Understanding the Features of Project Server 2003
| Project Server 2003 is a complex tool that requires a thorough understanding of both the technical and the business sides of EPM for its implementation. When considering Project Server 2003, it is important to understand its interfaces, architecture, components, configurations, settings, and the security model. Project Server InterfacesThere are two interfaces to Project Server 2003: Project Professional and PWA. Project Professional is where the project managers do most of the detailed work on their project, such as planning new tasks, tracking status, and assigning new resources. Project managers enter the scheduling information in Project Professional and keep it updated. Project managers use Project Professional to assign resources to tasks and track progress with updates received from project team members via PWA. Project Professional 2003 maintains the look and feel of earlier versions, as well as all nonenterprise features. PWA is the other interface where project managers can communicate about projects with the team members, and team members can communicate with project managers. All team members, including executives and managers, who want to view project or resource data need to have access to PWA. Architecture OverviewThe Microsoft Project 2003 EPM solution is based on four key elements: Project Professional, PWA, SQL Server 2000, and Windows SharePoint Services. All these components are kept synchronized by Project Server 2003. Figure 2.1 shows the links between these three components. Figure 2.1. Project 2003 architecture.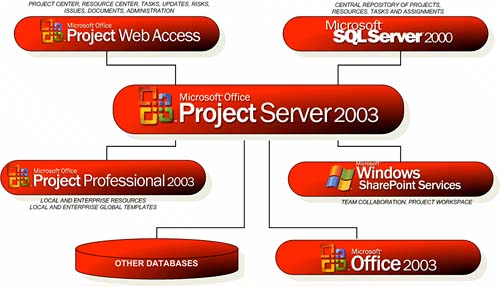 Project Professional is the application that allows project managers to develop and update their project schedules. PWA is the web interface for team members, resource managers, and other project stakeholders that allows them to review information about the project plan, send updates to the project manager, or communicate with other members of the team. Microsoft SQL Server 2000 is used to centrally store information and data about projects and resources. It also serves as a data repository for generating reports. Windows SharePoint Services is the application used to store project documentation, issues, risks, and certain information about tasks. Windows SharePoint Services provides an extensive customizable interface, which allows each project manager to tailor it to the specific needs of her team. Project Server 2003 establishes the link between these components and makes it possible to link to other Office applications, as well as to other enterprise systems. Project Web AccessThe following list presents some of the features available in PWA. As previously noted, Project 2003 is a role-based system and, as such, different users will have access to different features and functions dependent on their role in the organization. PWA allows users to
In addition, PWA serves as the primary interface for system administration, which is done by accessing the Admin page. The Admin page allows the system administrator to configure PWA, establish the roles of individuals and assign them the appropriate permissions, and configure the enterprise views and reports. It is important to note that only qualified individuals should have access to this page because it contains information and settings vital to good functioning of the system.
Microsoft Project ProfessionalProject Professional is the application that allows project managers to
Project Professional is also the application that allows system administrators to build and configure the Enterprise Global template. The Enterprise Global template provides the backbone structure for enterprise project schedule templates, and it is used to configure Enterprise Custom Fields and Outline Codes. Through Project Professional, you can also access the Enterprise Global Resource Pool that stores information about all resources in the database, generic and named. It is also important to remember that only system administrators should have access to modify the Enterprise Global template or Enterprise Global Resource Pool.
Windows SharePoint ServicesWindows SharePoint Services facilitates communication among various project stakeholders. Using Windows SharePoint Services, you can do the following:
Windows SharePoint Services also makes possible the management of the project workspace, which facilitates interaction and communication between project team members.
Overview of Project Server Configuration and SettingsFor your enterprise to make best use of the Project 2003 solution, you must set up and configure the system properly. This includes mapping your business process into the system, ensuring that the information in the database is accurate, and making sure that users can perform in the system those tasks required by their business role in the organization. The following list presents the main areas that must be covered in the initial setup and configuration of the system:
NOTE It is important that you read and understand the Microsoft Administrator's Guide before you start configuring Project Server 2003. |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 227
 bull;
bull;