Protocol Overview
| IPX/SPX (internetwork packet exchange/ sequenced packet exchange) is an OSI Reference model Layer 3 protocol suite used with Novell NetWare for transferring data from servers to clients (you learned about the OSI Reference model in Chapter 2, "Networking Principles"). Like TCP/IP, IPX/SPX is a suite of protocols used for network interactions, such as data transport and routing. IPX/SPX (was developed by Novell for use with the NetWare operating system (version 4 and earlier). NetWare's IPX/SPX network protocols removed many of the client-configuration issues that were inherent with other legacy protocols. Because of this, the release of version 3.11 quickly earned market share and a great reputation for stability, quick installation, and very low maintenance. In NetWare 5 and 6, IPX no longer is required, but rather is an option. TCP/IP is now the default communications protocol. In this chapter, you learn about the following protocols:
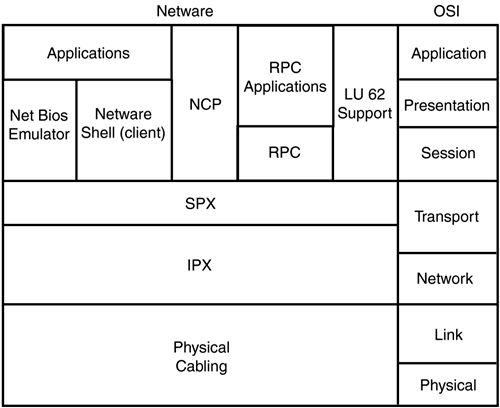
IPXThe IPX protocol operates at Layer 3 of the OSI Reference model and can share addressing schemes with the IP protocol. This sharing capability makes IPX easy to configure and administer in the network. Just like an IP address, an IPX address is divided into a network identifier (which is 4 octets) and a node (host) address. The node address is combined with the physical MAC address of the network interface card (NIC) located inside the node. Figure 6.1 shows how Novell NetWare protocols including IPX match up to the OSI Reference model. Figure 6.1. The Novell NetWare protocol stack compared to the seven-layer OSI Reference model. IPX addresses can be found in several formats, but hexadecimal is the most common format. A hexadecimal address of 0000018A.0000.834A.AD66, for example, can be broken down into two parts . The first part consists of the 8 hexadecimal digits, 0000018A, and indicates the network the node resides in. The other 12 hexadecimal digits, 0000.834A.AD66, indicate the node address. Most of the time, when you see the network portion of the address, the 0s preceding the network number are dropped. Therefore, the full IPX network address, including the network and node, would appear as 18A.0000.834A.AD66.
IPX EncapsulationNetWare uses encapsulation, as well as a framing method, to add an IPX datagram at Layer 3 to an appropriate Layer 2 frame. An important piece of knowledge in troubleshooting Novell is the framing process and how it relates to Ethernet, token ring, and Fiber Distributed Data Interface ( FDDI ) physical topologies. There are several different IPX frame types and it is possible to set the wrong frame types for the network. When an IPX frame type mismatch exists in the network, the IPX networked components cannot communicate, because this situation is somewhat similar to two people trying to communicate in two different languages without a translator. The following are the five Ethernet IPX frame types (the Cisco identifier name that is used to set the frame type is in parentheses):
Depending on the Cisco IOS you are using, you can view the configuration and frame types configured on the router by using the following commands:
|
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 213