Timed Portion Lab Rules -
No static routes or floating static routes are used unless specifically stated. -
Follow the instructions exactly. Be careful to propagate routes only where and when instructed. Use the PVCs only as directed by the instructions. -
Primary configurations might need to be modified for Part II only when you have finished the primary configurations. -
You can use the configuration guides and the Cisco Documentation CD-ROM for your only reference material. -
You have 8 1/2 hours to complete the lab. Do not talk to anyone during this phase. -
It is recommended that you read the entire lab before beginning. -
Make an accurate and precise network illustration. -
Use Figure 18-8 as a reference for the physical layout of the lab. Figure 18-8. Network Diagram for "The Enchilada" 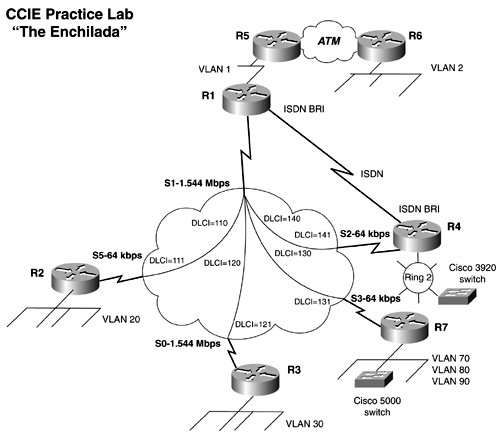 Section I: Basic IP Configuration -
Access server: Configure the access server/router so that all the routers and the switches can be accessed through reverse Telnet. Password-protect all routers and switches with the password cisco. -
IP address assignment: Assign an IP addresses to all physical interfaces, as denoted in Figure 18-8. Use the major network of 155.100. x.x on all interfaces. Use a 24-bit mask on all interfaces except for the following: R1: Use a 25-bit address on VLAN 1 between R1 and R5. R2: Use a 27-bit address on VLAN 20. R3: Use a 28-bit address on VLAN 30. R4: Assign Ring 2 an IP address of 10.11.10.0/24. -
Full IP and IPX connectivity to all Ethernet, Token Ring, and loopback interfaces will be expected unless noted. -
Document the network thoroughly; include all OSPF areas, IP/IPX address, IPX networks, and so on. Section II: Catalyst/LAN Configuration -
Configure the VLANs as depicted in Figure 18-8. VLAN 70, VLAN 80, and VLAN 90 reside off the 100-MB port on R7. Configure the router to route between the VLANs. -
Configure the Catalyst Ethernet and Token Ring switches so that they can be managed through Telnet from any router in the lab. -
Configure the Token Ring segments at this time. Do not use the default Token Ring VLAN. -
Configure a full-duplex 802.1Q trunk on port 1/1 of the Catalyst switch. Prevent STP for VLANs 70, 80, and 90 from being propagated down this trunk. It is not important whether this link is attached; the configuration of the switch will be the same. Section III: OSPF and Frame Relay Configuration -
Configure the Frame Relay network as shown in Figure 18-8. -
R1, R2, and R3 should share the same IP subnet; use subinterfaces only on R1. Configure this subnet to be in Area 0. Do not change the OSPF network type on R1. Configure the Frame Circuit between R1 and R7 to be in OSPF Area 10. -
Configure VLAN 20 to be in OSPF Area 20. Configure VLAN 30 to be in OSPF Area 30. Configure VLANs 70, 80, 90 to be in OSPF Area 70. -
Configure Area 30 to send link-state type 7's, to any new OSPF routers that might be on VLAN30. -
Authenticate Area 0 with Type II authentication. Use cisco as the password. Section IV: Routing Protocols and Redistribution -
Configure IGRP on Ring 2 and on the Frame Relay circuit between R1/R4. Ensure full IP reachability to the OSPF network. -
Prevent the subnet of the Token Ring network on R4 from reaching R7. Section V: ATM and EIGRP -
R5 and R6 both connect to the ATM switch. Configure classical IP over ATM between the routers so that the routers can ping each other. -
Configure EIGRP on VLAN 1 of R5 and over the ATM cloud to R6. Redistribute EIGRP into OSPF. Make sure that the entire EIGRP network is reachable from the IGRP and OSPF domains. Section VI: ISDN Configuration -
Configure the ISDN interfaces on R1 and R4. Make only R4 place the call to R1. Be sure that you can ping the R1/R4's ISDN interfaces before moving on. -
Configure the ISDN interfaces as part of the IGRP backbone. Ensure that the link becomes active only upon loss of IGRP routes from R1. Section VII: Voice over IP -
Configure Voice over IP between R2 and R3. Use the FXS ports to create a ringdown circuit between the two routers. Section VIII: IPX Configuration -
Configure IPX on VLAN 1, VLAN 20, and VLAN 30. -
Configure IPX EIGRP on R1, R2, R3, and R5. Configure IPX on Ring 2 of R4; use IPX RIP/SAP on the frame link between R4 and R1. Ensure that all routers see all IPX networks. -
Configure IPX SAP on R5, which supports file services. This SAP is called fakefserver and has socket 452. Ensure that all routers can see this SAP. -
On R2, apply a SAP filter blocking all SAPs that start with the letters "fake." -
Configure VLAN 30 so that SAPs are advertised only when a new server comes online. Section IX: Miscellaneous Cisco IOS Software Configuration -
Workstations on VLAN 20 need to gain their IP addresses through the DHCP server on VLAN1. Configure R2 to support this. -
Configure R3 so that workstations VLAN 30 can dynamically locate their default gateway. They are not using DHCP. -
Configure multicast routing on R1, R2, and R5. Configure R1 as a member of the multicast group 224.0.7.7. R1 should respond to ping s from R2 and R5. -
Configure R1, R2, and R5 to dynamically configure the Cat5k for multicast. |
