LOGISTICS
So while it is easy to build a website that can take secure online orders, getting the product to the customer can be problematic. That last yard — completing the sale to the satisfaction of the customers so they return and order again — takes planning and organization. The key word is “completing” and the sale is not complete until the product is in the customer’s hands and the customer is satisfied. It’s the least glamorous part of operating a web-based business and it’s the hardest to get right. The complex process of getting a product from the website’s virtual checkout counter to the customer’s doorstep is what order fulfillment is all about.
Logistics moves the right product to the right place at the right time. For an e-commerce business to be profitable, it must reduce its order fulfillment/logistical costs. Don’t think you are alone in your struggle; order fulfillment is a logistical challenge for the whole e-commerce community. This is why many of the major brick-and-mortar websites offer only a limited number of products.
E-commerce logistics requires integration of systems that run from your shopping cart clear through to the shipper’s tracking system so that you and the customer can keep apprised of a package’s whereabouts. But that’s just the beginning. E-commerce logistics also requires managing the complexity of delivering daily thousands of mostly small packages to their unique destinations. To do this cost-effectively you must integrate your inventory and distribution systems. But, with few exceptions, e-commerce operators have simply ignored this necessity. Before making the leap into e-commerce you must consider how your business will:
- Process orders.
- Manage multiple suppliers seamlessly.
- Provide a comprehensive exception-handling process.
- Handle the issue of returned products.
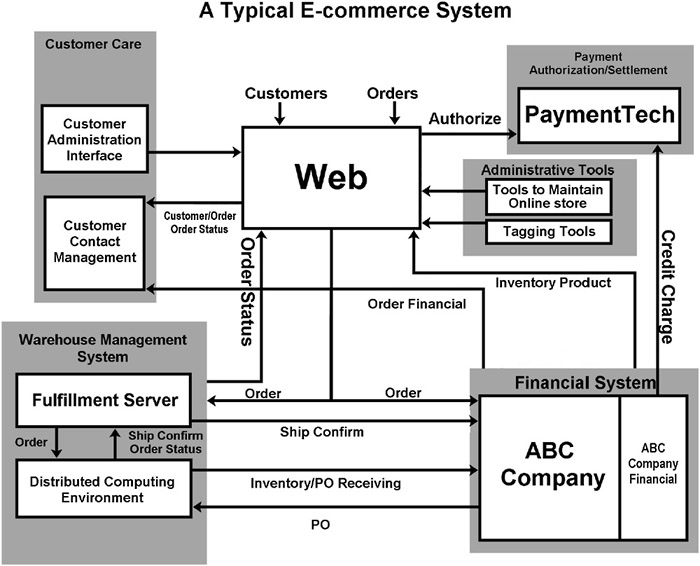
Figure 27: This diagram depicts a typical e-commerce system including order fulfillment processes.
Thankfully, an e-commerce operator needn’t become an immediate expert in logistics and fulfillment; but someone in the value chain must be an expert and that expert can come from outside your organization. In fact, it isn’t that difficult for a new e-commerce business to outsource virtually all of its back-end logistical functions including:
- Order management.
- Warehousing and inventory management (including forecasting).
- IT systems integration to connect the front and back systems.
- Fulfillment.
- Post-sales services like warranty repair, returns management, customer care centers, spare parts fulfillment.
Note however, that if you outsource your entire fulfillment needs, you risk isolating your business and its brand from your customers. Thus, although a number of e-commerce startups initially choose to outsource their logistics and fulfillment chores, many soon move these processes in-house. They quickly realize that to succeed they must make logistics and fulfillment a key part of their internal business process.
To determine whether you should outsource or keep everything in-house, ask yourself: What makes the most business sense at the moment? Assess your order fulfillment requirements and then balance them against the resources available in-house.
EAN: N/A
Pages: 159