3.1 In-House TV Wiring
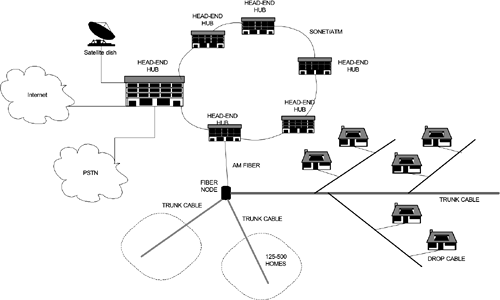
3.1.1 In-House Wiring ConfigurationIn a new construction, coaxial cables are connected from a central location near the TV signal source, be it a cable TV or a satellite dish, to every room where an in-house TV wiring connection should be available. This configuration forms a star topology. A multiport splitter is located at the center of the star. Depending upon the number of rooms to be served, some times an amplifier is inserted between the video source and the multiport splitter to raise the signal level, compensating signal losses caused by branch splitting. Assuming that signal separation loss is 15 dB between two output ports of every splitter stage, the minimal signal separation loss is 15 dB between coaxial cable outlets. For in-house wiring installed by cable TV companies on existing homes, splitters are usually randomly installed at the cable TV entrance point and some other convenient splitting points. This configuration forms a star daisy-chain topology similar to that of the in-house telephone wiring except a splitter is used at every cable branch point. The maximum signal separation loss for the general star daisy-chain follows the same rule of thumb described for the star topology. 3.1.2 Hybrid Fiber Coaxial and Tree Branch Distribution PlantFigure 3.1 shows the general arrangement of the cable TV hybrid fiber coaxial and tree branch distribution network connecting all subscribers. TV signals are originated from the head end. Two-way services such as cable modem for Internet access and POTS are also terminated and managed at the head end. A dual optical ring is used to connect all head ends and hubs over the SONET and ATM infrastructure for delivering and exchanging digital programs. AM fiber links are extended to a number of fiber nodes. From each fiber node, a few coaxial trunk cables, each of which serves a few hundred subscribers, are further extended to neighborhoods. Subscribers are connected to trunk cables through drop coaxial cables. The configuration illustrates that there might be some possibilities of interference between neighboring cable TV subscribers if in-house wiring is used for a high throughput home network. However, the degree of interference is minimized by additional drop cable losses and the signal-splitting loss introduced inside the Tap devices. Figure 3.1. A Cable TV Hybrid Fiber Coaxial and Tree Branch Distribution Network
|
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 97