Introducing Windows Mail
The popularity of e-mail attacks led Microsoft to completely re-write the Windows e-mail client. The new version was renamed Windows Mail to differentiate from prior versions of Outlook Express and Outlook. While substantial changes have been made to Windows Mail, this section will focus on the security improvements. New security features include:
-
Phishing detection
-
Improved junk mail detection
-
Sender white lists and black lists
-
Top-level domain blocking
-
Character set blocking
-
Simplified e-mail storage
| Note | Several popular, but risky, Outlook Express features have been removed in Windows Mail, including the ability to have multiple e-mail identities and HTML e-mail account support (HTML support is available in Windows Live Mail). Keep in mind, however, that Windows Mail is exclusively considered a personal e-mail client. It is not intended to access organizational mail servers, such as Microsoft Exchange Server. For readers who are solely interested in organizational e-mail protection, this section may prove of interest only insofar as it highlights security steps that should be taken in the mail clients they use. Microsoft Outlook 2007 contains many of the same improvements seen in Windows Mail. |
Phishing Detection
Phishing e-mails continue to be a huge problem, and are predicted to remain at a high percentage of overall makeup rate or grow over the next few years. Windows Mail contains built-in phish detection that is separate from Internet Explorer 7's new anti-phishing mechanisms. All incoming e-mail is inspected for characteristics and content associated with phishing messages.
As Figure 10-6 shows, Windows Mail isn't shy about pointing out suspected phishing messages. It highlights the e-mail summary in red and gives the user the ability to unblock or to delete the message.
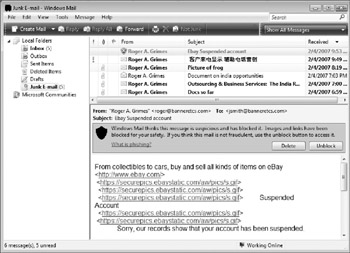
Figure 10-6: Windows Mail is very conspicuous about suspected phishing messages.
The anti-phishing feature can be disabled or modified as shown in Figure 10-7.
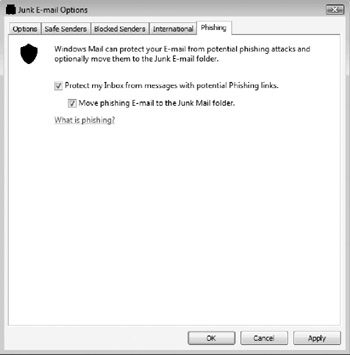
Figure 10-7: The anti-phishing features can be disabled or modified.
| Note | Windows Live Mail's ability to move phish e-mail to the Junk Mail folder only applies to e-mail arriving POP and IMAP (and not HTTP). |
| Note | Look for many of the e-mail security settings discussed in this chapter under E-mail safety options under the Tools menu bar option in Windows Live Mail. |
Improved Junk Mail Detection
Client-side junk mail detection has been added to Windows Mail. Several detection levels (as shown in Figure 10-8) are available, along with a built-in Junk e-mail folder.
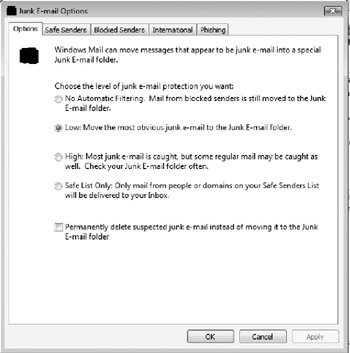
Figure 10-8: Windows Mail contains client-side junk-mail protection.
| Note | Windows Live Mail has the additional ability to report e-mail marked as Junk Mail to Microsoft and its partners in order to increase overall junk e-mail detection accuracy through end-user community involvement. |
Sender White Lists and Black Lists
By default, all e-mail recipients are added to Windows Mail's Safe Sender white list (see Figure 10-9), although additional e-mail addresses can be added as well.
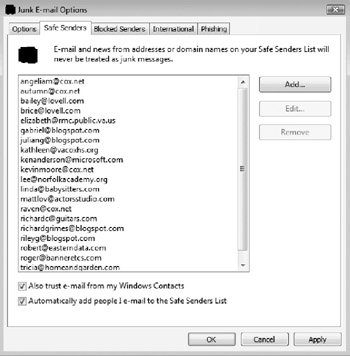
Figure 10-9: Windows Mail contains a "Safe sender" list feature.
Messages from people on the Safe Sender list are never blocked as junk mail. Windows Mail also comes with an e-mail black list under Blocked Senders (see Figure 10-10), although e-mail address-level black lists are of limited value in most environments. Phishers and spammers rarely re-use an e-mail address after its use in a malicious campaign.
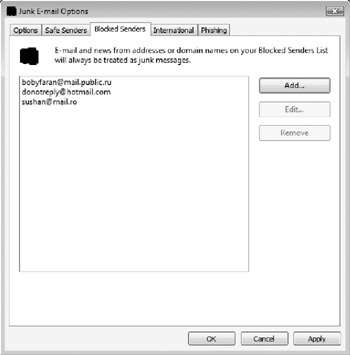
Figure 10-10: The "blocked senders" list may primarily be useful to block messages from people you do not want to talk to.
Top-Level Domain Blocking
Many foreign countries are doing a poor job at blocking malicious e-mail senders. Some countries appear to actually encourage it and offer safe havens to spammers and phishers. Windows Mail allows a user to block all e-mails from a top-level domain (TLD) (for example, an entire country). As Figure 10-11 shows, Windows Mail offers various country top-level domains to choose from. While not overly accurate, Windows Vista allows the user to set country-specific blocks.
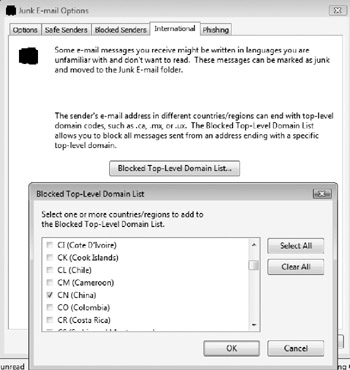
Figure 10-11: You may block messages from a particular TLD.
| Note | Windows Live Mail has the additional ability to bounce back blocked e-mail to the sender and the ability to automatically unsubscribe the user's e-mail address from blocked mailing lists. Neither option is enabled by default and we agree with the decision as enabling both of these options may lead to more unsolicited e-mail. |
The author of this chapter has never believed in country-specific blacklists because it means the potential e-mail receiver will never receive any legitimate e-mail from the blocked country either, and that can be a big risk to take for a business user. Who knows what legitimate, foreign friend you might make in the future? And months or years later, would you remember to remove the country-specific block when needed? However, many readers will probably enable country-specific blocks and immediately kill a huge portion of their spam, while not endangering any current e-mail contacts.
Another, more accurate feature is shown in Figure 10-12. Windows Mail allows messages encoded in foreign character sets to be automatically moved into the Junk e-mail folder. For example, if the reader does not understand Simplified Chinese character sets, all e-mail messages containing Simplified Chinese can be blocked by default.
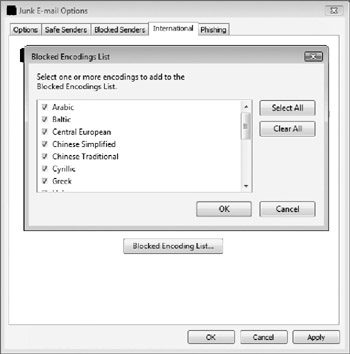
Figure 10-12: You may block messages using certain character encodings.
Of course, it would be very easy for a criminal, such as a phisher or spammer, to modify encodings, TLDs, and any other variable in a particular message. These blocking techniques are all highly insufficient as a comprehensive protection mechanism. At the end of the day, the only thing that will protect people from criminals is a highly developed sense of paranoia.
Simplified E-mail Storage
Windows Mail stores all e-mails in searchable *.eml files (see Figure 10-13). EML files are Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (MIME) formatted, file system-based text files. Each e-mail is stored as a separate file. This allows e-mails to be searchable, not only for indexing purposes, but to simplify the job of anti-malware tools. In previous e-mail clients, the various e-mail storage file formats complicated the job for protection products. Now, all content, malicious or not, can be searched and easily manipulated.
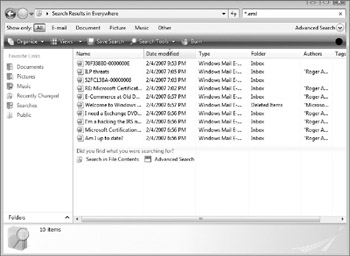
Figure 10-13: Windows Mail stores all e-mail messages as text files.
Windows Mail has significant improvements in client-side security. Only time will tell how well Windows Mail stands up to years of constant attacks.
EAN: N/A
Pages: 163