9.8 Multimedia Session in UMTS
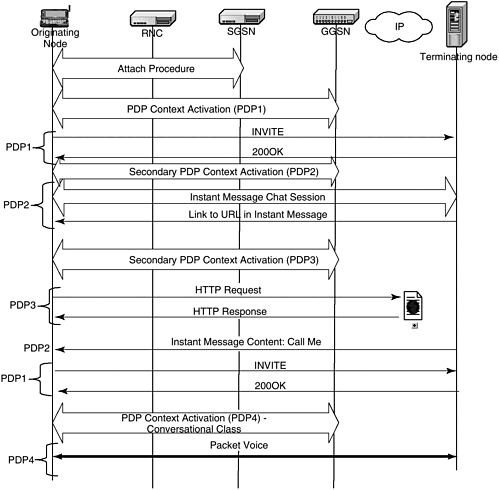
| The UMTS network is architected to enable new types of services to be developed and deployed in addition to enhancing capacity, supporting legacy services, and making packet data access spectrally more efficient. While the new air interfaces and technology provide higher bit rates, that in itself is not a driver for widespread adoption of UMTS. New services must be created in order to utilize fully the features of 3G networks. One of the things that 3G UMTS networks enable is multiple applications run at the same time or services that intertwine multiple applications. For example, an instant messaging session is enhanced to include a voice session as well as Web browsing. Such capabilities and services will be the differentiator between second-generation and third-generation networks. Figure 9-10 shows an example of a multimedia session. Figure 9-10. Multiple session example. Figure 9-10 illustrates the capability of the UMTS network wherein multiple sessions with different QoS characteristics are set up as part of a multimedia call. Such types of applications can only be enabled by 3G networks due to the availability of more bandwidth and improved provisioning of QoS. Figure 9-10 shows the establishment procedures for different multimedia sessions using primary and secondary PDP context activation. The details of PDP context activation procedures are omitted for brevity. The primary PDP context (PDP1) is activated first as the base PDP context. It selects certain parameters such as PDP (MS IP) address and APN that are not modified by the secondary PDP contexts. It is mainly used for exchanging application signalling. In our example, SIP is the application level signalling. INVITE and 200 OK messages are exchanged on PDP1 with the terminating node to establish a data connection. The secondary PDP contexts (PDP2, PDP3, and PDP4) are activated for different data sessions. They reuse PDP address and other information from the primary context, but may change QoS for different sessions depending on the need. PDP2 is activated for an instant message chat session. During the chat session, the MS is sent a URL for downloading a Web page. Assuming that the same APN is used for connecting to the Web server, the MS initiates another secondary PDP context, PDP3, for the Web page. It transfers HTTP messages with the Web server on PDP3. After the download, the MS may terminate PDP3 without terminating PDP1 and PDP2. After Web page download, the MS is asked on the instant message chat session (PDP2) for voice call. The MS first establishes a new SIP connection for the voice call with terminating node on PDP1. After that it establishes the PDP4 for the voice call using conversational class QoS. |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 164