Network-Enabled M-Business Services
|
Extrapolating existing business approaches and paradigms into new areas is the most obvious way of looking into the future. After all, we are comfortable with what we see today and can easily see how it can be used tomorrow. For m-business, the problem with this approach—treating m-business as a simple extrapolation of e-business—is that it fails to take into account the dramatic differences (as well as different capabilities) between the two. Some of the most dramatic differences are screen size [3] and the mobile user experience. But, equally important is the fact that m-business services will be built (assembled) from different "piece-parts" than e-business. Wireless service operators will deliver some of these "new" piece-parts, and many of these are being discussed and implemented today. Examples include location information Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) and services. Needless to say, there will be other, as-yet-unknown service piece-parts.
There are obviously many m-business applications developed and deployed today. All major overnight package delivery services utilize specialized terminals and have Web pages on which customers can track delivery progress. These solutions are developed directly for companies by systems integrators or IT suppliers. They are typically limited to using wireless services already offered by operators, although the size of some of these companies means that they are able to get special services developed and deployed by service operators. There will obviously continue to be a large market for customer-specific data services that utilize wireless transport and messaging services. There is also a substantial standardization under way to develop and deploy network services APIs that allow third parties to tap into and directly interface with network services. This is clearly a first step toward network enabling of data services.
Network enabling, however, can mean much more than just offering access to network-based data services and APIs for location, messaging, etc. A useful way to look at network enabling is in terms of successive categories associated with implementation or business focus. Shown in Figure 2 is a progression of m-business value addition, as the service offering moves from mere data transport to additional services to APIs for network services, and finally to complete integrated service solutions. It is at the right-hand extreme of Figure 2 that the true revolutionary potential of m-business becomes evident. In the following paragraphs, we describe the progressively higher stages of value addition and service integration.
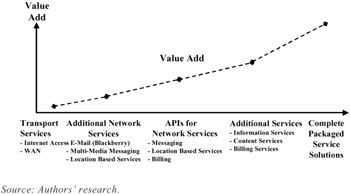
Figure 2: A Progressive Model of M-Business Value Addition
Basic Data Transport Services
At the most basic level, adding data transport capabilities to simple mobile voice telephony opens some opportunities for m-business. The evolution of Web-browsing from today's slow WAP speeds to higher data rates will revitalize some of this market. Pure data transport to support custom terminal-based network applications, like those used by today's package delivery services, will continue to grow as enterprises start to capitalize on higher-speed data transport to develop new business productivity and enhancement applications.
Additional Network Services
Enhancing basic mobile data access and Web-browsing capabilities with additional network services and specialized terminals adds more value to the m-business concept. Examples of this include the Blackberry handheld device, which provided mobile e-mail and messaging capabilities. Finland's Benefon provides GPS capabilities in the mobile phone, making it a useful device for navigating in cities as well as in the wilderness. Multimedia messaging is certainly positioning itself as a major value-added service, replacing today's SMS as a key data service. Some network data services will utilize location information, for example, delivering messages only in certain areas.
APIs for Network Services
The APIs for network services allow for tighter service integration of messaging, location-based services, usage monitoring, and billing. These APIs are intended to be used by third parties or business enterprise applications to offer services that are more closely integrated with network services, utilize network billing, or deliver services that are based on where the user is located.
Additional Services
As an additional value-adding step, the wireless operator can offer additional m-business-oriented services providing complete value-added information, tracking, billing, or messaging services. Business customers can utilize these complete service packages in order to develop more complete applications for their users.
Complete Integrated Service Packages
Finally, as an ultimate value-adding step, the m-business service provider can design and offer fully integrated service packages that solve complete problems. In the next main section of this chapter, we illustrate and assess such service packages.
Crystallizing the Concept of Network Enabling
Together, these five areas of service "add-ons" represent the concept of network enabling, i.e., by integrating services with capabilities inherent in the network or offered by the network service providers, services become enabled by these.
Looked at in a slightly different way, they can be viewed as "value-adds" to the core "transport function" of the wireless network. They also represent a migration of the business that wireless operators are striving for. The wireless service operators want to move from basic "telephone" service to more value-added services. Network enabling, the gradual enhancement of service offerings, with network capabilities, is an important implementation aspect of this move. M-business services can, of course, be implemented in a simple fashion by using only transport services from wireless operators. Such services are in use today and are basically terminal applications that communicate with the business enterprise IT systems. But the future evolution of m-business services will be more network enabled by adding and integrating various value-added network services to the way they operate and are implemented.
[3]While it is unlikely that people will walk around with 17" display terminals, it is likely that large-format, flat, and foldable mobile terminals would appear as replacements for paper copies of newspapers and magazines.
|
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 139