Advanced DHCP Concepts
| DHCP has been an unassuming network service as of late. The simplicity of the protocol is another reason for its success because it is not cursed by a high degree of administrative complexity. However, greater control over a DHCP environment can be achieved through the understanding of some advanced concepts regarding its use. Some of these concepts are new to Windows Server 2003, and some were introduced in Windows 2000. These improvements can help you to gain control over a DHCP environment, and provide for more security and ease of use. DHCP SuperscopesA DHCP Superscope is used for environments in which multiple network subnets encompass a single scope environment. In these cases, a Superscope can be created to contain multiple scopes. The individual scopes are subsequently dependent on the master Superscope. If it is turned off, they will also be deactivated. Figure 10.10 illustrates a sample DHCP Superscope. Figure 10.10. A DHCP Superscope.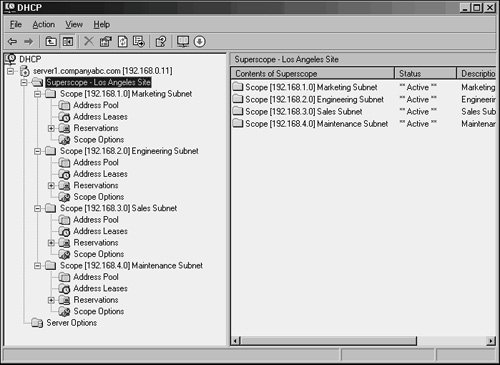 DHCP Multicast ScopesA Multicast scope is created to allow clients to be assigned multicast IP addresses. A multicast IP address is one in which destination hosts can each have the same IP address, which is useful in one-to-many forms of communications such as Webcasts and videoconferencing sessions. Delegating Administration of DHCPIt is never wise to hand over full administrative privileges to individuals who need to perform only a specific network function. If a small group of administrators needs control over the DHCP environment, Windows Server 2003 makes it easy to delegate administrative capabilities to them through the inclusion of a group called DHCP Administrators. Adding users or, preferably, groups to this Security Group will enable those users to administer the DHCP servers in an environment. Netsh Command-Line UtilityWindows Server 2003 has made great strides in allowing virtually all administrative functions to be performed through the command line. This not only helps those users who are used to command-line administration, such as that in Unix operating systems, but also allows for the execution of scripts and batch files, which can automate administrative processes. The Netsh command-line utility is one such utility that effectively allows administrators to accomplish virtually all DHCP tasks that can be run through the MMC GUI interface. For a full listing of potential functions with Netsh, run netsh /? from the command line, as illustrated in Figure 10.11. Figure 10.11. Netsh command-line options.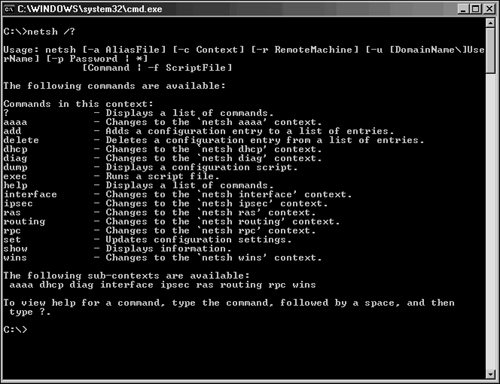 Performing DHCP Database MaintenanceThe DHCP database is stored in the dhcp.mdb file, located in \%systemroot%\system32\dhcp. This database is structured using Microsoft JET database technology, the same technology used for Exchange Server, Active Directory, and many other databases in the Microsoft world. As any administrator who has worked with JET databases will attest, frequent maintenance of the DHCP database is required to keep it functioning properly and to groom it for defragmentation and recovery of whitespace. By default, DHCP is configured to perform online maintenance to the database, but only during intervals in which it is not being used for client requests. For busy, large DHCP servers, there may never be downtime, so it is therefore important to run offline maintenance against the dhcp.mdb file on a quarterly to semi-annual basis. You can run maintenance against the dhcp.mdb DHCP database file by using the jetpack utility in Windows Server 2003. From the command line, enter the following commands, illustrated in Figure 10.12, to stop the DHCP Server service, compact the database, and restart the service: Figure 10.12. DHCP database maintenance.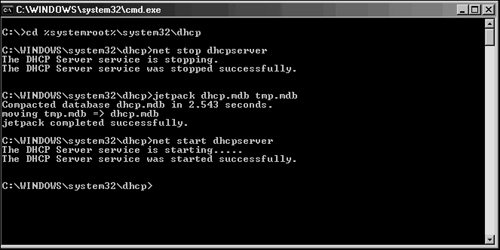
Note A maintenance schedule for DHCP and all other Microsoft JET-based databases should be established, in addition to any other maintenance schedules that may be in effect. Such a schedule will help to keep these network services environments in top shape. Using redundant servers that will take over while the database is down can also minimize downtime from this maintenance. |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 499