2.8 MTU
2.8 MTU
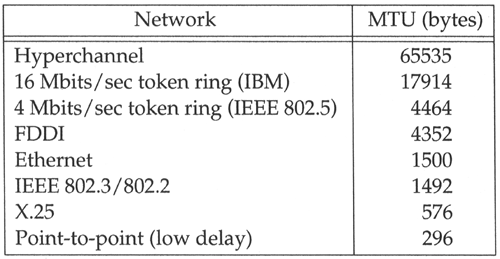
As we can see from Figure 2.1, there is a limit on the size of the frame for both Ethernet encapsulation and 802.3 encapsulation. This limits the number of bytes of data to 1500 and 1492, respectively. This characteristic of the link layer is called the MTU, its maximum transmission unit. Most types of networks have an upper limit.
If IP has a datagram to send, and the datagram is larger than the link layer's MTU, IP performs fragmentation, breaking the datagram up into smaller pieces ( fragments ), so that each fragment is smaller than the MTU. We discuss IP fragmentation in Section 11.5.
Figure 2.5 lists some typical MTU values, taken from RFC 1191 [Mogul and Deering 1990]. The listed MTU for a point-to-point link (e.g., SLIP or PPP) is not a physical characteristic of the network media. Instead it is a logical limit to provide adequate response time for interactive use. In the Section 2.10 we'll see where this limit comes from.
Figure 2.5. Typical maximum transmission units (MTUs).
In Section 3.9 we'll use the netstat command to print the MTU of an interface.
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 378