CHAPTER 15
|
| < Day Day Up > |
|
-
Every computer is given an IP address. The IP address is generally assigned by your system administrator.
The screen that displays the IP address of a PC is shown in Figure C.8.
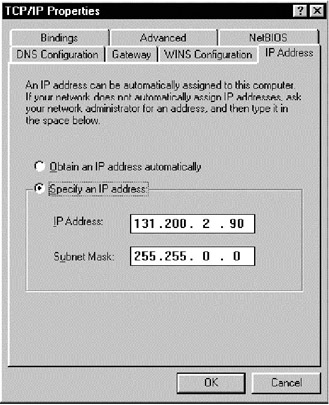
Figure C.8: IP address of a computer.To obtain this screen, do the following:
-
Right click on Network Neighborhood icon and select the Properties option from the pop-up menu. The following screen (Figure C.9) will appear:
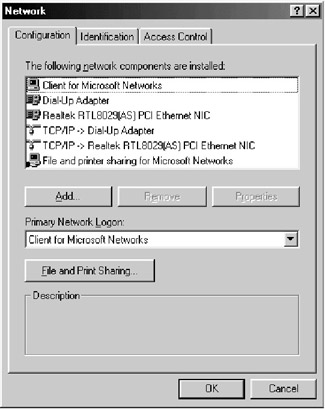
Figure C.9: Selection of the network interface card. -
In the screen seen in Figure C.9, select TCP/IP => Realtek RTL8029(AS) PCI Ethernet NIC and click Properties. Note that you need to select the correct Ethernet network interface card installed on your PC to obtain the properties. (Realtek is the name of the company that manufactures the Ethernet cards.)
-
-
When you access a Web site through a browser, the Domain Name Service of your Internet service provider gives the IP address of the origin server in which the resource is located. Then the TCP connection is established between the client and the origin server. When you see the message Connecting to followed by the IP address of the Web server, it is an indication that the DNS of your ISP has done its job. If the DNS is down, you will not get this message and will not be able to access the URL. Note that the DNS may be working, but still you may not be able to access the resource if the origin server is down.
-
The Ethernet LAN uses a maximum packet size of 1526 bytes. X.25 network uses a maximum packet size of 1024 bytes. In both cases, the packet size is variable. Variable packet size leads to more processing by the switches. Also, the switches should have variable size buffers. However, if large size packet is negotiated, data transfer is fast, and protocol overhead is less. Fixed-size packets certainly can be switched much faster. In Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) networks, fixed-size packets are used.
-
ATM uses a fixed packet size of 53 bytes. This is a small packet compared to Ethernet or X.25 packet sizes. The small size causes fast packet switching and fixed size buffers at the switches. The only disadvantage is slightly higher overhead. Out of the 53 bytes, 5 bytes are for header information.
|
| < Day Day Up > |
|
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 313