Network Topology
|
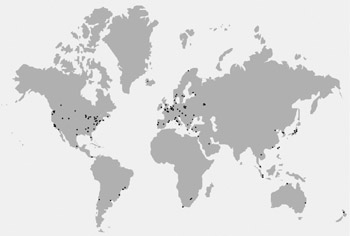
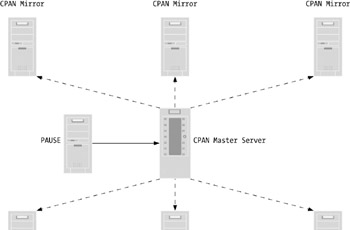
CPAN is composed of servers spread across the globe (over 200 as I write). Every server provides access to the same data. Figure 1-1 shows a map of CPAN servers. You can explore the CPAN network interactively at http://www.mirror.cpan.org. CPAN is modeled on a hub-and-spokes topology, shown in Figure 1-2. At the center of the CPAN network is the main CPAN server, ftp.funet.fi, in Finland. Most of the CPAN servers mirror this main server directly. To mirror is to maintain a synchronized copy of the files between two machines. CPAN servers use either FTP or rsync to automatically mirror files. Modules enter CPAN through a system called PAUSE, short for the Perl Author Upload SErver. I'll provide more details about PAUSE in Chapter 4. Since CPAN is a network, you can choose a mirror close to you that may offer faster download times than http://www.cpan.org. At http://www.mirror.cpan.org you'll find a search facility that enables you to search for mirrors by country.[4]
[4]Of course, the fastest way to access CPAN is by running your own mirror. See http://www.cpan.org/misc/cpan-faq.html#How_mirror_CPAN for details. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 110