The Hardware Platform
| For adequate report and query performance, it is very important to have sufficient "horsepower" with the hardware platform. Scalability is of utmost importance. Controlled ChaosDo not despair if your computer environment looks like the one in Figure 2.1. This is more often the case than not in organizations of any size. What exists can at best be described as controlled chaos! Figure 2.1. Controlled Hardware Chaos Accompanying the hardware chaos are usually a huge portfolio of disparate software and a large staff with only enough skills to support the existing systems. In order to minimize the chaos, most organizations implementing a BI decision-support environment have to consider at least four imperatives in hardware platform selection.
Hardware Platform RequirementsThe hardware must have sufficient power to handle complex access and analysis requirements against large volumes of data. It has to support not only predefined, simple queries on summary data but also ad hoc complex queries on detailed data. It must also be scalable because rapid changes will occur in:
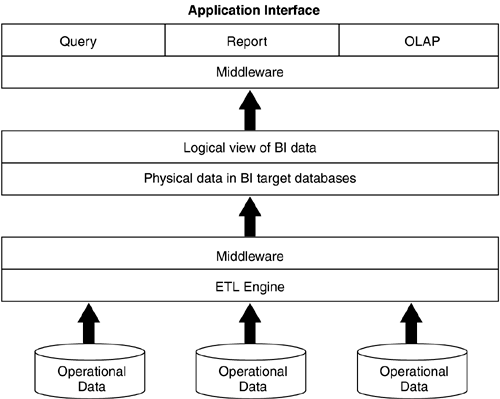
It is useful to think of a BI decision-support environment in terms of a three- tier computing architecture (Figure 2.2). First, the extract/transform/load (ETL) engine extracts , cleanses, and transforms operational data. Then, using middleware, the BI target databases are populated . Finally, when data is requested , it is mapped into suitable representations for the business community at the interface level for running queries, reports, and online analytical processing (OLAP) applications. The interface level can be a customized graphical user interface (GUI) application, an enterprise portal, or Extensible Markup Language (XML) Web services. Figure 2.2. Three-Tier Computing Architecture |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 202