cs)
|
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 202
