TITLE Statement
Specifies title lines for SAS output
Valid: anywhere
Category: Output Control
See: TITLE Statement in the documentation for your operating environment.
Syntax
TITLE < n > < text text >;
Without Arguments
Using TITLE without arguments cancels all existing titles.
Arguments
n
-
specifies the relative line that contains the title line.
-
Range: 1-10
-
Tip: The title line with the highest number appears on the bottom line. If you omit n , SAS assumes a value of 1. Therefore, you can specify TITLE or TITLE1 for the first title line.
-
Tip: You can create titles that contain blank lines between the lines of text. For example, if you specify text with a TITLE statement and a TITLE3 statement, there will be a blank line between the two lines of text.
text text
-
specifies text that is enclosed in single or double quotation marks.
-
You can customize titles by inserting BY variable values (# BYVAL n ), BY variable names (#BYVAR n ), or BY lines (#BYLINE) in titles that are specified in PROC steps. Embed the items in the specified title text string at the position where you want the substitution text to appear.
-
#BYVAL n #BYVAL( variable- name )
-
substitutes the current value of the specified BY variable for #BYVAL in the text string and displays the value in the title.
-
Follow these rules when you use #BYVAL in the TITLE statement of a PROC step:
-
Specify the variable that is used by #BYVAL in the BY statement.
-
Insert #BYVAL in the specified title text string at the position where you want the substitution text to appear.
-
Follow #BYVAL with a delimiting character, either a space or other nonalphanumeric character (for example, a quotation mark) that ends the text string.
-
If you want the #BYVAL substitution to be followed immediately by other text, with no delimiter , use a trailing dot (as with macro variables ).
-
-
Specify the variable with one of the following:
-
n
-
specifies which variable in the BY statement that #BYVAL should use. The value of n indicates the position of the variable in the BY statement.
Example: #BYVAL2 specifies the second variable in the BY statement.
-
-
variable-name
-
names the BY variable.
-
Example: #BYVAL(YEAR) specifies the BY variable, YEAR.
-
Tip: Variable-name is not case sensitive.
-
-
-
#BYVAR n #BYVAR( variable-name )
-
substitutes the name of the BY variable or label that is associated with the variable (whatever the BY line would normally display) for #BYVAR in the text string and displays the name or label in the title.
-
Follow these rules when you use #BYVAR in the TITLE statement of a PROC step:
-
Specify the variable that is used by #BYVAR in the BY statement.
-
Insert #BYVAR in the specified title text string at the position where you want the substitution text to appear.
-
Follow #BYVAR with a delimiting character, either a space or other nonalphanumeric character (for example, a quotation mark) that ends the text string.
-
If you want the #BYVAR substitution to be followed immediately by other text, with no delimiter, use a trailing dot (as with macro variables).
-
-
Specify the variable with one of the following:
-
n
-
specifies which variable in the BY statement that #BYVAR should use. The value of n indicates the position of the variable in the BY statement.
-
Example: #BYVAR2 specifies the second variable in the BY statement.
-
-
variable-name
-
names the BY variable.
-
Example: #BYVAR(SITES) specifies the BY variable SITES.
-
Tip: variable-name is not case sensitive.
-
-
-
#BYLINE
-
substitutes the entire BY line without leading or trailing blanks for #BYLINE in the text string and displays the BY line in the title.
-
Tip: #BYLINE produces output that contains a BY line at the top of the page unless you suppress it by using NOBYLINE in an OPTIONS statement.
-
See Also: For more information on NOBYLINE, see BYLINE System Option on page 1484.
-
-
-
Tip: For compatibility with previous releases, SAS accepts some text without quotation marks.
-
Tip: When writing new programs or updating existing programs, always surround text with quotation marks.
-
See Also: For more information about including quotation marks as part of the title, see Expressions in SAS Language Reference: Concepts .
Details
In a DATA Step or PROC Step A TITLE statement takes effect when the step or RUN group with which it is associated executes. Once you specify a title for a line, it is used for all subsequent output until you cancel the title or define another title for that line. A TITLE statement for a given line cancels the previous TITLE statement for that line and for all lines with larger n numbers .
Operating Environment Information: The maximum title length that is allowed depends on your operating environment and the value of the LINESIZE= system option. Refer to the SAS documentation for your operating environment for more information.
Comparisons
You can also create titles with the TITLES window.
Examples
Example 1: Using the TITLE Statement
The following examples show how you can use the TITLE statement:
-
This statement suppresses a title on line n and all lines after it:
title n ;
-
These are examples of TITLE statements:
-
title 'First Draft';
-
title2 "Year's End Report";
-
title2 'Year''s End Report';
-
Example 2: Customizing Titles by Using BY Variable Values
You can customize titles by inserting BY variable values in the titles that you specify in PROC steps. The following examples show how to use #BYVAL n , #BYVAR n , and #BYLINE:
-
title 'Quarterly Sales for #byval(site)';
-
title 'Annual Costs for #byvar2';
-
title 'Data Group #byline';
Example 3: Customizing Titles and Footnotes by Using the Output Delivery System
You can customize titles and footnotes with ODS. The following example shows you how to use PROC TEMPLATE to change the color , justification, and size of the text for the title and footnote.
/********************************************* *The following program creates the data set * *grain_production and the $cntry format. * *********************************************/ data grain_production; length Country $ 3 Type $ 5; input Year country $ type $ Kilotons; datalines; 1995 BRZ Wheat 1516 1995 BRZ Rice 11236 1995 BRZ Corn 36276 1995 CHN Wheat 102207 1995 CHN Rice 185226 1995 CHN Corn 112331 1995 IND Wheat 63007 1995 IND Rice 122372 1995 IND Corn 9800 1995 INS Wheat . 1995 INS Rice 49860 1995 INS Corn 8223 1995 USA Wheat 59494 1995 USA Rice 7888 1995 USA Corn 187300 1996 BRZ Wheat 3302 1996 BRZ Rice 10035 1996 BRZ Corn 31975 1996 CHN Wheat 109000 1996 CHN Rice 190100 1996 CHN Corn 119350 1996 IND Wheat 62620 1996 IND Rice 120012 1996 IND Corn 8660 1996 INS Wheat . 1996 INS Rice 51165 1996 INS Corn 8925 1996 USA Wheat 62099 1996 USA Rice 7771 1996 USA Corn 236064 ; run; proc format; value $cntry 'BRZ'='Brazil' 'CHN'='China' 'IND'='India' 'INS'='Indonesia' 'USA'='United States'; run; /***************************************** *This PROC TEMPLATE step creates the * *table definition TABLE1 that is used * *in the DATA step. * *****************************************/ proc template; define table table1; mvar sysdate9; dynamic colhd; classlevels=on; define column char_var; generic=on; blank_dups=on; header=colhd; style=cellcontents; end; define column num_var; generic=on; header=colhd; style=cellcontents; end; define footer table_footer; end; end; run; /*********************************************************************** *The ODS LISTING CLOSE statement closes the Listing * *destination to conserve resources. * * * *The ODS HTML statement creates HTML output created with * *the style defintion D3D. * * * *The TITLE statement specifies the text for the first title * *and the attributes that ODS uses to modify it. * *The J= style attribute left justifies the title. * *The COLOR= style attributes change the color of the title text * *"Leading Grain" to blue and "Producers in" to green. * * * *The TITLE2 statement specifies the text for the second title * *and the attributes that ODS uses to modify it. * *The J= style attribute center justifies the title. * *The COLOR= attribute changes the color of the title text "1996" * *to red. * * The HEIGHT= attributes change the size of each * *individual number in "1996". * * * *The FOOTNOTE statement specifies the text for the first footnote * *and the attributes that ODS uses to modify it. * *The J=left style attribute left justifies the footnote. * *The HEIGHT=20 style attribute changes the font size to 20pt. * *The COLOR= style attributes change the color of the footnote text * *"Prepared" to red and "on" to green. * * * *The FOOTNOTE2 statement specifies the text for the second footnote * *and the attributes that ODS uses to modify it. * *The J= style attribute centers the footnote. * *The COLOR= attribute changes the color of the date * *to blue, * *The HEIGHT= attribute changes the font size * *of the date specified by the sysdate9 macro. * ***********************************************************************/ ods listing close; ods html body='newstyle-body.htm' style=d3d; title j=left color=blue "Leading Grain " color=green "Producers in"; title2 j=center color=red height=28pt "1" height=24pt "9" height=20pt "9" height=16pt "6"; footnote j=left height=20pt color=red "Prepared " color=green "on"; footnote2 j=center color=blue height=24pt &sysdate9; /*********************************************************** *This step uses the DATA step and ODS to produce * *an HTML report. It uses the default table definition * *(template) for the DATA step and writes an output object * *to the HTML destination. * ***********************************************************/ data _null_; set grain_production; where type in ('Rice', 'Corn') and year=1996; file print ods=( template='table1' columns=( char_var=country(generic=on format=$cntry. dynamic=(colhd='Country')) char_var=type(generic dynamic=(colhd='Year')) num_var=kilotons(generic=on format=comma12. dynamic=(colhd='Kilotons')) ) ); put _ods_; run; ods html close; ods listing; 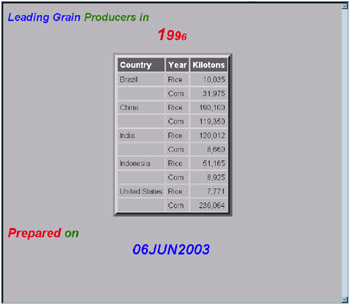
Display 7.1: Output with Customized Titles and Footnotes
See Also
Statement:
-
FOOTNOTE Statement on page 1206
System Option:
-
LINESIZE= System Option on page 1544
The TEMPLATE Procedure in SAS Output Delivery System: User s Guide
EAN: N/A
Pages: 704