12.2 Technology Introduction
| Table 12-1 provides a summary of the Bluetooth technology. More in-depth details are covered in later sections. It is estimated that by 2005 there will be over 500 million Bluetooth devices in various forms on the market. The technology will be used in a wide variety of devices like computers, mobile phones, PDA, and other personal devices for a vast number of applications by means of data transfer between these devices. Table 12-1. Bluetooth Summary
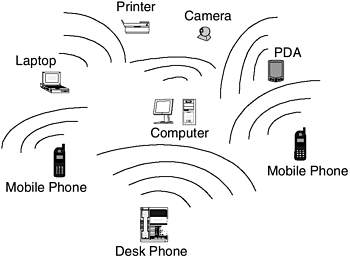
Bluetooth will replace the wiring around your desktop computers connecting the monitors , speakers , printers, and even the keyboard and mouse. Bluetooth can replace the wiring around your gaming consoles, and you will be able to synchronize your daily e- mails , phone, calendar, and other personal data in your Bluetooth-enabled PDA without any physical connections to your laptop or desktop. These possibilities are illustrated in Figure 12-1. The user data rates of 721 Kbps will enable digital cameras and MP3 devices to transfer loads of files without any cables. The Bluetooth SIG has specified numerous other usage profiles for other applications. Figure 12-1. Bluetooth device communications. Other commercial applications involve Bluetooth access points to provide network access at hotspots and kiosks to access e-mail, Web browsing, and other office applications. Another important application is the idea of the wireless personal area network (WPAN), where up to eight different Bluetooth devices can communicate with each other simultaneously within a short range by forming a small network called a piconet. A more complex network of piconets, called a scatternet, can be formed for wider ad hoc communication applications. |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 164