| 1. B 2. D 3. D 4. B, D 5. A, B 6. A, B 7. D 8. A, B, D 9. D, E 10. A 11. C 12. B 13. A, D, E 14. B, D 15. C 16. E 17. D 18. C, D 19. A, B 20. A, C 21. E 22. C 23. A, C 24. E 25. C, E 26. E 27. B 28. E 29. C 30. A, B, E 31. B, D, E 32. A, D 33. E 34. A, B 35. A 36. A, B, D 37. C, D 38. A, C 39. A, C 40. A 41. B 42. A, C, E 43. B, E 44. A, B, D 45. A, B, E 46. A, B 47. D, E 48. C 49. D 50. B 51. A, D 52. A, C 53. A, C, D, E 54. A 55. B 56. C 57. B 58. A, C, D, E 59. B 60. A, B, C, D, E | | | | A1: | Answer B is the correct solution. It assigns the correct number of switches to each floor. Answer C is incorrect because it does not assign the correct number of switches to each floor. Answers A and D are incorrect because they use repeaters to connect the two floors. The distance between the two floors is at most 12 meters , far less than what is required for repeaters. Repeaters will also do nothing to help route traffic. Separate subnets were introduced to remove a congestion problem. | | | | | A2: | Answer D is the correct answer. As congestion from unicast traffic appears to be the problem, the best solution is to replace the 20-port, 10Mbps hub with a Cisco Catalyst 2950 10/100Mbps hub. This will not only improve the bandwidth from 10 to 100Mbps ( assuming that the hosts have compliant Ethernet cards) but will also reduce the problem of unicast congestion. Answer B is incorrect because there is no wireless network. Answer A is incorrect because this situation does not call for a router. Answer C is incorrect because although a 100Mbps hub will increase performance, it will not remove the unicast traffic problem, as hubs forward unicast traffic on all ports. The performance difference between a hub and a switch is quite significant. | | | | | A3: | Answer D is correct. Class C address spaces have the subnet mask 255.255.255.0. This allows for a maximum of 254 addressable hosts on the network. When a class C address space is subnetted , a certain amount of hosts are allowed for each particular subnet mask. A subnet mask of 255.255.255.128 allows 126 addressable hosts. A subnet mask of 255.255.255.192 allows 62 addressable hosts. A subnet mask of 255.255.255.224 allows 30 addressable hosts. A subnet mask of 255.255.255.240 allows 14 addressable hosts. Answers A, B, and C are incorrect because the subnet masks for each location and the host addresses are incorrect. | | | | | A4: | Answers B and D are correct. Answer B provides for 510 hosts in Minneapolis, which meets the 300 host requirement. It provides for 254 hosts in Melbourne, which meets the 120 host requirement. It provides for 254 hosts in Vancouver, which meets the 28 host requirement. Answer D is correct as it provides 510 hosts in Minneapolis, 216 in Melbourne, and 62 in Vancouver. To support 300 hosts, a subnet mask of 255.255.254.0 or lower is required. In CIDR notation this is /23 or lower. To support 120 hosts, a subnet mask of 255.255.255.128 or lower is required. In CIDR notation this is /25 or lower. To support 28 hosts, a subnet mask of 255.255.255.224 or lower is required. In CIDR notation this is /27 or lower. Answer A is incorrect because it does not provide enough host addresses for the Minneapolis site. Answer C is incorrect because it does not provide enough host addresses at the Minneapolis site. | | | | | A5: | Answers A and B are correct. RIP and RIPv2 have a maximum hop count of 15 hops and hence would not be able to map the entire network at this university. Answer C is incorrect, as IGRP can handle routes in excess of 25 hops. Answer D is incorrect, as EIGRP can handle routes with hop counts in excess of 25 hops. Answer E is incorrect, as OSPF can all handle routes with hop counts in excess of 25 hops. | | | | | A6: | Answers A and B are correct. Answer A is correct, as RIPv2 is an open protocol standard supported by a multitude of vendors. Answer B is correct, as OSPF is an open protocol standard supported by a multitude of vendors . Answer C is incorrect, as Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP) was developed and is owned by Cisco. Answer D is incorrect, as Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) is a proprietary routing protocol developed by Cisco. Proprietary means that unless a vendor has specifically licensed the protocol implementation from Cisco, a third-party vendor will not support it. | | | | | A7: | Answer D is correct. Routers generally form the border between a LAN and a WAN link such as an ISDN line or a Frame Relay connection. Answer A is incorrect, as bridges do not perform this function. Answer B is incorrect, as Layer 2 switches cannot perform this function. Answer C is incorrect, as repeaters cannot perform this function. | | | | | A8: | Answers A, B, and D are correct. In this question you are asked to apply your judgment even though more than three answers could be correct. Cisco occasionally does this on its associate level exams. Of the six possibilities listed, routers, switches, and routing protocols are the most likely to be present in a modern corporate internetwork. Answer C is incorrect. Although hubs are possible, in general most networks have upgraded their hubs to switches. Apart from their wireless hubs, Cisco does not sell dedicated hubs anymore. Answer E is incorrect. Although repeaters do appear on corporate networks, they are not as likely to appear as routers, switches, and routing protocols. Answer F is incorrect. Bridges do appear on some modern networks, but like hubs they have been phased out in favor of newer technologies. | | | | | A9: | Answers D and E are correct. Answer D is correct because the first two quads are 128.250 and the mask specifies that they must be fixed. The last two quads are wild according to the mask. This will block the requisite traffic. Answer E is correct because the first two quads are 128.250 and the mask specifies that they must be fixed. The last two quads are wild according to the mask. This will block the requisite traffic. Access list B is incorrect as this will only block traffic from address 128.250.0.0. Access list C is incorrect as this will block traffic from all hosts except those whose last two quads equal 255. The secret to understanding access lists is to understand how the wildcard masks work. A 0 in the wildcard mask means that the corresponding quad must match. For example, in access list 1, A.B.C.D 0.0.255.255, any IP address that starts A.B will be covered by the access list. There can be any values for C and D but it will still be covered by this list. | | | | | A10: | Answer A is correct. The syntax of an extended IP access list is access-list [list number] {denypermit} protocol source source-wildcard destination destination-wildcard eq port/protocol name (for example, http, telnet, ftp). Answer A is correct because the source is any host and the destination is the host specified in the question, 192.168.81.114. The protocol specified is telnet. Answer B is incorrect, as this will block telnet traffic from host 192.168.81.114 to any host, but not prevent telnet traffic to this host. Answer C is incorrect as it will block all telnet traffic from network 192.0.0.0 /8. Answer D is incorrect as it deals with http rather than telnet traffic. | | | | | A11: | Answer C is correct. The question asks which protocols do not provide error correction. Although all WAN protocols provide error detection, the HDLC (High Level Data-Link Control) protocol does not provide error correction capability. Essentially HDLC will acknowledge that there is an error, but do nothing further. Answer A is incorrect, as SDLC can correct errors. Answer B is incorrect, as LAPB can correct errors. Answer D is incorrect, as PPP can correct errors. | | | | | A12: | Answer B is correct. PPP and LAPB (Link Access Procedure Balanced) WAN protocols support STAC (named for STAC electronics) and Predictor compression via Cisco's IOS. PPP also supports the MPPC (Microsoft Point to Point Compression) method of compression. Answer A is incorrect, as HDLC only supports the STAC method of compression via Cisco's IOS, it does not support Predictor. Answer C is incorrect, as HDLC only supports the STAC method of compression via Cisco's IOS; it does not support Predictor. Answer D is incorrect, as HDLC only supports the STAC method of compression via Cisco's IOS; it does not support Predictor. | | | | | A13: | Answers A, D, and E are correct. Answer A is correct, as RIPv2 is a routing protocol. Answer D is correct, as OSPF is a routing protocol. Answer E is correct, as EIGRP is a routing protocol. Answer B is incorrect, as IP is a routed protocol. Answer C is incorrect, as IPX is a routed protocol. Routing protocols inform routers of routes through the network. Routed protocols carry data traffic. | | | | | A14: | Answers A and B are correct. Answer A is correct, as NWLink is a routed protocol. Answer B is correct, as DECnet is a routed protocol. Answer C is incorrect, as BGP is a routing protocol. Answer D is incorrect, as RIP is a routing protocol. Answer E is incorrect, as IGRP is a routing protocol. | | | | | A15: | Answer C is correct. 192.168.20.1 /28 would translate as 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.240 in dotted decimal notation. This eliminates all but answers C and D. NO SHUT makes an interface active, making C the correct answer. Answer A is incorrect because it sets the incorrect subnet mask. Answer B is incorrect because it sets the incorrect subnet mask. Answer D is incorrect because it shuts down the interface. Answer E is incorrect, as it sets the incorrect subnet mask. | | | | | A16: | Answer E is the correct answer. There are two things to look for in answering this question. The first is that the correct Ethernet interface on the router is being addressed ”in this case ethernet1 instead of ethernet0. Answer A is incorrect, as Ethernet0 is being configured. Answer B is incorrect, as Ethernet0 is being configured. Answer C is incorrect, as Ethernet0 is being configured. Answer D is incorrect, as Ethernet0 is being configured. The second is to realize that /23 translates into decimal quad notation as 255.255.254.0. Answer F is incorrect, as it has the wrong subnet mask. | | | | | A17: | Answer D is correct The VTY password needs to be set before a router can be accessed remotely via the telnet protocol. Answer A is incorrect; the console password is used for those connections via console cable rather than remote telnet connections. Answer B is incorrect, as the enable password is used to enter privileged mode. Answer C is incorrect, as the auxiliary password is used for access via the auxiliary port. | | | | | A18: | Answers C and D are correct. Answer C is correct. The Auxiliary password must be set before access is available via the auxiliary port. Answer D is correct. The VTY password must be set before access is available via Telnet is available. Answer A is incorrect. Access is available from the console port regardless of whether a console password is set. Answer B is incorrect. Access is available from the console port regardless of whether the enable password has been set. | | | | | A19: | Answers A and B are correct. Answer A is correct. Each VLAN on a switch must reside on a separate logical subnet. Answer B is correct. Traffic passing between two ports on a switch that are members of separate VLANs must be transferred via a process at Layer 3 of the OSI model. Answer C is incorrect. Intra-VLAN traffic must pass through Layer 3. Answer D is incorrect; VLANs on the same switch must be on separate subnets. | | | | | A20: | Answers A and C are correct. Answer A is correct. One of the benefits of instituting VLANs is that it provides a way of limiting broadcast traffic to those ports that are members of the same VLAN. Answer C is correct. VLANs can also be configured on multiple switches. A broadcast frame transmitted on a port that is a member of VLAN 1 on a particular switch will not only be transmitted to all other ports that are members of VLAN 1 on that switch, but to ports on other switches connected to that switch that are also members of VLAN 1. Answer B is incorrect; broadcast traffic is only forwarded to ports on a switch that are members of the same VLAN. Answer D is incorrect; VLANs can span multiple compatible switches. | | | | | A21: | Answer E is the correct answer. The IOS command to display the membership of VLANS on a switch is show vlan-membership . Answer A is incorrect because show vtp will display VTP status. Answer B is incorrect. show running-config is used on routers to display their configuration. Answer C is incorrect. Show spantree [vlan] will display the spanning tree information for a particular VLAN. Answer D is incorrect. show start-config is used on routers to display their startup configuration. | | | | | A22: | Answer C is correct. Only answer C assigns each port to its correct VLAN. The other answers assign ports to incorrect VLANs. This question looks exceedingly complex, but can be reduced to the correct answer by eliminating obviously incorrect possibilities. Answer A is incorrect, as port 9 through 12 are assigned to the wrong VLAN. Answer B is incorrect, as port 7 is assigned to VLAN 1 instead of VLAN 2. Answer D is incorrect, as it assigns port 7 to VLAN 4 rather than VLAN 2. | | | | | A23: | Answers A and C are correct. Answer A is correct, as a file server is likely to send and receive a lot of information on the network. Answer C is correct, as a proxy server is likely to send and receive a lot of information on the network. Answer B is incorrect. Although there will be cases where workstations will want to send and receive at the same time, it is less critical than for the file and proxy server. Answer D is incorrect. Web servers tend to receive small amounts of incoming data yet provide large amounts of outgoing data. Even though you would most likely configure a Web server to also be full duplex, its requirements are not as great as that of the proxy or file server. This question again asked you to exercise a best choice given available options. | | | | | A24: | Answer E is correct. A switch will most effectively reduce unicast transmissions by hosts on the same segment by reducing the segment size to only the hosts connected to a single port (usually one). Answer B is incorrect. Repeaters forward all traffic and will do nothing to alter the size of a segment. Answer C is incorrect. Although a bridge will reduce network congestion caused by unicast transmission, it will not do so as effectively as a switch. Answer D is incorrect. Routers can reduce the size of segments, but will not do so as effectively as switches. | | | | | A25: | Answers C and E are correct. Answer C is correct. A router can reduce congestion caused by broadcast traffic. Answer E is correct. A switch that is configured with VLANs can reduce congestion caused by broadcast traffic. Answer A is incorrect. Repeaters forward broadcast traffic. Answer B is incorrect. Bridges forward broadcast traffic. Answer D is incorrect. Layer 2 switches forward broadcast traffic. | | | | | A26: | Answer E is correct. Trunk on will configure a port into trunk mode and start it negotiating with connected devices to establish a link in trunk mode. Answer A is incorrect, as it presents incorrect syntax. Answer B is incorrect, as Trunk nonegotiate bypasses this negotiation phase. Answer C is incorrect, as it represents incorrect syntax. Answer D is incorrect, as it represents incorrect syntax. Note that the configuration commands on a Catalyst 1900 switch can be different to those on other switches. | | | | | A27: | Answer B is correct. vtp server domain ROOSLAN will set the vtp domain name to ROOSLAN on a Catalyst 1900 switch. Answer A has incorrect syntax. Answer C has incorrect syntax. Answer D has incorrect syntax. Answer E has incorrect syntax. Other models of Cisco switch, such as the 6000 series, use the set vtp domain domainname command to set the vtp domain. | | | | | A28: | Answer E is correct. You need to change the CIDR notation of /29 to dotted decimal subnet notation. /29 is equivalent to 255.255.255.248. IP addresses are set on switches using the ip address ip-address subnet-mask command. Answer A is incorrect, as it presents the wrong subnet mask. Answer B is incorrect, as it presents the wrong subnet mask. Answer C is incorrect, as it presents the wrong subnet mask. Answer D is incorrect, as it presents the wrong subnet mask. Answer F is incorrect, as the config ip command will not perform the specified function. | | | | | A29: | Answer C is correct. Answer C represents the only answer where a network or broadcast address for a given network is not listed. Answer A is incorrect, as this is a network address given this subnet mask. Answer B is incorrect, as this is a broadcast address given this subnet mask. Answer D is incorrect, as this is a broadcast address given this subnet mask. Answer E is incorrect, as this is a broadcast address given this subnet mask. This question is answered by calculating which of the IP addresses listed are actually fully addressable given the corresponding subnet masks. | | | | | A30: | Answers A, B, and E are correct. Answer A is correct. Traffic from 192.168.10.20 will be blocked at the first line of the access list. Answer B is correct. Traffic from host 192.168.20.1 will be blocked by the first line of the access list. Answer E is correct. Traffic from host 10.240.34.8 will be blocked, as it is not allowed by the third line of the access list and hence will be implicitly denied . Answer C is incorrect. Traffic from host 10.10.100.155 will be blocked by line 2 of the access list. Answer D is incorrect. Traffic from host address 10.90.100.10 will be blocked by the implicit deny at the end of the access list. The first line of this access list denies traffic coming from any host from 192.X.X.X. That means if the first quad of the host address is 192, the traffic will be discarded. The second line of the access list denies traffic coming from any host with the address 10.10.X.X. The third line of the access list allows traffic from any host with the address 10.15.30.x. At the end of any access list is an implicit deny statement. | | | | | A31: | Answers B, D, and E are correct. Recall that the question asked for which statements are false rather than true. So although these answers are false, they are correct in this context. Answer B is false (hence correct) as traffic accessing the SSL Web site on host 192.168.10.21 will be blocked by the implicit deny at the end of the access list. Answer D is false (hence correct), as line 2 of the access list will block this traffic. Answer A is true (hence incorrect). The first line of the access list makes statement A true. Answer C is true (hence incorrect). Line two of the access list blocks FTP traffic from 10.x.x.x to the FTP server on 192.168.10.21. Answer F is true (hence incorrect). Because of the implicit deny at the end of all access lists, telnet traffic coming from host 10.20.50.30 (not covered by any access list entry) will be blocked. | | | | | A32: | Answers A and D are correct. Answer A is correct. Frame relay networks are multi-access, which means that they can have more than two end points. Answer D is correct. The line between a router and the nearest frame relay switch is the access link. Answer B is incorrect. Routers are referred to as data terminal equipment. Answer C is incorrect. Switches are referred to as data communications equipment. Answer E is incorrect. Virtual circuits exist between DTE/routers. | | | | | A33: | Answer E is correct. DLCI is the frame relay address used to identify a virtual circuit. Answer A is incorrect. DTE (Data Terminal Equipment) is the routers that form endpoints in a frame relay system. Answer B is incorrect. DCE (Data Communications Equipment) is the switches that carry frame relay traffic. Answer C is incorrect SVC (Switched Virtual Circuit) is a dynamic rather than static virtual circuit that exists as required. Answer D is incorrect. CIR (Committed Information Rate) is the agreed upon bandwidth of the VC. | | | | | A34: | Answers A and B are correct. Answer A is correct as it represents a MAC or Ethernet address. Answer B is correct as it represents a Mac or Ethernet address. Layer 2 addresses are made up of a 12-digit hexadecimal sequence. These addresses are written to the network card. Answer C is incorrect. IP addresses are represented at Layer 4 of the OSI model. Answer D is incorrect. IP addresses are represented at Layer 4 of the OSI model. Answer E is incorrect, as it is a NetBIOS rather than MAC/Ethernet address. Answer F is incorrect, as it is an FQDN address (used by DNS) rather than a MAC address. | | | | | A35: | Answer A is correct. A MAC address is made up of 12 characters consisting of the numerals 0 “9 and characters A “F. This can be expressed more simply by saying 12 hexadecimal characters. Hexadecimal is Base16 to decimal's Base10; the extra numbers in hexadecimal are represented by the characters A “F. Answer B is incorrect. MAC addresses are fixed rather than dynamically allocated. Answer C is incorrect. MAC addresses are not binary but hexadecimal. Answer D is incorrect. MAC addresses are not binary but hexadecimal. Answer E is incorrect; MAC addresses are 12 characters in length. Answer F is incorrect, MAC addresses are 12 characters in length and static. | | | | | A36: | Answers A, B, and D are correct. Answer A is correct. Repeaters operate at Layer 1 of the OSI model. Answer B is correct, as bridges operate at Layer 2. Answer D is correct; routers operate at Layer 3 of the OSI model. Answer C is incorrect; switches operate at Layer 2. Answer E is incorrect; gateways (which provide protocol translation) operate at Layers 4, 5, 6, and 7. Some devices such as switches have multiple layer functionality, hence the term Layer 3 switching. However, the question asked about the core functionality, and the core functionality of a switch is to shift frames at Layer 2. | | | | | A37: | Answers C and D are correct. Answer C is correct. Switches work with frames at Layer 2. Answer D is correct. Routers work with packets at Layer 3. Answer A is incorrect. Repeaters work with bits at Layer 1. Answer B is incorrect; bridges work with frames at Layer 2. Answer E is incorrect; routers work with packets at Layer 3. Answer F is incorrect. Bridges work with frames, and routers work with packets at Layer 3. | | | | | A38: | Answers A and C are correct. Answer A is correct. Even though the router in building one has failed, this does not influence the connectivity of building two to building four which are directly linked. Answer C is correct. If it has no router, hosts in building one cannot contact hosts in other buildings. Answer B is incorrect. The path between buildings two and three goes through building one. If the router in building one fails, these hosts will be unable to communicate. Answer D is incorrect. The path between building four and building three exists through buildings two and one. If building one's router is down, this path is broken. 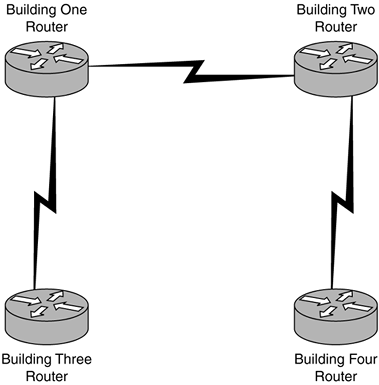 | | | | | A39: | Answers A and C are correct. Answer A is correct. Although there are some hosts on VLAN 1 that are hosted off switch 3, there are some that are hosted off switch 1 and switch 2 ”hence these will still be able to contact each other. Answer C is correct. As switch 4 has hosts on both VLAN 3 and VLAN 4, some of these hosts will be able to contact each other regardless of the status of switch 3. Answer B is incorrect, as some hosts on VLAN 1 were hosted off switch 3. Because the connection between VLAN 2 and VLAN 4 goes through switch 3, answer D is incorrect. 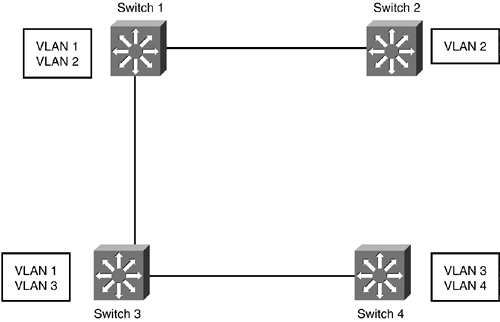 | | | | | A40: | Answer A is correct. The correct syntax of the IOS command to log a message each time a router intercepts or transmits an RIP update on a TCP/IP network is debug ip rip . Answer B is incorrect. IGRP is another routing protocol, Interior Gateway Routing Protocol. Answer C is incorrect; this syntax is invalid. Answer D is incorrect; this syntax is invalid. Answer E is incorrect; this syntax is invalid. Answer F is incorrect; this syntax is invalid. | | | | | A41: | Answer B is correct. The debug command can be used to write messages to a log file for later examination in understanding a router's performance. Answer A is incorrect, as this command does not exist. Answer C is incorrect, as this command does not exist. Answer D is incorrect, as this command does not exist. Answer E is incorrect; the show command does not perform this function. | | | | | A42: | Answers A, C, and E are correct. The private IP address range as defined by RFC 1918 is 10.0.0.0 “10.255.255.255 for Class A, 172.16.0.0 “ 172.31.255.255 for Class B, and 192.168.0.0 “192.168.255.255 for Class C. Answer A is correct, as this address falls within the Class A private range. Answer C is correct, as this falls within the Class B private range. Answer E is correct, as this falls within the Class C private range. Answer B is incorrect; this address does not fall within the private IP address range. Answer D is incorrect. This address does not fall within the private IP address range. | | | | | A43: | Answers B and E are correct. Answer B will provide a 254-host network within the private address range. Answer E is correct. Answer E will provide a 254-host network within the private address range. Answer A is incorrect. This will not provide enough hosts and is not within the private address range. Answer C is incorrect. It does not fall within the private address range. Answer D is incorrect; this network does not provide enough hosts. | | | | | A44: | Answers A, B, and D are correct. Answer A is correct. It represents a network broadcast address and hence cannot be used. Answer B is correct. It represents a network address and hence cannot be used. Answer D is correct. Answer D represents a network address given this particular subnet mask. Answer C is incorrect. This host address can be used given this subnet mask. Answer E is incorrect. This host address can be used given this subnet mask. | | | | | A45: | Answers A, B, and E are correct. Answer A is correct. It is a standard 255.255.255.0 network; hence .0 and .255 are off limits. Answer B is correct. It is a 255.255.240.0 network; hence a range of addresses will be off limits, including 224.0 and 240.0. Answer E is correct. It is a 255.255.248.0, which makes 232.0, 240.0, 248.0 all network addresses. Answer C is incorrect. It is a 255.255.192.0 network; hence 224.0 will not represent a network address but a host address. Answer D is incorrect. It is a 255.255.224.0 network; hence 240.0 will be an addressable host. | | | | | A46: | Answers A and B are correct. Answer A is correct. If the subnet mask were incorrectly set (for example, 255.255.0.0 rather than 255.255.255.0), host ALPHA could have trouble determining which traffic to send to the default gateway and which traffic is on the same subnet. Answer B is correct. If the default gateway is incorrectly set, traffic destined for remote networks will not be forwarded to those networks. Answer C is incorrect. If two hosts had the same IP address, neither would be able to receive traffic. Answer D is incorrect. DNS is irrelevant in this situation. | | | | | A47: | Answers D and E are correct. Answer D is correct. In this situation, you are able to ping your router, which indicates that it has not failed. The inability to ping the ISP's router suggests that either it or the ISDN line connecting your router to the ISP's router may have failed. Answer E is correct. The inability to ping the ISP's router suggests that either it or the ISDN line connecting your router to the ISP's router may have failed. Answer A is incorrect. If your UTP cable had failed, you would not be able to ping your router. Answer B is incorrect. If your switch had failed, you would be unable to ping your router. Answer C is incorrect, as you are able to ping the router. | | | | | A48: | Answer C is correct. Access lists are processed sequentially. Once a packet matches a line of the access list, the access list is no longer processed. Because line three has a mask of 0.255.255.255, it allows all traffic from hosts in the 10.x.x.x range to pass through. The fourth and fifth lines of the access list will not be processed . Answer A is incorrect. There is an implicit deny at the end of all access lists. Answer B is incorrect; line three is where the problem in this list lies. Answer D is incorrect, as line one only allows traffic starting with 10.20.x.x, rather than 10.x.x.x as suggested in the answer. | | | | | A49: | Answer D is correct. None of the lines of the access list directly influence traffic on port 80 from 10.40.22.23 to 192.168.10.22. For this reason, the implicit deny at the end of all access lists blocks this traffic. Answer A is incorrect. Although answer A is factually true, it does not explain why the Web server is unable to be accessed. Answer B is incorrect. The third line does not address hosts on the 10.40.x.x network. Answer C is incorrect. The first line of the access list does not address hosts on the 10.40.x.x network. | | | | | A50: | Answer B is correct. The show process command will display the processor utilization over the last five seconds, last minute, and last five minutes. This will give an overview figure of how much work the processor is doing at any point in time. Cisco recommends avoiding sustained processor usage exceeding 65%. Answer A is incorrect; this command will not provide the desired output. Answer C is incorrect; this command will not provide the desired output. Answer D is incorrect; this command will not provide the desired output. | | | | | A51: | Answer A and D are correct. Answer A is correct. When PAP is used, the username and password are transmitted without encryption from the dialing router. Answer D is correct. When CHAP is used, a challenge which includes a random number is sent from the dialed to router. This random number is input into an MD5 algorithm to provide the encryption key with which to send authentication information between routers. Answer B is incorrect; CHAP uses encryption. Answer C is incorrect; no such challenge occurs when PAP is used over a WAN connection. | | | | | A52: | Answers A and C are correct. STP works by locking down all but one active path between any two collision domains on a switch-based LAN. Without this happening, frames could bounce indefinitely from switch to switch, taking a different path back and forth as they attempt to reach their destination. This would render such a network inoperable. Answer B is incorrect; only one path can exist. Answer D is incorrect; STP stops frames from looping indefinitely. | | | | | A53: | Answers A, C, D, and E are correct. Only switch BETA will have all ports set to the forwarding state by STP, as it has been elected the root bridge. The ports on the other switches which have the lowest cost to BETA will be set to the forwarding state also. Ports connected to other switches will be set to the blocking state to stop redundant pathways to BETA existing. If the link between BETA and another switch is broken, STP will re-converge the network in such a way as all switches will again be able to communicate with each other without generating switching loops . Answer B is incorrect as all ports on BETA will transmit frames received from other ports and forward received frames as it is the root bridge. | | | | | A54: | Answer A is correct. Spanning tree information for VLAN 2 can be shown using the command show spantree 2 Answer B is incorrect. The command show spantree 1 will show the spanning tree information  for VLAN 1. Answer C is incorrect. show trunk will show the trunking information on the for VLAN 1. Answer C is incorrect. show trunk will show the trunking information on the  switch. Answer D is incorrect; show cdp neighbors will display information about the CDP switch. Answer D is incorrect; show cdp neighbors will display information about the CDP  neighbors of the switch. Answer E is incorrect. show config vlan 2 will return an error. neighbors of the switch. Answer E is incorrect. show config vlan 2 will return an error. | | | | | A55: | Answer B is correct. The show spantree statistics command will display the spanning tree protocol BPDU communication statistics. Answer A is incorrect. This is not a legitimate switch command. Answer C is incorrect; this is not a legitimate switch command. Answer D is incorrect; this is not a legitimate switch command. Answer E is incorrect. Answer E will only show basic information about the spanning tree protocol and does not include detailed information such as BPDU statistics. | | | | | A56: | Answer C is correct. The reason why LAN B will often outperform LAN A is that in a switched environment, Unicast traffic is transmitted only to the destination host. Where all hosts are connected to a hub, they will all receive Unicast traffic, whether it is directed to them or not. When one host is transmitting to another host on a switched network, other hosts on the network are also free to start communication. On a network where all hosts are connected via hub, all hosts must wait until a single host making a Unicast transmission finishes that transmission before initiating their own. Answer A is incorrect, as LAN B will always out perform LAN A. Answer B is incorrect. Broadcast traffic on LAN B will reach every host. Answer D is incorrect. Unicast traffic on LAN B will only reach its intended destination host. | | | | | A57: | Answer B is correct. Of the protocols listed, only BGP qualifies as an exterior routing protocol. Exterior routing protocols are used between routers that are not part of the same networks: for example, a router on an ISP's network talking to an upstream provider. Exterior routing protocols deal with the network borders, hence Border Gateway Protocol. Answer A is incorrect. RIPv2 is an interior routing protocol. Answer C is incorrect. IGRP is an interior routing protocol. Answer D is incorrect. EIGRP is an interior routing protocol. Answer E is incorrect. OSPF is an interior routing protocol. | | | | | A58: | Answers A, C, D, and E are correct. RIPv2, IGRP, EIGRP, and OSPF are all interior routing protocols. Interior routing protocols are used on networks where each of the routers on the network is within the control of a single organization. Answer B is incorrect. BGP is an exterior routing protocol. | | | | | A59: | Answer B is correct. The maximum routing metric value of the RIP (and RIPv2) routing protocol is 15 hops. A route with 16 hops is considered of infinite length. Answer A is incorrect; the maximum routing metric is 15 hops. Answer C is incorrect; the maximum routing metric is 15 hops. Answer D is incorrect; the maximum routing metric is 15 hops. Answer E is incorrect; the maximum routing metric is 15 hops. Answer F is incorrect; the maximum routing metric is 15 hops. | | | | | A60: | Answers A, B, C, D, and E are correct. IGRP uses bandwidth, delay, load, reliability, and MTU to generate route metric values. By default, IGRP uses delay and bandwidth in route selection but these other factors can influence the value. Answer F is incorrect; IOS version has no influence on routing metric. |
|

