Fundamentals of the IPX Protocol
The Internetwork Packet Exchange (IPX) protocol was developed by Novell and was derived from the Xerox Network System (XNS) protocol suite. IPX is a network layer protocol that allows a network address field in the IPX packet header. This allows IPX packets to be routed from one network to another. Figure 13-1 illustrates the IPX protocol suite as it compares to the OSI reference model.
Figure 13-1. IPX Protocol Suite versus OSI Reference Model
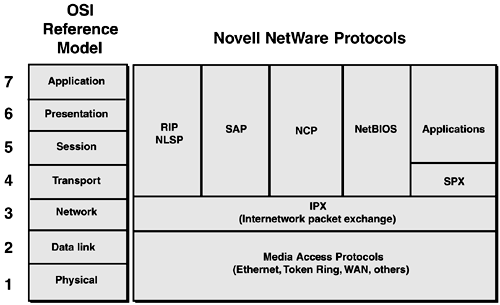
IPX uses it own version of the Routing Information Protocol (RIP) that allows the exchange of IPX routes (this will be covered in Chapter 14, "Routing IPX ").
IPX also use the Service Advertisement Protocol (SAP) to announce network services such as file and print servers to Novell clients on the network. SAP advertisements are sent out every 60 seconds, and Novell file servers and clients keep a table of such services, known as a SAP table. Clients learn of Novell servers by sending Get Nearest Server (GNS) requests upon booting. The first server to respond to the request is considered the nearest server, and the Novell client uses the network address from that server as its network address as well.
IPX addresses consist of two components :
network-number.node-number
The network number can be up to eight digits (32 bits) in length and is expressed as a hexadecimal number. Usually any preceding zeros are dropped from the network number, so the network number might appear as less than eight digits.
The node-number has 12 digits (48 bits) and is usually the MAC address of the interface on which IPX has been configured. The node number also is displayed in hexadecimal format. On serial interfaces, the node number can be manually assigned. By default, a serial interface will use the MAC address of a connected Ethernet or Token Ring interface. This does not cause a problem with Cisco routers because the network number will be different than the interface from which it borrowed the MAC address.
A valid IPX address would appear as follows :
2DC4AB13.0c19.ab93.0102
or
1.0c32.45ce.139a
IPX does support multiple IPX networks on one interface, but each network must have a different media encapsulation. Table 13-1 lists all supported IPX media encapsulation types with their appropriate Novell and Cisco names .
Table 13-1. Novell Versus Cisco Naming for Encapsulation Types
| Media Type | Novell IPX Name | Cisco Name |
|---|---|---|
| Ethernet | Ethernet_802.3 Ethernet_802.2 Ethernet_II Ethernet_SNAP | novell- ether sap ARPA snap |
| Token Ring | Token-Ring_SNAP Token-Ring | snap sap |
| FDDI | FDDI_SNAP FDDI_802.2 FDDI_Raw | snap sap novell-fddi |
This is a quick overview of IPX. For a complete description of the Novell IPX protocol, refer to Chapter 10 of Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices .
| |
| Top |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 127