Instant Capacity Overview
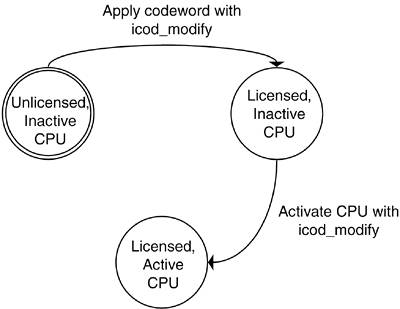
| HP's Instant Capacity offering allows an nPartition server to be purchased with unlicensed hardware components that include cells, CPUs, and memory. Having unlicensed hardware components in the server from the time of purchase makes it possible to immediately increase compute resources without procuring additional servers, allocating floor space, and performing the other tasks associated with new hardware acquisitions. Instead, when the unlicensed components are required by workloads, a right-to-use (RTU) license is purchased. A codeword is then applied to the system and the hardware is available for immediate activation. When a right-to-use license is purchased for a cell, the license also contains a right-to-use license for zero or more CPUs, all of the memory, and all of the I/O associated with the cell. This flexibility allows a cell and all of its memory and I/O to be activated while leaving a portion of CPUs unlicensed. At a later time, another RTU license can be purchased that allows a portion of the remaining CPUs to be activated. The version of Instant Capacity discussed in this book is supported only on HP nPartition servers with at least one nPartition running the HP-UX operating system. In nPartitions running Linux, Microsoft Windows, or OpenVMS, HP assumes all of the processors are active. Consequently, sufficient hardware must be licensed for all of the hardware in nPartitions running Linux, Microsoft Windows, or OpenVMS. The licensing of Instant Capacity components is on a complex-wide basis. The number of licensed cells, the amount of active memory, and number of active processors is not considered solely on a per-nPartition basis. Therefore, a CPU can be deactivated in one nPartition and a CPU can be activated in a separate nPartition without changing the number of licensed CPUs in the complex. Chapter 15, "Workload Manager," demonstrates the use of Instant Capacity technology for the purpose of migrating CPU resources between nPartitions to meet service-level objectives without purchasing additional Instant Capacity components. The number of unlicensed components is maintained in the firmware on the management processor of each nPartition server. When a right-to-use license is purchased and a codeword is applied, the number of unlicensed components stored in firmware is updated. The Instant Capacity data stored in firmware is then used by the Instant Capacity software to determine whether unlicensed components may be activated and whether the system is in compliance. Figure 10-1 shows the process of activating unlicensed CPUs. The figure depicts the case where the Instant Capacity CPUs are located in a licensed cell that is active. The CPUs are initially inactive, or deactivated. A codeword is then applied using the icod_modify command. Applying the codeword licenses one or more CPUs for use, but it does not activate any CPUs. CPUs can then be activated immediately with a separate command, or if applications running within an OS do not appropriately account for dynamic CPU additions, the activation of Instant Capacity CPUs can be deferred until the next reboot. Figure 10-1. Activation Process of Instant Capacity CPUs
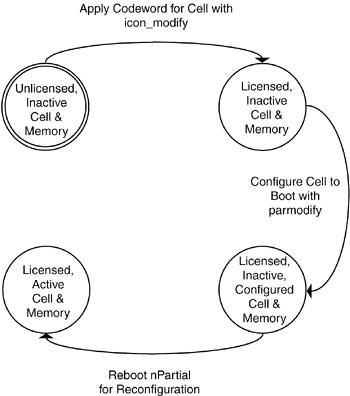
Instant Capacity cells are generally assigned to an nPartition, but the Use on Next Boot flags for the cells are set to No. The cells remain inactive when the nPartition is booted. Because the cells are inactive, the memory and I/O associated with the cells is also inactive. The nPartition configuration tools parmgr, parmodify, and parcreate can be used to change the Use on Next Boot flag as described in Chapter 4, "nPartition Servers"; the operation will be allowed only after a codeword has been applied that licenses the cell. After applying a codeword, the Use on Next Boot flag must be changed and a reboot for reconfiguration must be performed on the nPartition to activate the cell. In Figure 10-2, the process of activating an Instant Capacity cell is illustrated. Initially the cell is assigned to an nPartition but the cell is inactive because the cell's Use on Next Boot flag is set to No. When a codeword is applied, the cell, zero or more CPUs, all of the cell's memory, and all of the cell's I/O can be activated. It is not necessary to license all of the CPUs to activate a cell. In fact, an Instant Capacity cell can be activated without licensing any of its CPUs. Figure 10-2. Activation Process of Instant Capacity Cells
After applying a codeword for the cell and CPUs, the cell must be configured to boot with the nPartition. This is done with either parmgr or the parmodify command by setting the Use on Next Boot flag to Yes. Setting the Use on Next Boot flag does not immediately activate the cell. A reboot for reconfiguration must be performed on the nPartition in order for the cell to be activated. In this case, the icod_modify command is used to apply the codeword, but it is not used to activate resources. Instead, the parmodify command indirectly causes hardware resources to become active after the reboot for reconfiguration is performed. |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 197