The Poisson Distribution
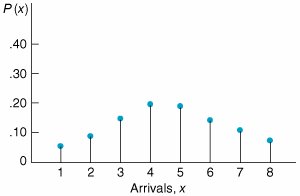
| The formula for a Poisson distribution is where l = average arrival rate (i.e., arrivals during a specified period of time) x = number of arrivals during the specified time period e = 2.71828 x ! = the factorial of a value, x [i.e., x ! = x ( x 1) ( x 2) . . . (3) (2) (1)] As an example of this distribution, consider a service facility that has an average arrival rate of five customers per hour ( l = 5). The probability that exactly two customers will arrive at the service facility is found by letting x = 2 in the preceding Poisson formula: The value .084 is the probability of exactly two customers' arriving at the service facility. By substituting values of x into the Poisson formula, we can develop a distribution of customer arrivals during a 1-hour period, as shown in Figure C.1. However, remember that this distribution is for an arrival rate of five customers per hour. Other values of l will result in distributions different from the one in Figure C.1. Figure C.1. Poisson distribution for l = 5 |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 358