Voice Over IP
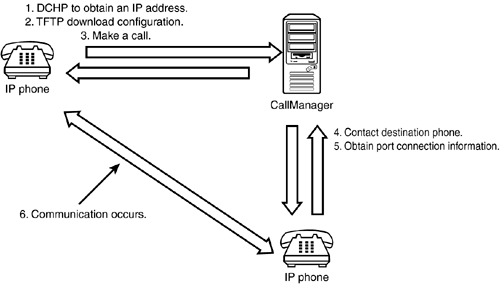
| Voice over IP (VoIP) is not one protocol but a term used for several types of protocols that provide telephone call “like connections across IP networks. Protocols such as SCCP, SIP, and H.323 are covered here. The Skinny Client Control ProtocolSkinny Client Control Protocol (SCCP) is typically just called Skinny . Cisco uses this simplified protocol for its VoIP phones and CallManager servers. The basis of Skinny is its interoperability with another protocol called H.323, which is discussed later. When an IP phone first boots, it requests an IP address from a DHCP server. Then, the phone downloads its configuration from a TFTP server and is ready for use. When a call is made, the client's phone sends a signal connection to a CallManager server, which then contacts the destination phone and acquires the UDP port the phone needs for audio communication. Next, the server passes this information back to the calling phone so that the source and destination phones can connect. Figure 8.3 shows that basic high-level flow for a connection. Figure 8.3. Basic Skinny VoIP flow. Some of the application inspection problems with Skinny include the use of inside addresses and the dynamic destination port numbers . If the clients are behind NAT, the embedded IP information must be changed to reflect the external Internet addresses. The fixup protocol for Skinny monitors and changes the internal address used by NAT to an external address. It also dynamically creates connection slots to allow traffic to pass as needed.
The following command enables the SCCP protocol to function across the PIX firewall: pixfirewall(config)# fixup protocol skinny 2000 The Session Initiation ProtocolSession Initiation Protocol (SIP) is another VoIP protocol that allows connections between audio devices using IP. This protocol is similar to Skinny; at a high level, the process of making a call is the same. The caller contacts what is known as a VoIP gateway . This gateway locates the destination phone for the caller and helps the two get connected. The default port for VoIP gateways is UDP port 5060. The following command enables SIP fixups: pixfirewall(config)# fixup protocol sip 5060 H.323H.323 is a complicated hybrid protocol that can be used for VoIP, video, and data. Like other multimedia protocols, but unlike VoIP, H.323 requires several ports to connect two devices. The protocol is actually a suite of other protocols put together to make the connections desired. The following lists standards used between two H.323 devices:
Several vendors use H.323 for their products; however, each vender implements this protocol in a slightly different way. So, not all H.323 applications are supported on the PIX firewall. The following is list of supported H.323 applications:
Each of these applications needs its own special adjustments for available ports. See Cisco's Web site for detailed configurations needed for each application. Here are variations of the basic command to enable H.323: pixfirewall(config)# fixup protocol h323 1720 pixfirewall(config)# fixup protocol h323 1718-1719 |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 218