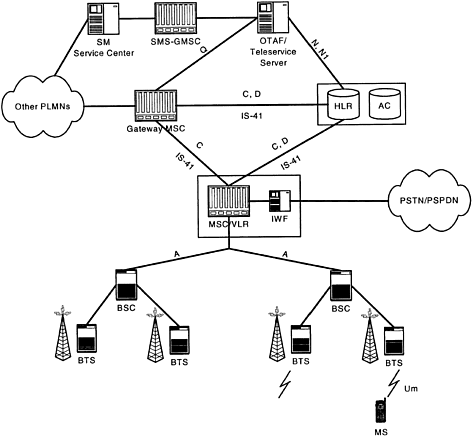
Before describing the details of IS-136 data services, in Figure 5-1 we provide an overview of an IS-136 network.
The architecture of IS-136 is very similar to the one of GSM. Several network interfaces have been assigned the same name , even if the protocols over the interfaces are substantially different.
As described in Figure 5-1, an IS-136 network consists of the following main network elements:
Home location register: The HLR is a central database for the IS-136 network to store subscription information of users. It keeps the information about service profile, location, and activity status of a subscriber. HLR is connected to MSCs and VLRs using the IS-41 protocol.
Mobile switching center: The MSC performs call control for calls originated or terminated to the mobile station. MSC supports also mobility management and radio resource management. It also captures charging information from the services used by the mobile station to support the creation of billing information. The MSC is connected to the BSS using the IS-136 A interface protocol. The gateway MSC is a gateway to a PLMN and provides call routing to/from other PLMNs and PSTNs. The SMS-GMSC is the GMSC for support of short message service. The MSC contains the VLR function, which contains subscriber information needed in servicing a roaming MS in a visited network. When an MS roams into a visited network, its information is transferred from the HLR to the VLR using the location update procedure.
Interworking function: The IWF performs protocol conversion to allow an IS-136 MS to connect with data networks over PSTN. More details are provided later in Section 5.5. The IWF may be integrated with the MSC or operate independently.
Authentication center: The AC authenticates mobile stations by verifying the authentication information received by the MSC. As a result of a successful authentication, AC also provides encryption parameters for ciphering over-the-air interface.
OTAF/ teleservice server: The over-the-air activation function/teleservice server supports teleservices in IS-136 and is also called the message center. Among other services, described later in this chapter, the function supports delivery of short messages to the MS (cellular messaging teleservice, CMT). The OTAF/teleservice server may communicate with other network entities through SS7 or IP. In particular, IS-41 is used to communicate with the HLR and the MSC.
Base station controller: The BSC controls a set of BTSs. It provides cellular-specific functions, like radio resource management and handover power control.
Base transceiver station: The BTS handles the radio interface. In IS-136, the interface connecting the BTS to the BSC in not an open interface. This means that no complete standard exists, and manufacturers implement the interface in different ways.
Interworking function: The IWF provides a mechanism for transferring digital data signals from the GSM PLMN to the other types of network (e.g., PSTN, ISDN, or PSPDN). The interworking function also performs any protocol conversion between the two dissimilar networks. More information is provided later in this chapter.
Mobile station: A mobile station has IS-136-specified call control, mobility management, and radio interface. It is connected to the network using air interface (Um).