Using the Porter Model to Drive Value
|
The Porter Model provides an industry view of the business. The strength of the model is that it identifies where a firm must improve its competitive position. This model forces you to identify your competitors and benchmark your company against your competition, suppliers, and buyers. This comparative analysis will result in areas of competitive strengths and weaknesses. It also causes management to understand its position in the value chain.
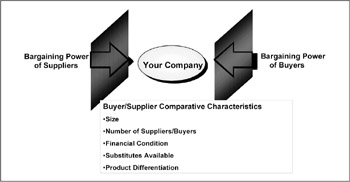
Exhibit 5-4 depicts the value chain and comparative characteristics that can be used to compare buyers and suppliers. A value or supply chain places your company on a continuum between suppliers or the purveyors of resources to your company and buyers or your customers. Bargaining power can be determined by comparing company size, number of suppliers/buyers, financial condition, substitutes available, and product differentiation. Superior size and financial position, as well as a limited number of buyers or suppliers, tend to improve bargaining power. If there are substitute products available, the bargaining power of the supplier will erode. If your firm is in an industry where substitute products are available, your bargaining power will decrease. The possession of products that are differentiated tends to increase the bargaining power of suppliers and the bargaining power of your firm in selling to your buyers.
Exhibit 5-4: The value chain and the Porter Model.
The strength of the Porter Model lies in its identification of threats to entry and substitute products that managers can use to identify weaknesses in their existing strategies. Management may decide to shift market position, channels, or its customers, based on pressures from the five forces. The weakness of the model is that it is industry-specific. This can tend to create industry myopia. Executives can be overly focused on industry pressures and not look outside their own competitive space for different ways of doing business. Many standards for customer service are often set outside particular industries. For example, customer service expectations set by catalog retailer Lands' End have been imposed on other industries like insurance.
|
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 117